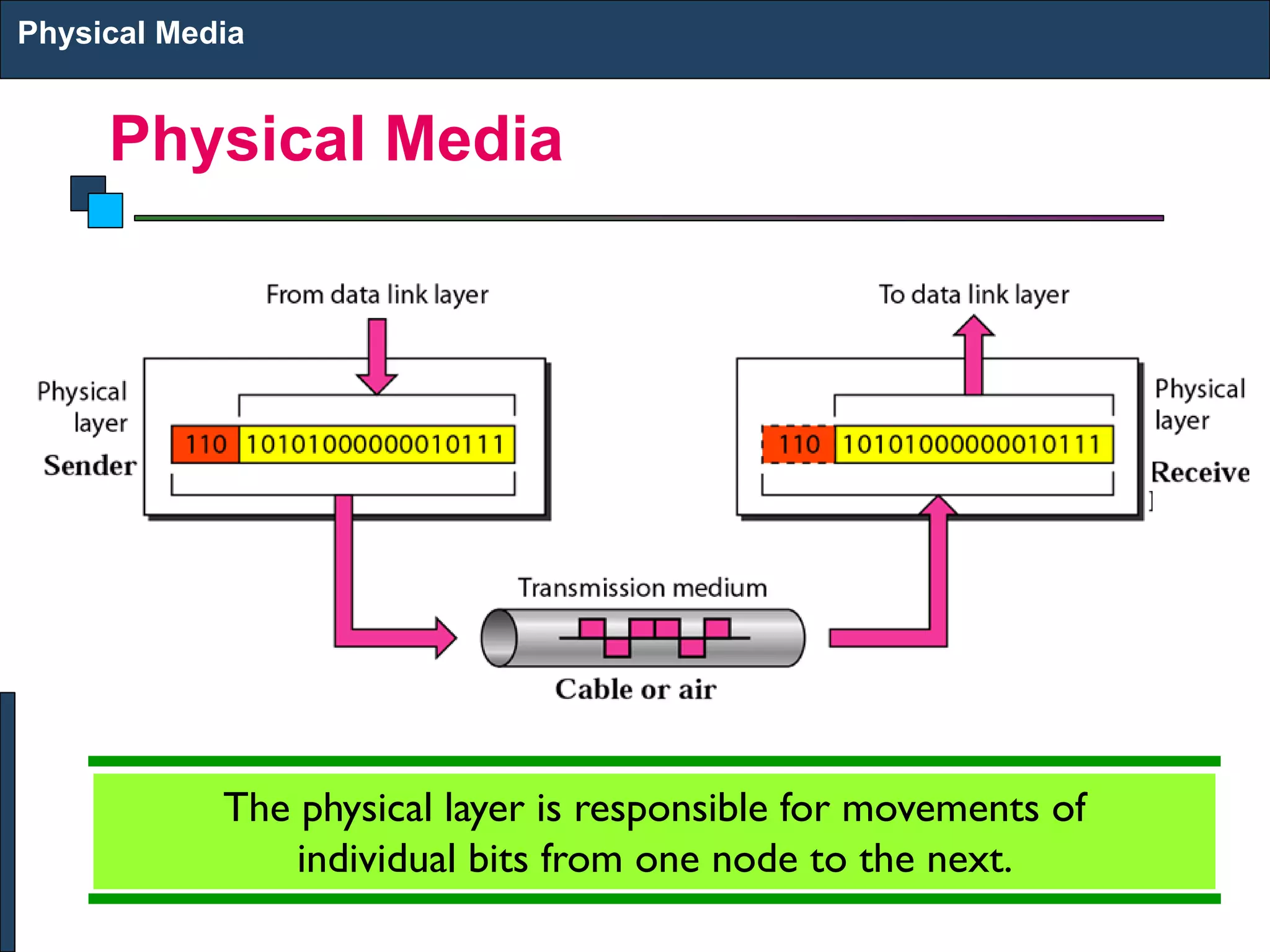
1) The physical layer is responsible for transmitting individual bits between nodes using physical media like copper cables, fiber optic cables, or wireless transmission.
