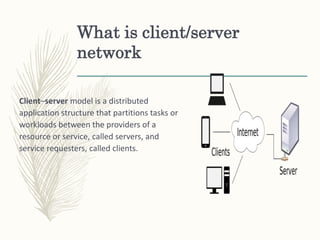
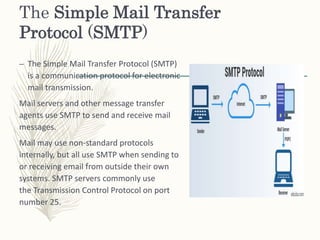
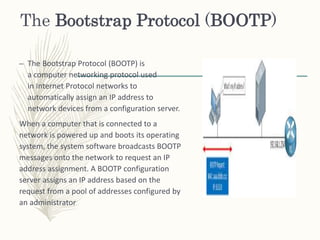
The document primarily discusses client/server protocols and networks, outlining their definitions and functions. It details key protocols like TCP, HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP, and BOOTP, explaining their roles in data transmission and communication. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of client/server networks, such as centralized control and scalability versus traffic congestion and server dependency.