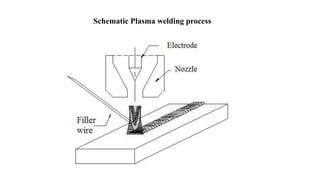
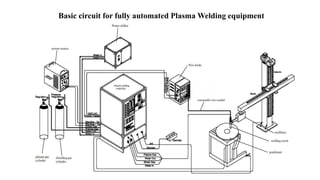
The plasma arc welding process is an advanced welding technique that operates in three modes: micro plasma, medium plasma, and keyhole plasma, using an arc between an electrode and a workpiece to fuse metal in an inert atmosphere. It involves specialized equipment, including a welding torch, gas cylinders, and a power source, and is characterized by its ability to produce directional arcs with high temperatures that enable deep penetration and high-quality welds. Advantages of plasma arc welding include reduced assembly costs, minimal heat-affected zones, and the capability to weld various materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous alloys.