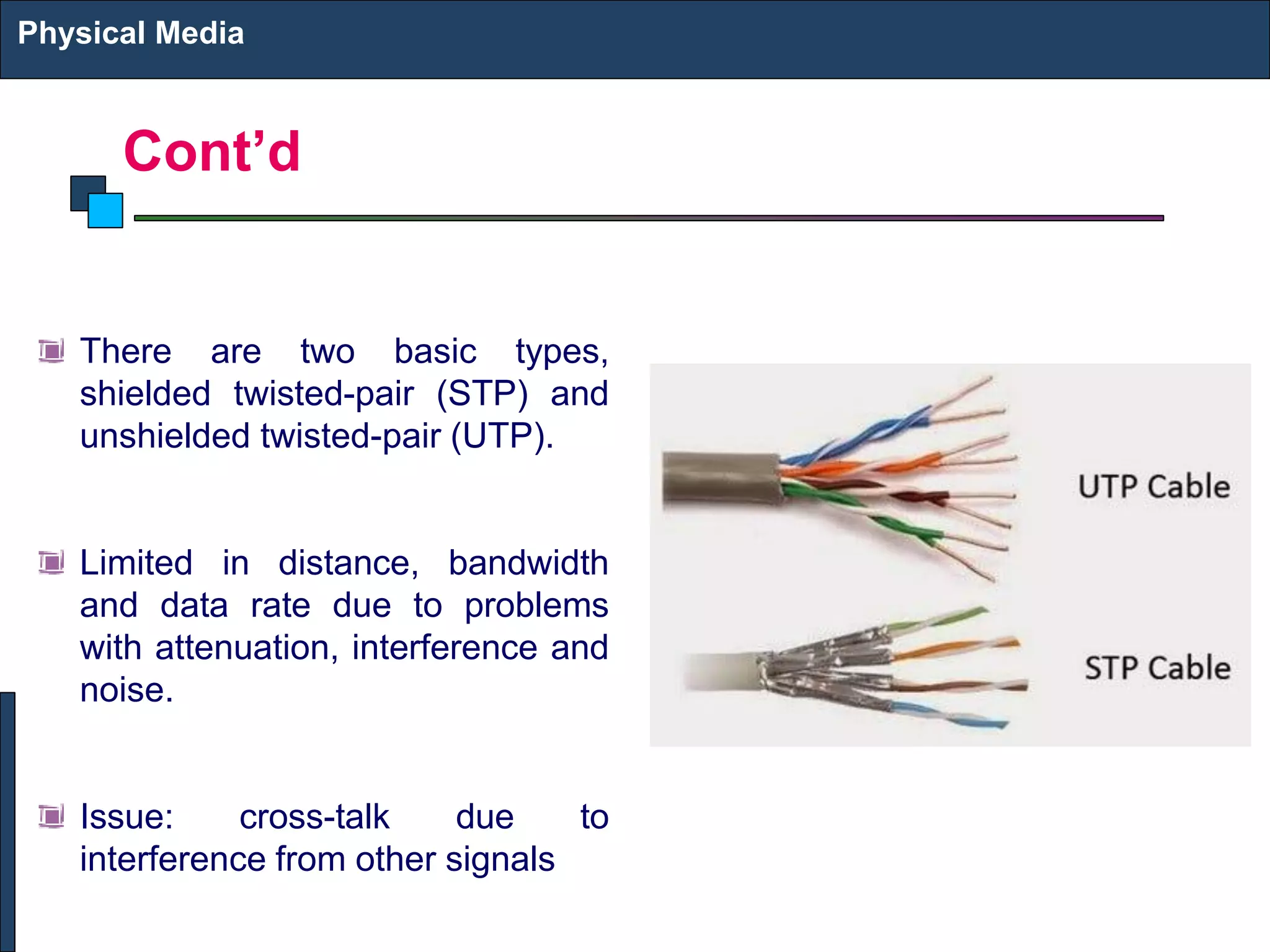
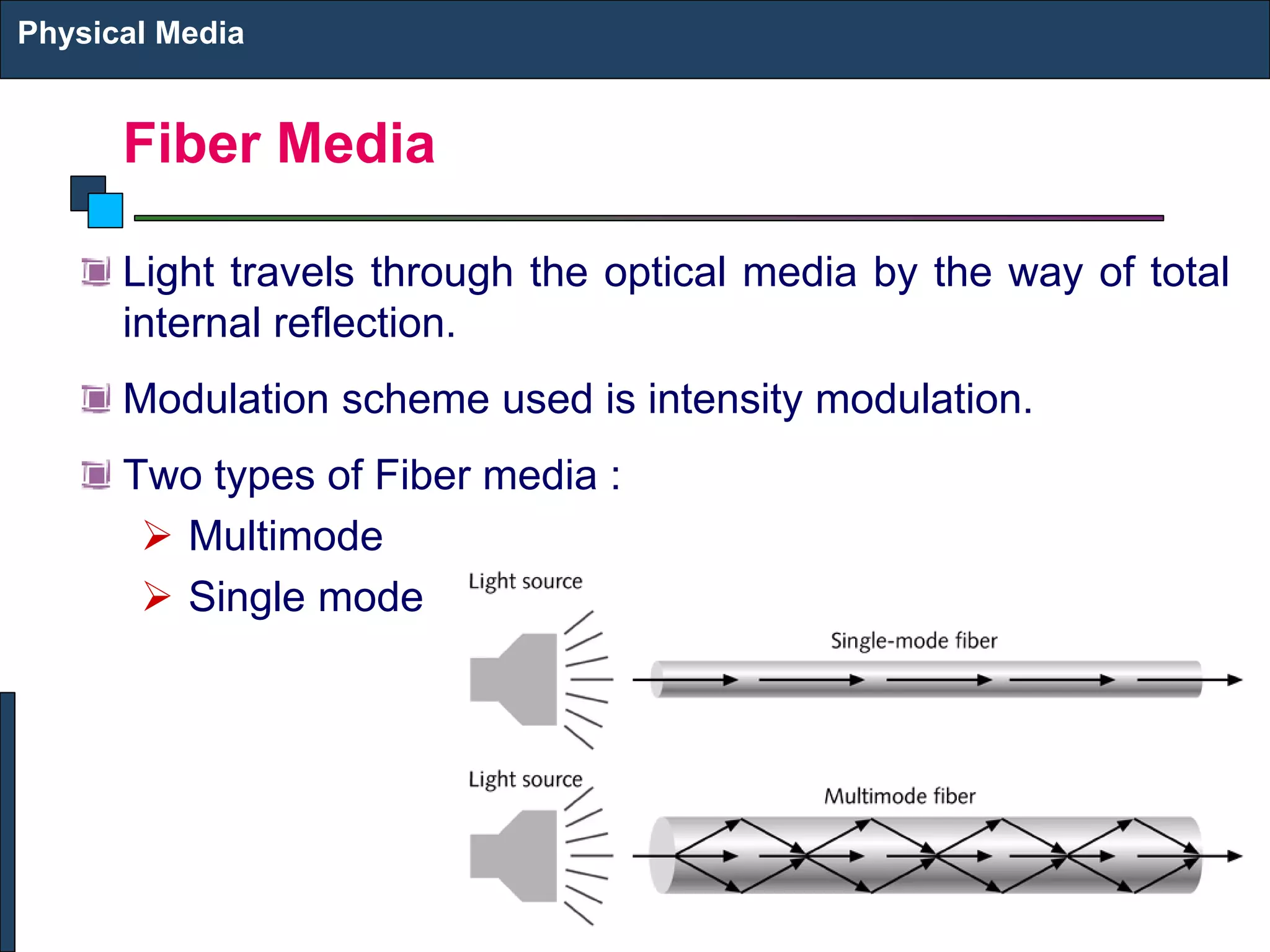
