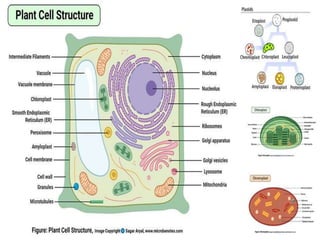
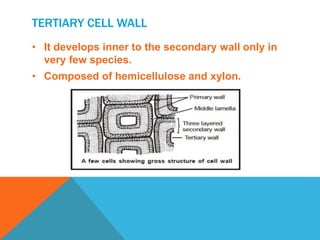
This document summarizes plant cell envelopes and cell walls. It describes that plant cells have cell walls that provide structure, protection, and prevent water movement into cells. The cell wall is made of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin and lignin. It differentiates into a primary wall, secondary wall and sometimes a tertiary wall. The cell wall provides shape, structure and acts as a protective barrier for the cell.