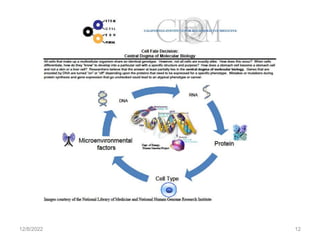
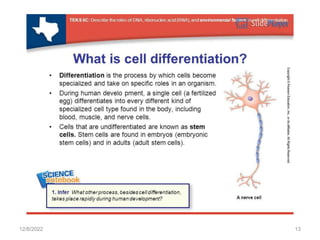
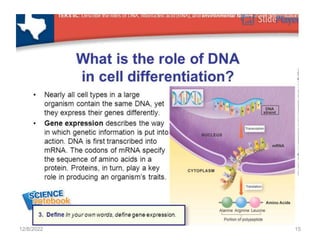
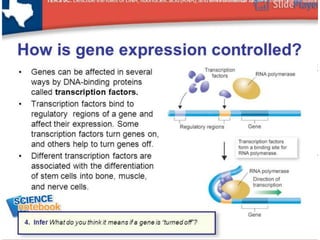
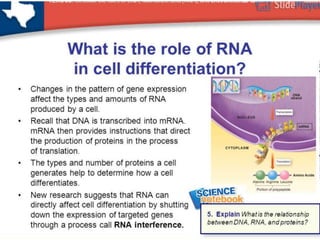
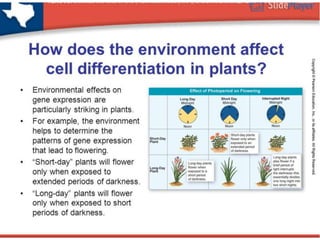
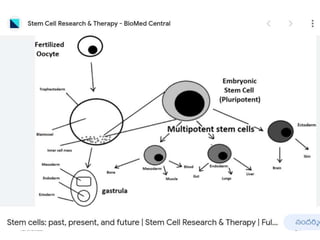
This document provides information about cell differentiation from a lecture presented by Dr. SHWETA SINGH. It defines cell differentiation as the process by which a cell undergoes changes in gene expression to become a more specialized cell type. This allows multicellular organisms to develop uniquely functional cell types and body plans. The document discusses how all organisms begin as a single cell and must undergo cell division and differentiation to form the complex tissues and organ systems of the adult body. It provides examples of cell differentiation in animal development and plant growth from a single cell.