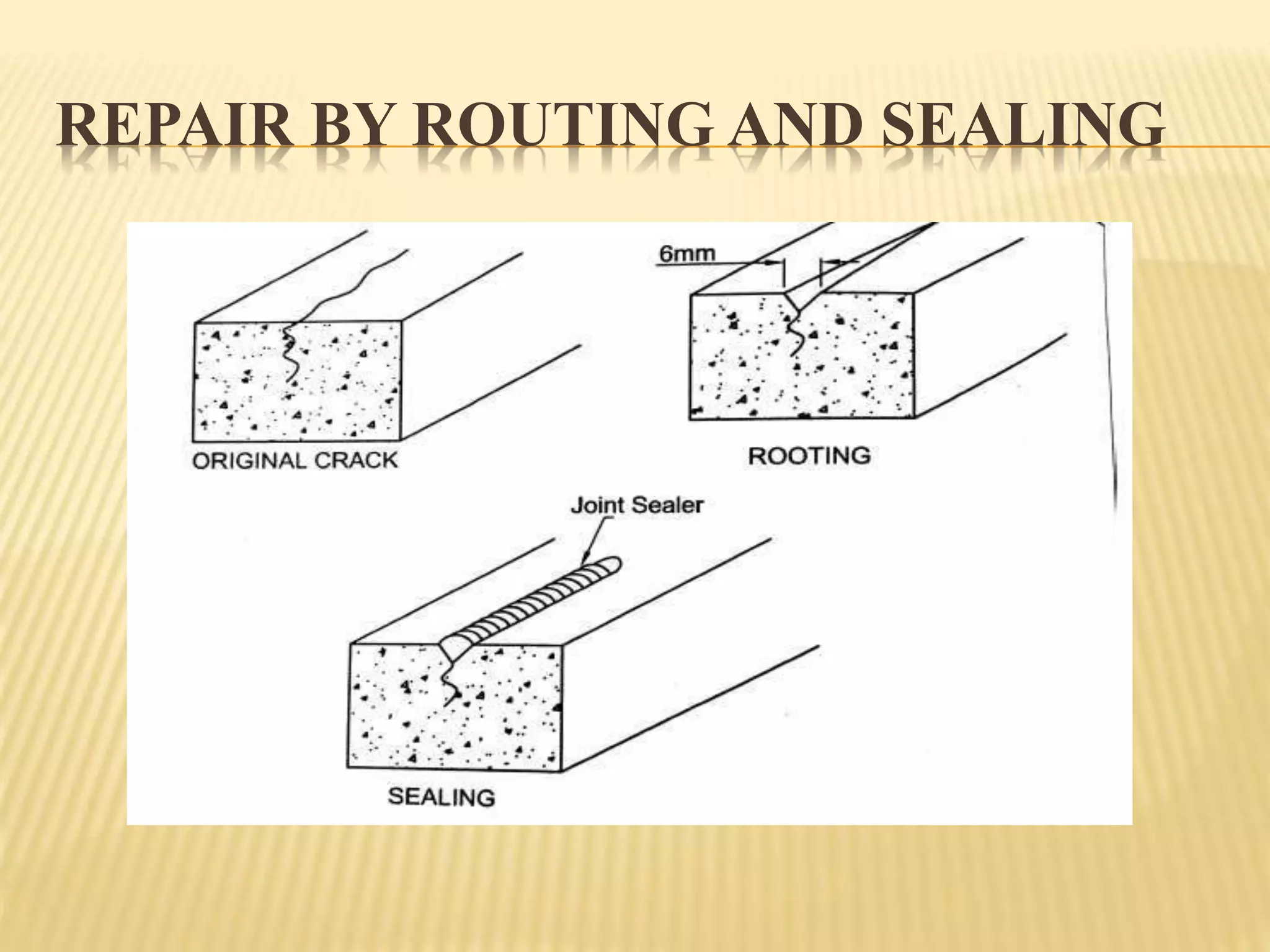
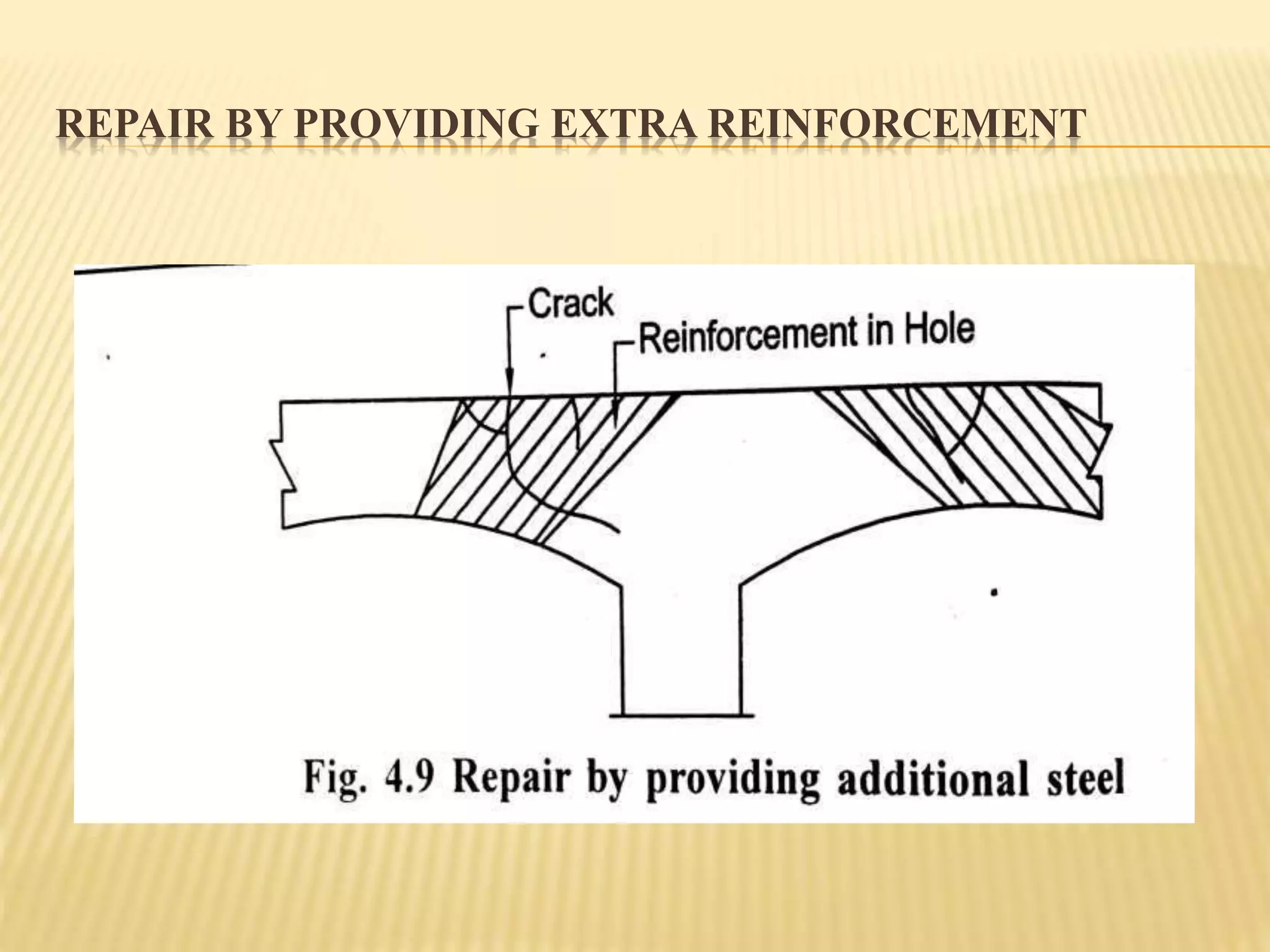
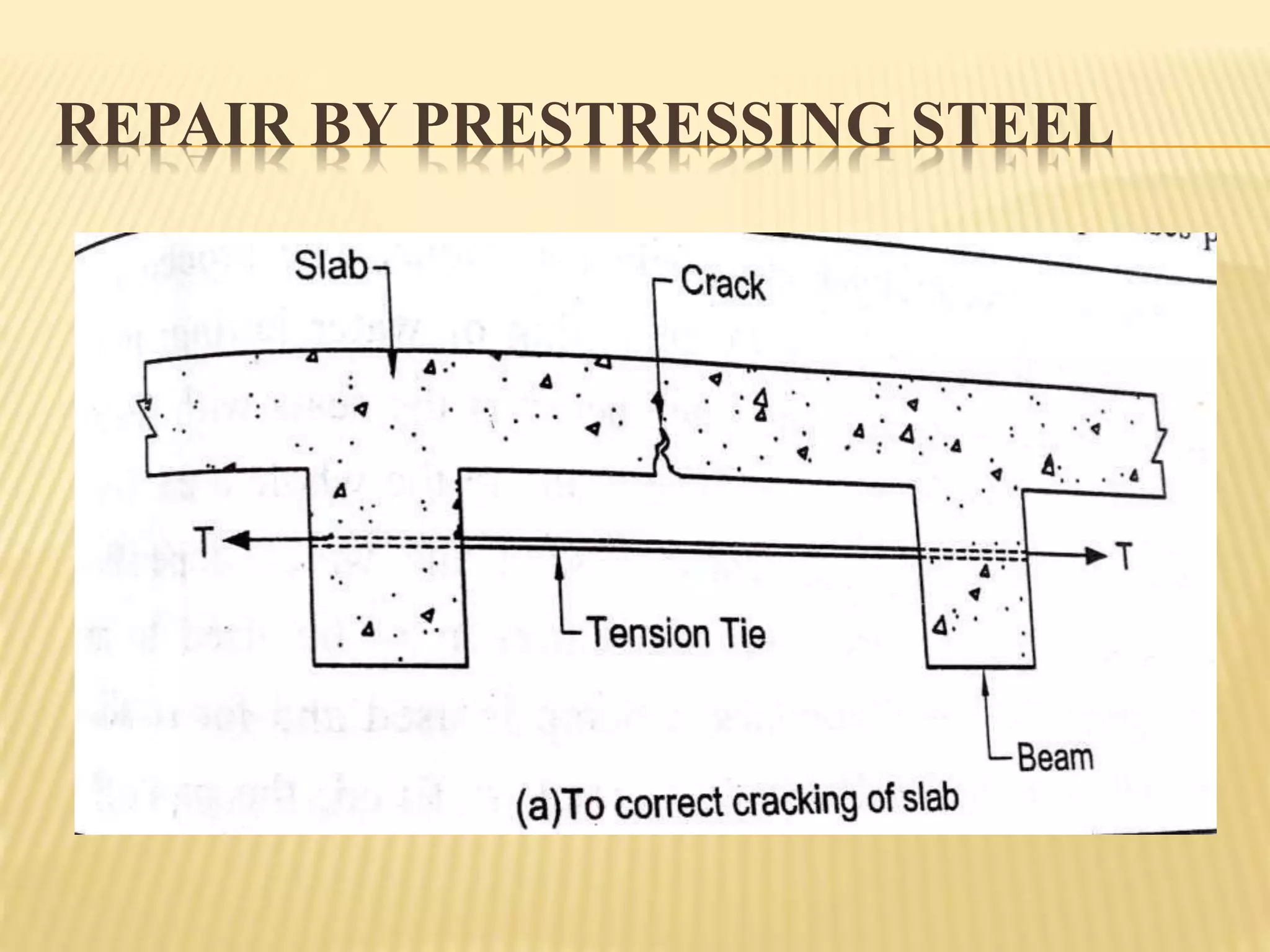
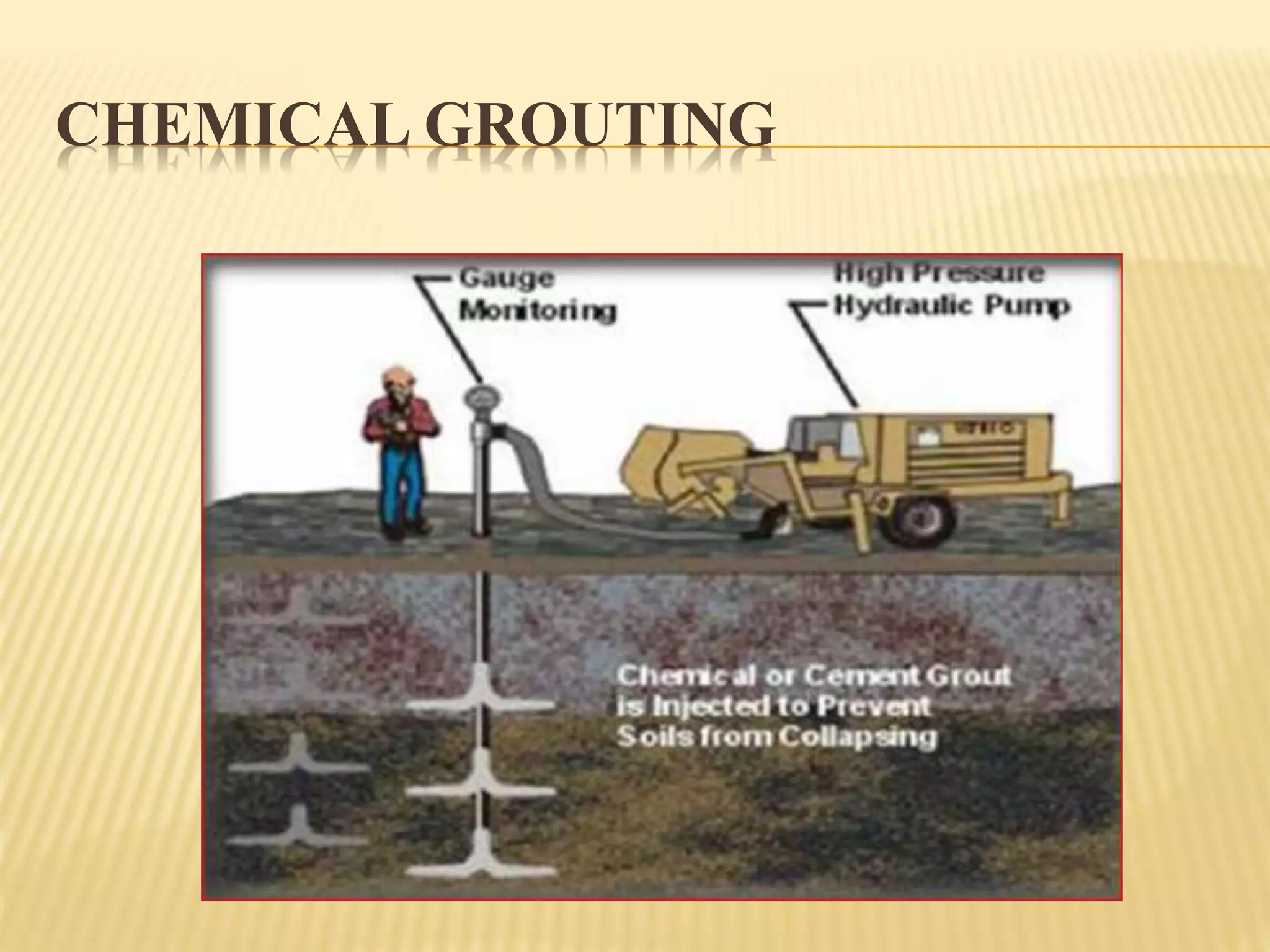
Rehabilitation and strengthening of existing structures involves repair techniques, underpinning, and addressing causes of damage. Repair restores structures to their previous condition while rehabilitation considers strength. Retrofitting modifies structures to increase resistance to seismic activity. Common repair techniques include crack injection, routing and sealing cracks, adding reinforcement, prestressing steel, and grouting. Underpinning strengthens foundations by extending them deeper or wider. Mass concrete and mini-pile underpinning are two types. Causes of damage to masonry buildings include heavy weight, low tensile strength, brittle behavior, and weak structural connections.