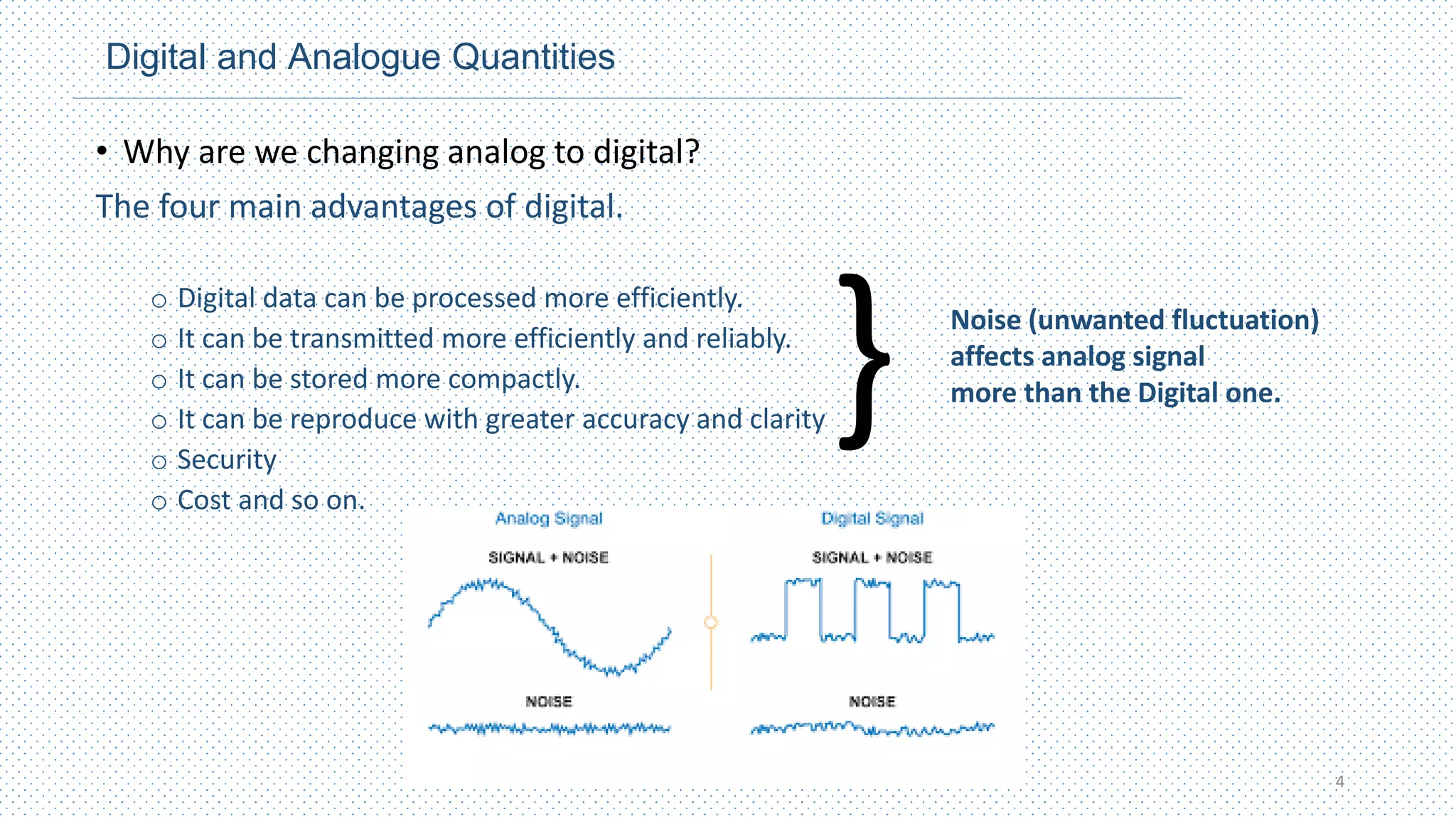
