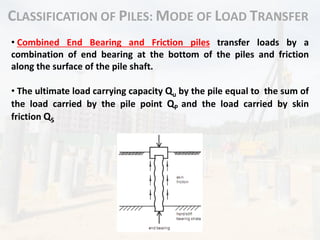
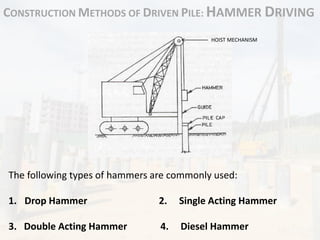
The hammers are raised and guided by a hoist mechanism to
ensure proper impact on the pile head.
�CONSTRUCTION METHODS OF DRIVEN PILE: VIBRATORY PILE DRIVING
- Vibratory pile driving uses a mechanical vibrator instead of a drop hammer.
- The vibrator is attached to the pile and transmits high frequency, low amplitude
vibrations into the pile and soil.
- This causes the soil particles to rearrange and densify, allowing the pile to
penetrate without application of large impact forces.
- Vibratory driving is suitable for cohesive and loose granular soils.
- It is faster than conventional impact driving but may not be suitable for hard