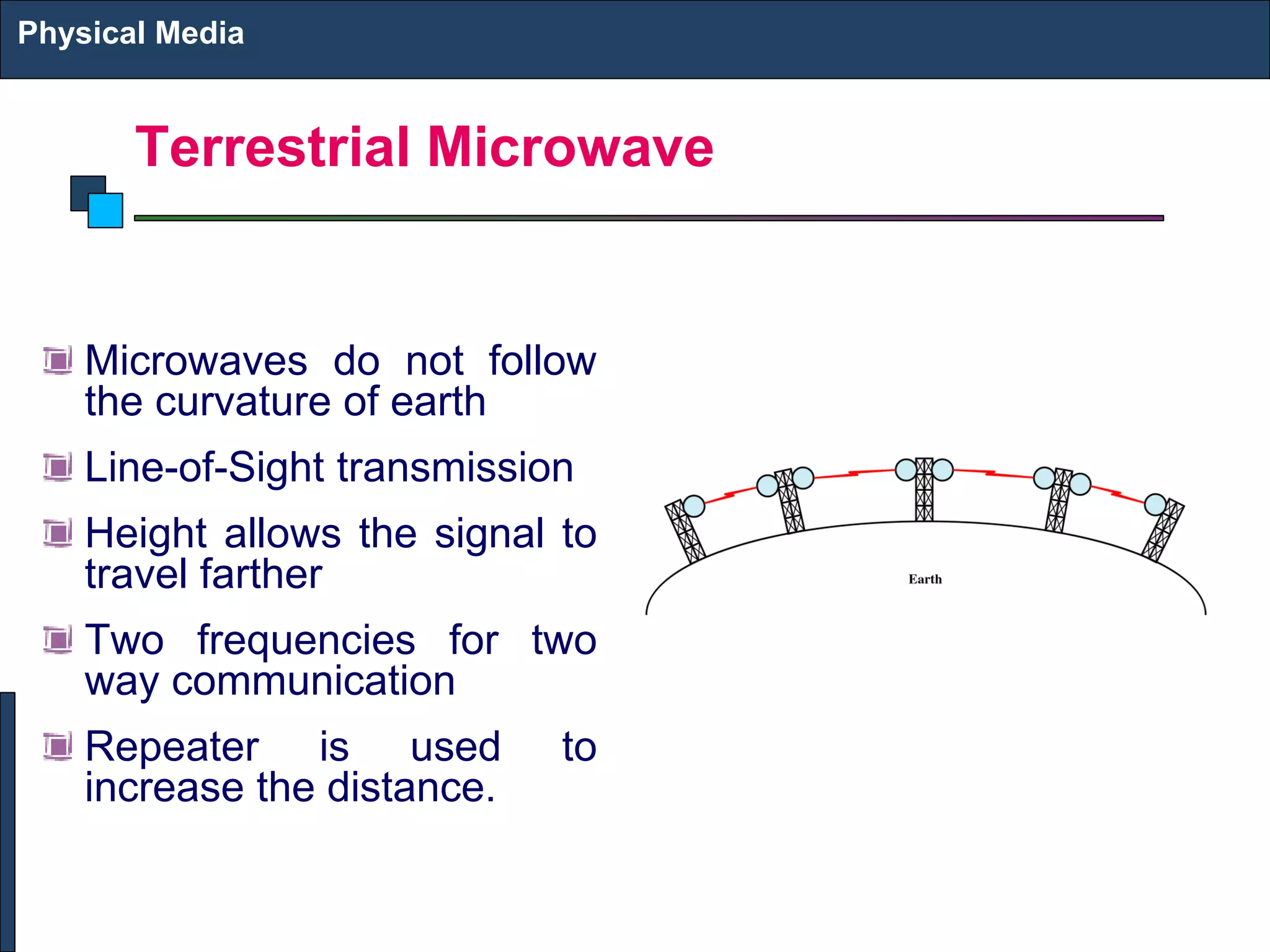
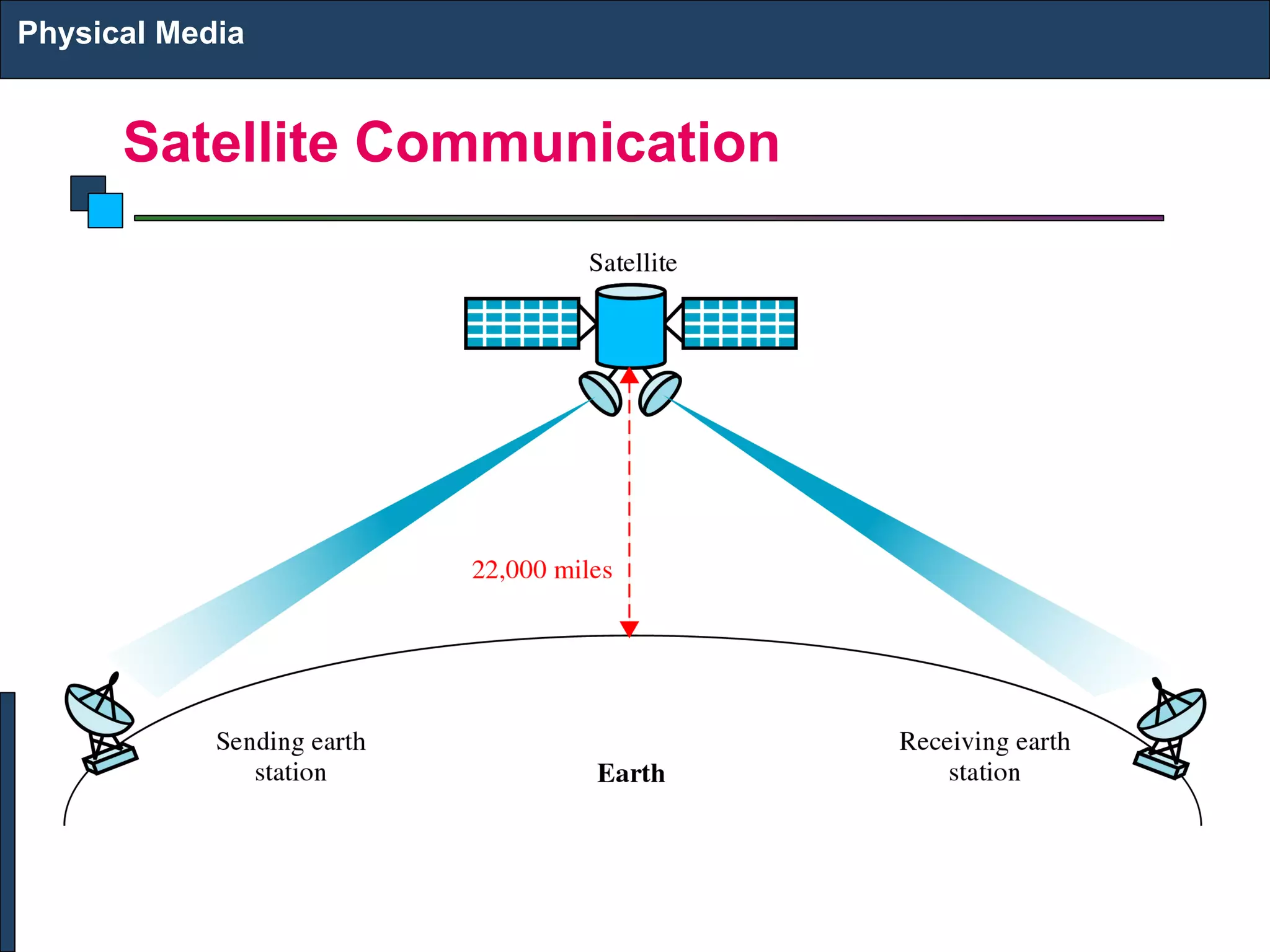
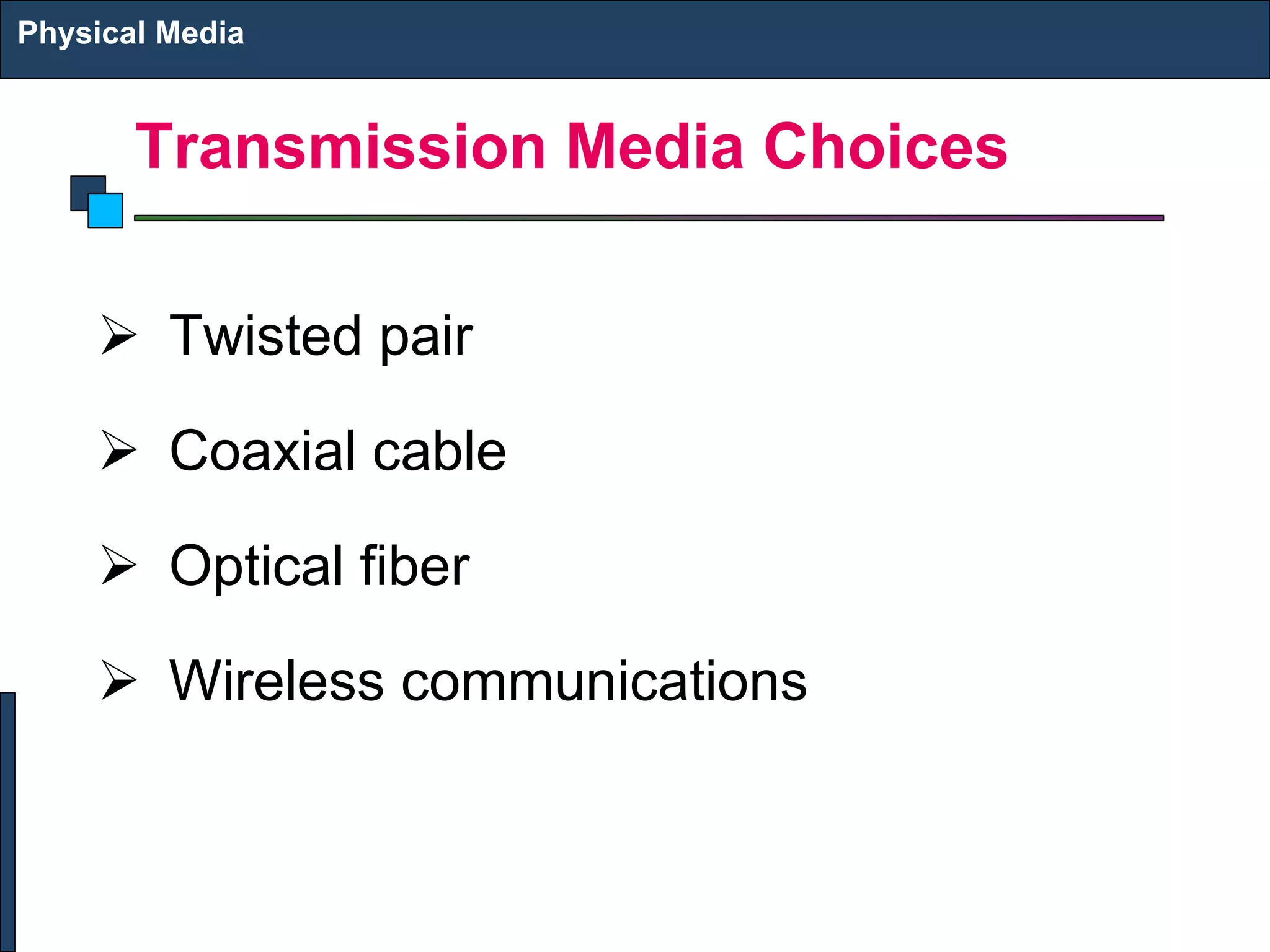
2) There are different types of physical media including twisted pair copper cables, coaxial cables, fiber optic cables (single-mode and multi-mode), and wireless transmission using technologies like infrared, microwave, radio, and satellite communication.
