This document discusses methods for estimating welding preheat requirements when the grade or composition of carbon or low-alloy steel is unknown. Key points:
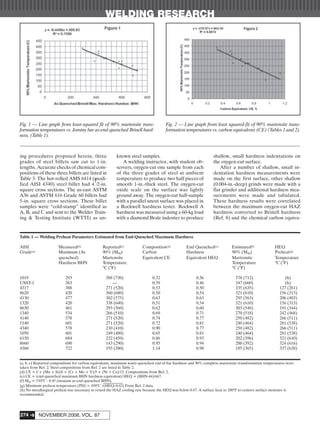
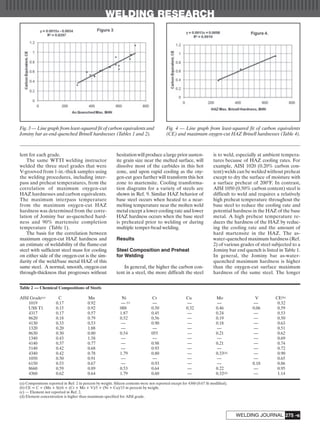
- Oxygen cutting a sample of the unknown steel and measuring the maximum hardness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) can help estimate preheat needs. Higher HAZ hardness indicates a higher preheat.
- Alloy content, including carbon percentage, affects weldability - higher carbon and alloy steels are more difficult to weld and require higher preheats to reduce HAZ cooling rates.
- Data from Jominy end-quenched hardness tests on known steel grades was used to correlate maximum HAZ hardness with the estimated temperature for