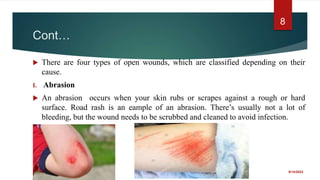
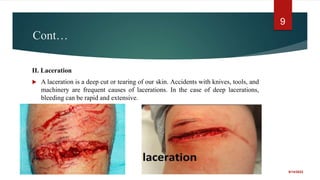
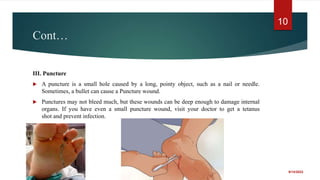
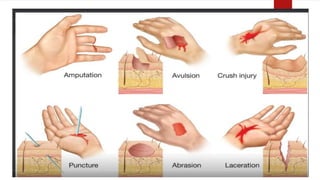
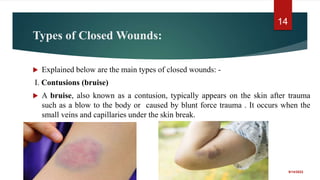
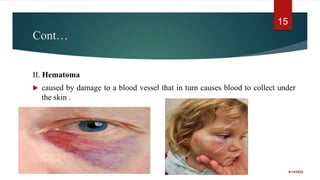
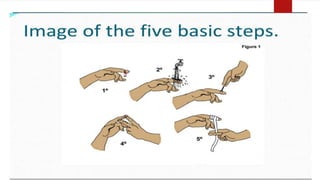
The document provides a comprehensive overview of wounds, including definitions, types (open and closed), and first-aid treatments. It explains various categories of open wounds like abrasions, lacerations, punctures, and avulsions, as well as closed wounds such as bruises and contusions. The document also outlines general care steps for minor wounds, when to seek medical attention, and specific instructions for treating puncture and major wounds.