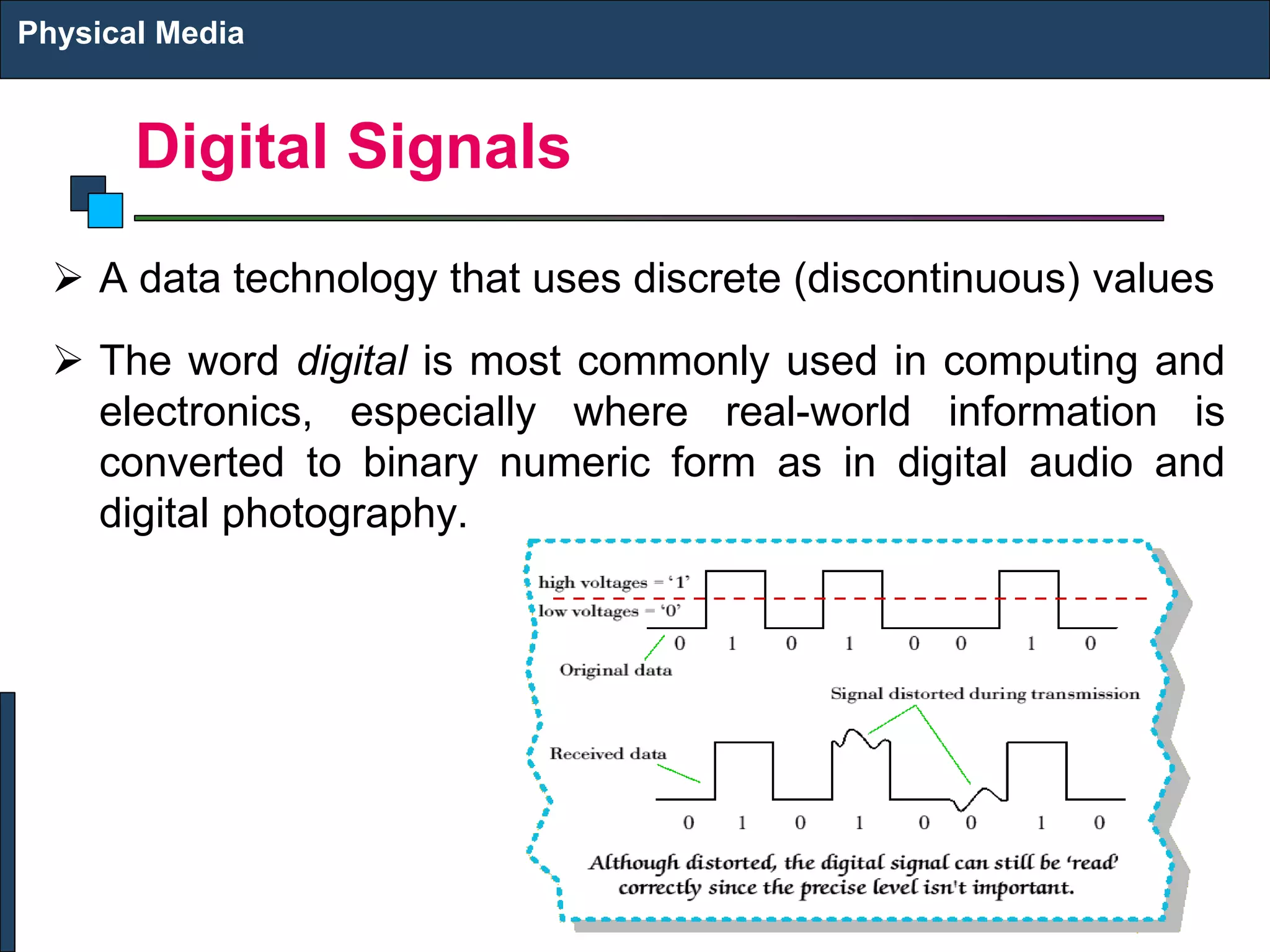
3) Each physical medium has its own characteristics regarding bandwidth, distance capability, noise immunity, and data transmission speed that make some better suited for certain applications over others. Selection depends on network needs and environment.








![Cont’d
Divided into two basic categories
for coax used in LANs.
– 50-ohm cable [baseband]
– 75-ohm cable [broadband or
single channel baseband]
In general, coax has better noise
immunity for higher frequencies
than twisted pair.
Coaxial cable provides much
higher bandwidth than twisted
pair.
However, cable is ‘bulky’.
Physical Media
Category Impedance Use
RG-59 75 W Cable TV
RG-58 50 W
Thin
Ethernet
RG-11 50 W
Thick
Ethernet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicallayer-transmissionmedia-230927063740-c943c5c3/75/Physical-Layer-Transmission-Media-pdf-13-2048.jpg)