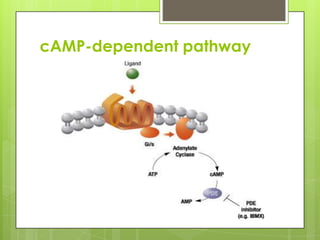
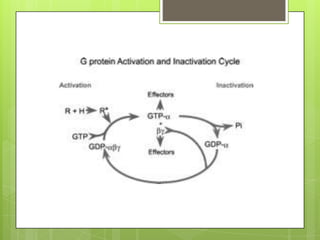
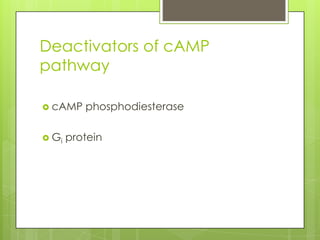
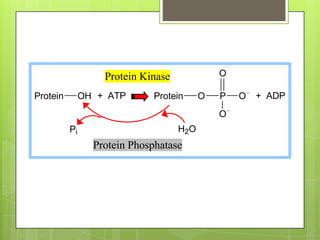
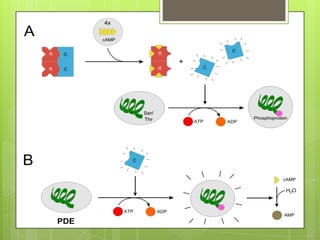
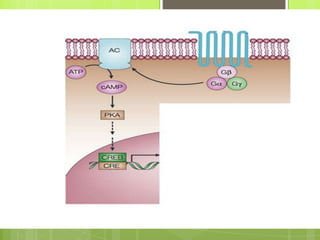
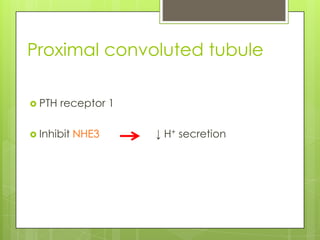
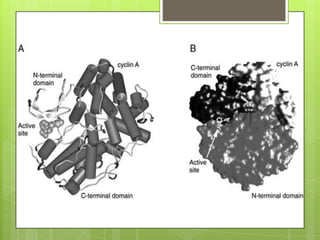
Protein kinase A (PKA) is an enzyme involved in the cAMP-dependent pathway. It is activated when cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels rise in response to stimuli like hormones or neurotransmitters. PKA then directly phosphorylates other proteins to regulate various cellular processes either rapidly through direct phosphorylation or slowly through activating transcription factors. PKA activity is regulated by anchoring proteins and feedback loops, and it functions in many tissues to modulate processes like metabolism, ion transport, gene expression, and more.