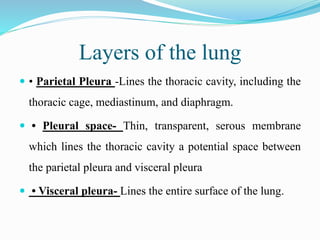
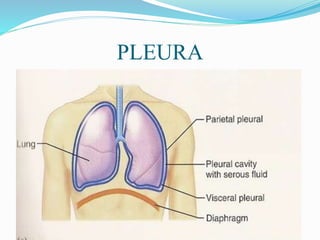
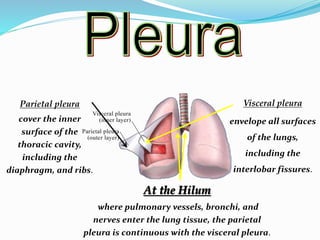
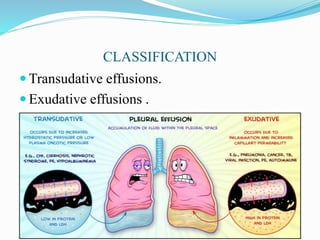
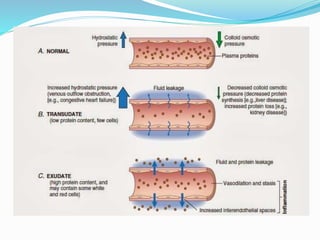
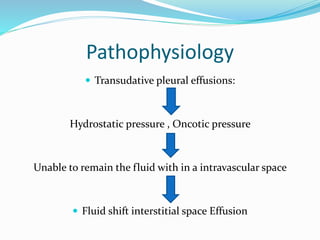
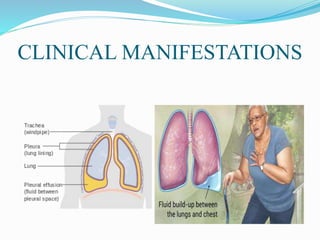
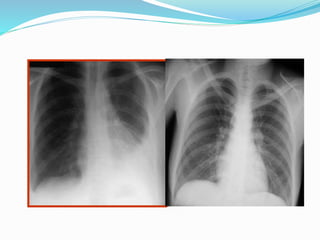
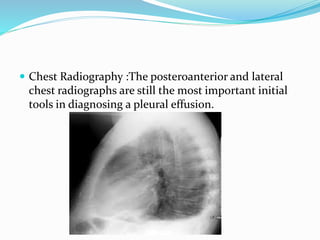
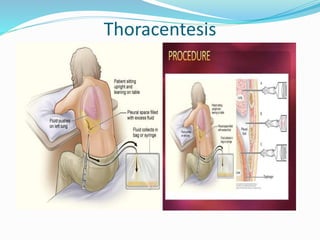
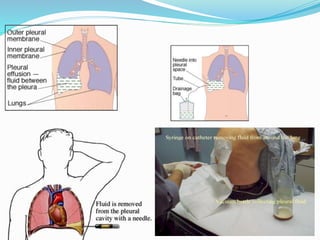
Pleural effusion occurs when an abnormal amount of fluid collects in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It can be caused by conditions that increase hydrostatic pressure or decrease oncotic pressure (transudative), or by inflammation from infections, cancer, pulmonary embolism (exudative). Symptoms include shortness of breath, cough, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray and thoracentesis to analyze fluid. Treatment focuses on resolving the underlying cause, relieving symptoms by draining fluid, and preventing reaccumulation through procedures like pleurodesis. Nursing care centers around breathing treatments, pain management, infection prevention, and monitoring for complications.