Embed presentation
Downloaded 128 times



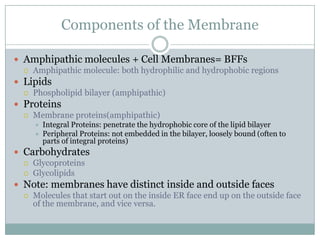



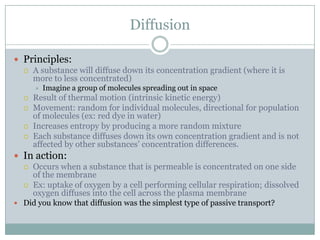








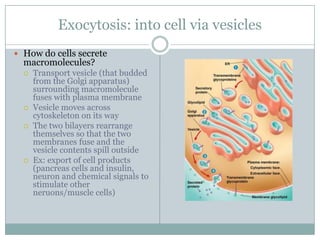
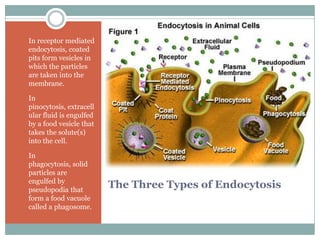

The document summarizes key concepts about cell transport and homeostasis. It discusses the selective permeability of the plasma membrane and how it controls traffic across the membrane using passive and active transport mechanisms. Passive transport includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. Active transport requires energy and includes processes like the sodium-potassium pump that transports ions against their concentration gradients. The document also describes endocytosis and exocytosis for transporting larger molecules and particles across the membrane.























