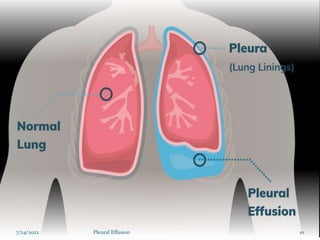
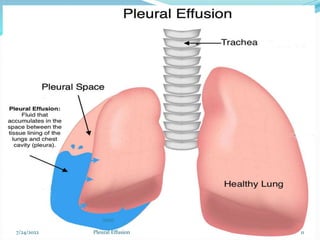
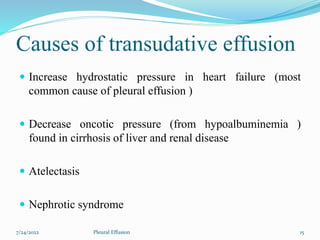
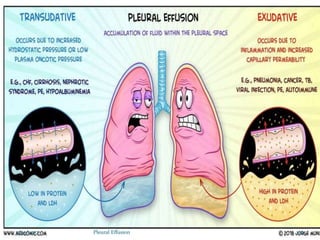
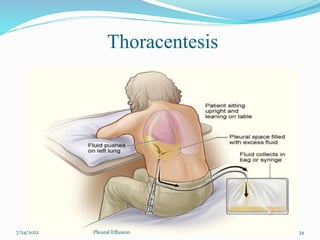
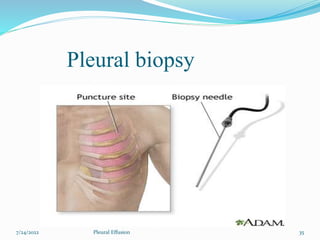
The document provides information about pleural effusion including its definition, causes, types, signs and symptoms, diagnostic evaluation, management, and nursing care. Pleural effusion occurs when an abnormal amount of fluid collects in the pleural space, impairing lung expansion. It is usually caused by conditions that interfere with fluid balance such as heart failure, infection, cancer, or liver/kidney disease. Pleural effusions are classified as transudative or exudative based on the fluid characteristics. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging, and fluid analysis. Treatment focuses on resolving the underlying condition while draining excess fluid and preventing complications.