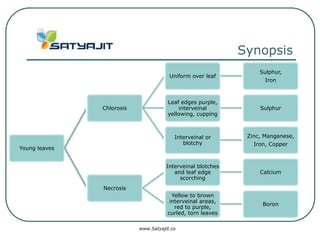
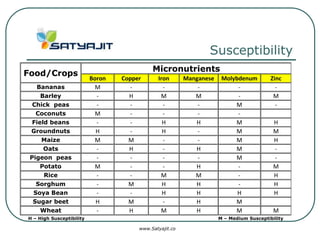
This document discusses plant nutrient basics, including macro and micro nutrients, nutrient interactions, mobility, deficiency and toxicity symptoms, and susceptibility of different crops. It provides information on the natural roles of nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. It also outlines mobility of nutrients in plants and soils. Optimum ranges and deficiency/toxicity symptoms are described for various nutrients. Finally, it discusses how different food crops are susceptible to deficiencies in specific micronutrients like boron, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum and zinc.