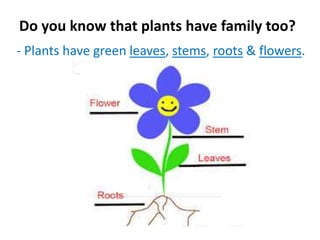
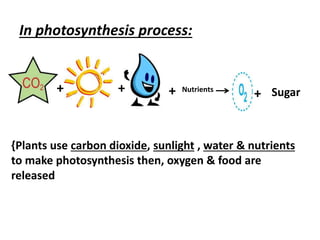
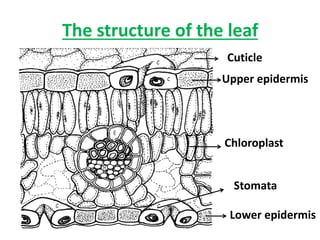
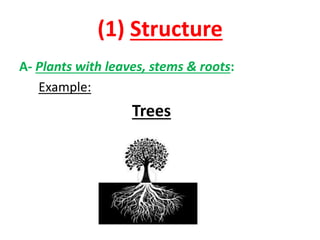
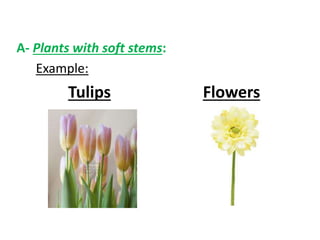
Plants have families with different parts that each have important jobs. Flowers attract insects and birds to help make seeds, stems carry water and nutrients, roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil, and leaves make food through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water to make food and release oxygen. Plant leaves have structures like the cuticle, epidermis, chloroplasts, and stomata that help them survive. Plants can be classified by their structure, root type, stem type, whether they produce seeds or spores, and if they are edible.