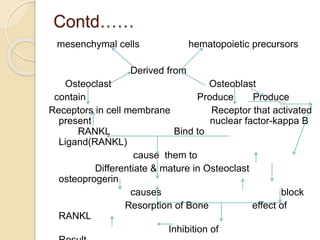
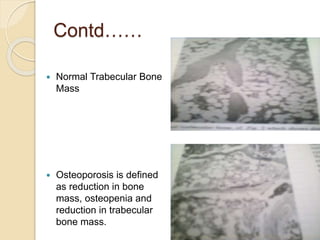
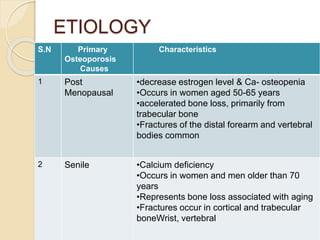
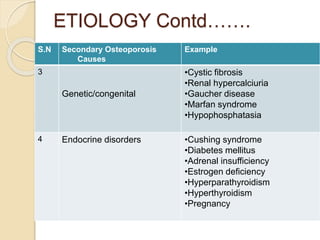
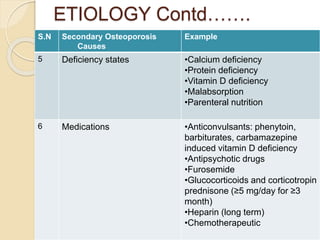
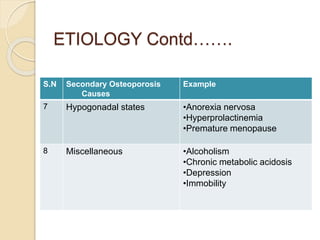
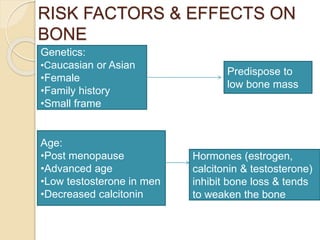
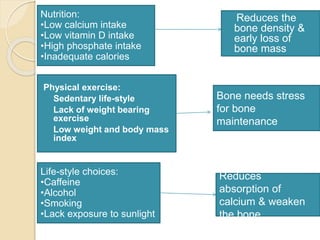
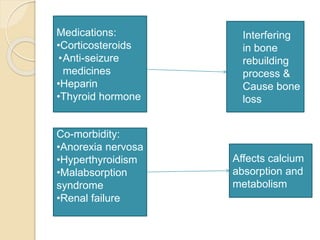
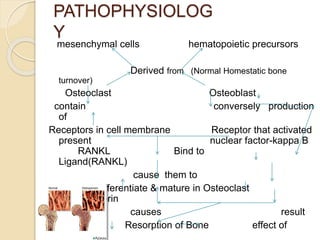
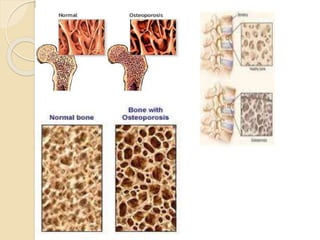
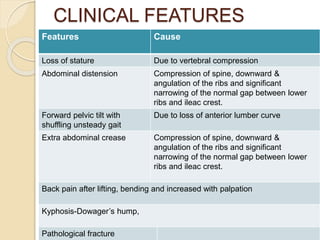
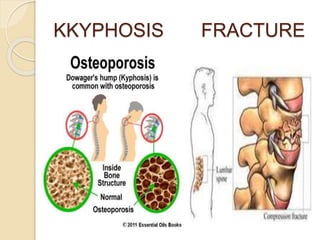
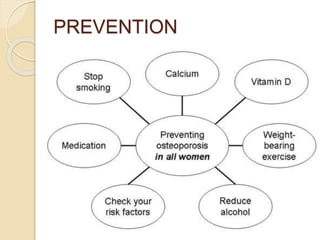
Osteoporosis is a chronic, progressive skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration, leading to increased fracture risk, especially among postmenopausal women and the elderly. It results from an imbalance in bone remodeling, where bone resorption surpasses bone formation, influenced by various factors including hormonal changes, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions. Prevention and management strategies include dietary changes, exercise, and pharmacological treatments such as bisphosphonates and hormonal therapies.