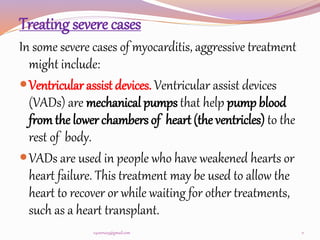
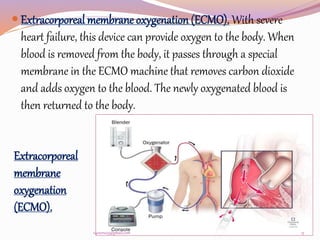
This document discusses myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle. It can be caused by various infections, autoimmune disorders, or allergic drug reactions. Symptoms may include chest pain, arrhythmias, shortness of breath, edema, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves collecting a medical history, physical exam, blood tests, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and potentially a myocardial biopsy. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, managing heart failure symptoms, and supporting heart function through devices or transplants in severe cases. Nursing diagnoses for patients include risks of decreased cardiac output and ineffective tissue perfusion due to reduced blood flow and pressure, as well as acute pain, deficiency in knowledge, and anxiety.