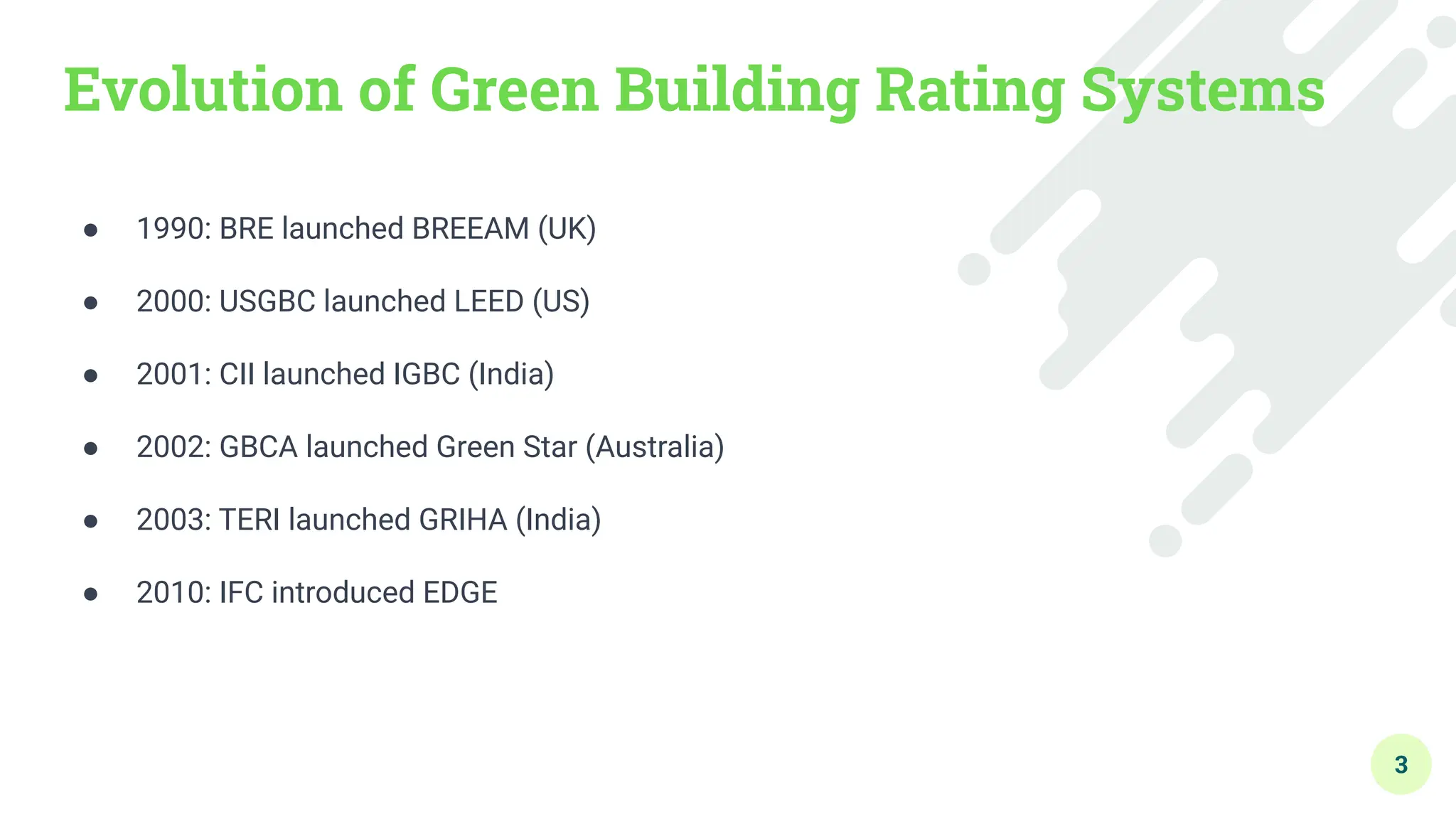
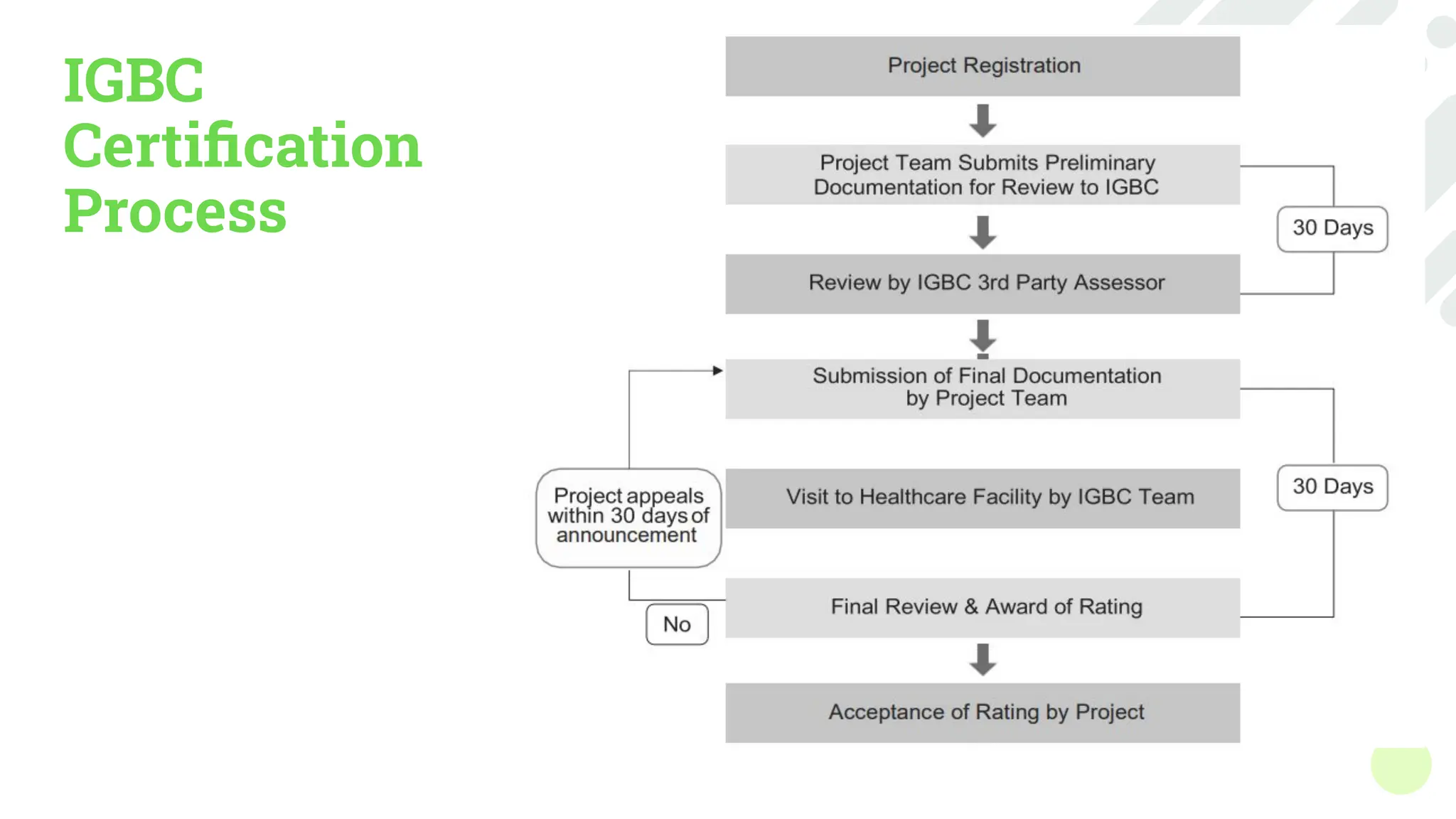
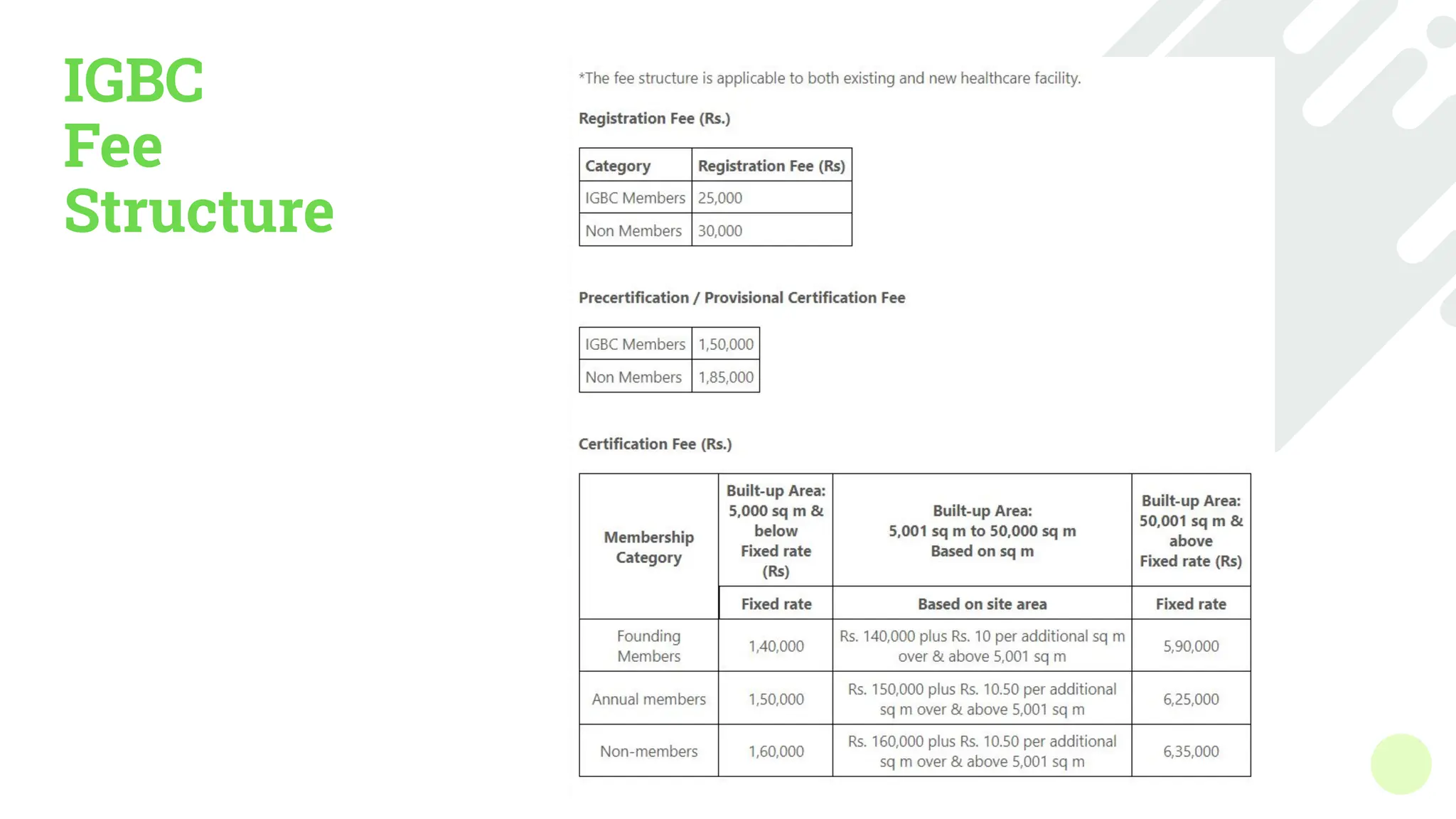
The document outlines various green building rating systems, including BREEAM, LEED, GRIHA, and IGBC, which assess and certify the environmental performance of buildings to promote sustainable practices and reduce ecological impact. It details the evolution of these systems, highlighting key milestones and shifts in focus toward areas like well-being and circular economy. The document also provides insights into the certification processes, categories assessed, and the global reach of these initiatives.