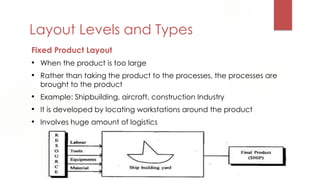
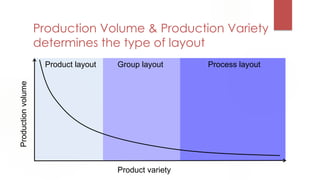
The document discusses factors to consider when determining a plant's location and layout. It outlines key location factors like availability of resources, infrastructure, and labor. It also describes different types of plant layouts based on production volume and variety, including process, product, and group layouts. The objectives, costs, and advantages of different layout types are presented. Methods for analyzing relationships between activities and determining optimal layout configurations like activity relationship diagrams and Muther grids are also covered.