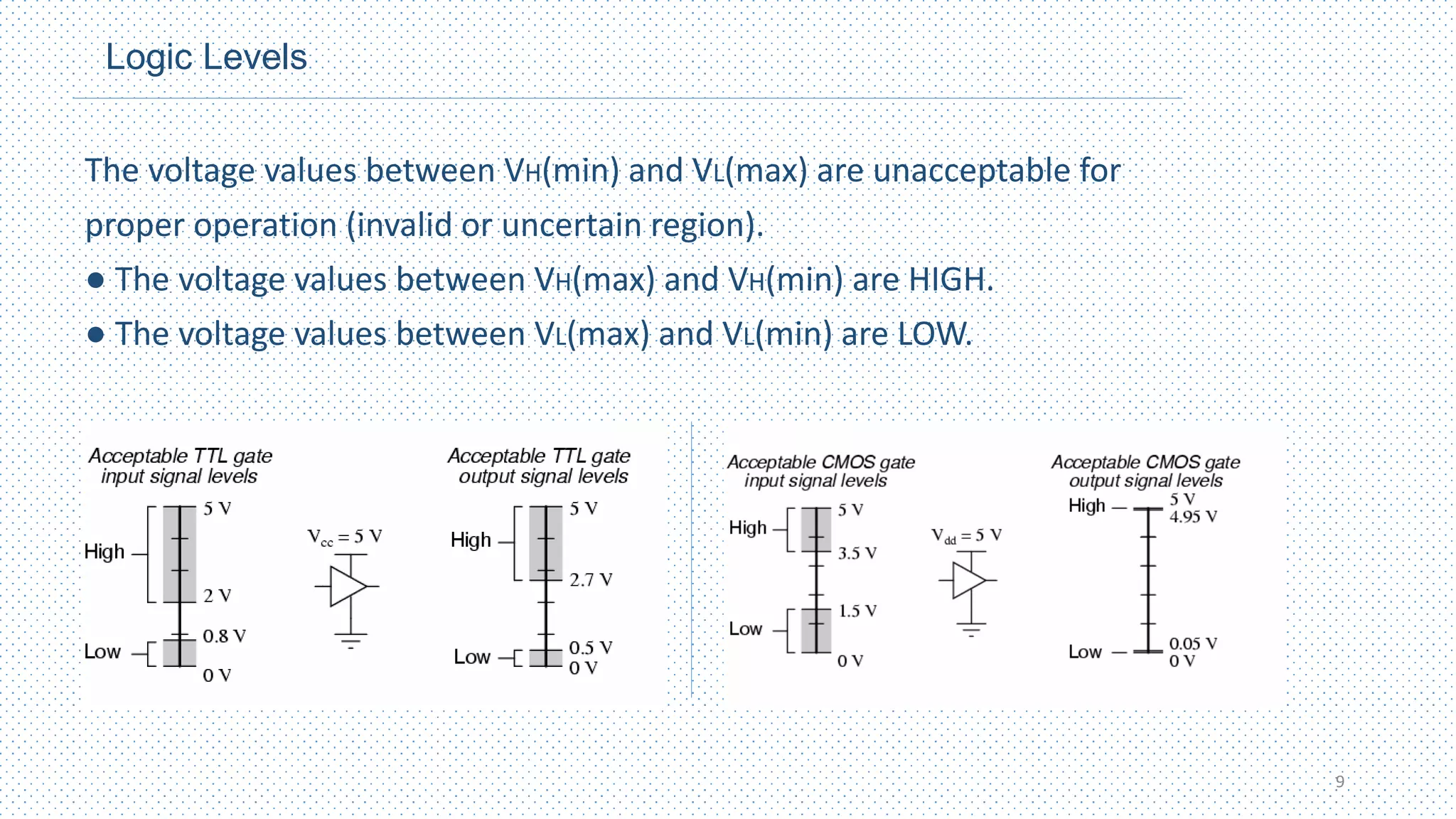
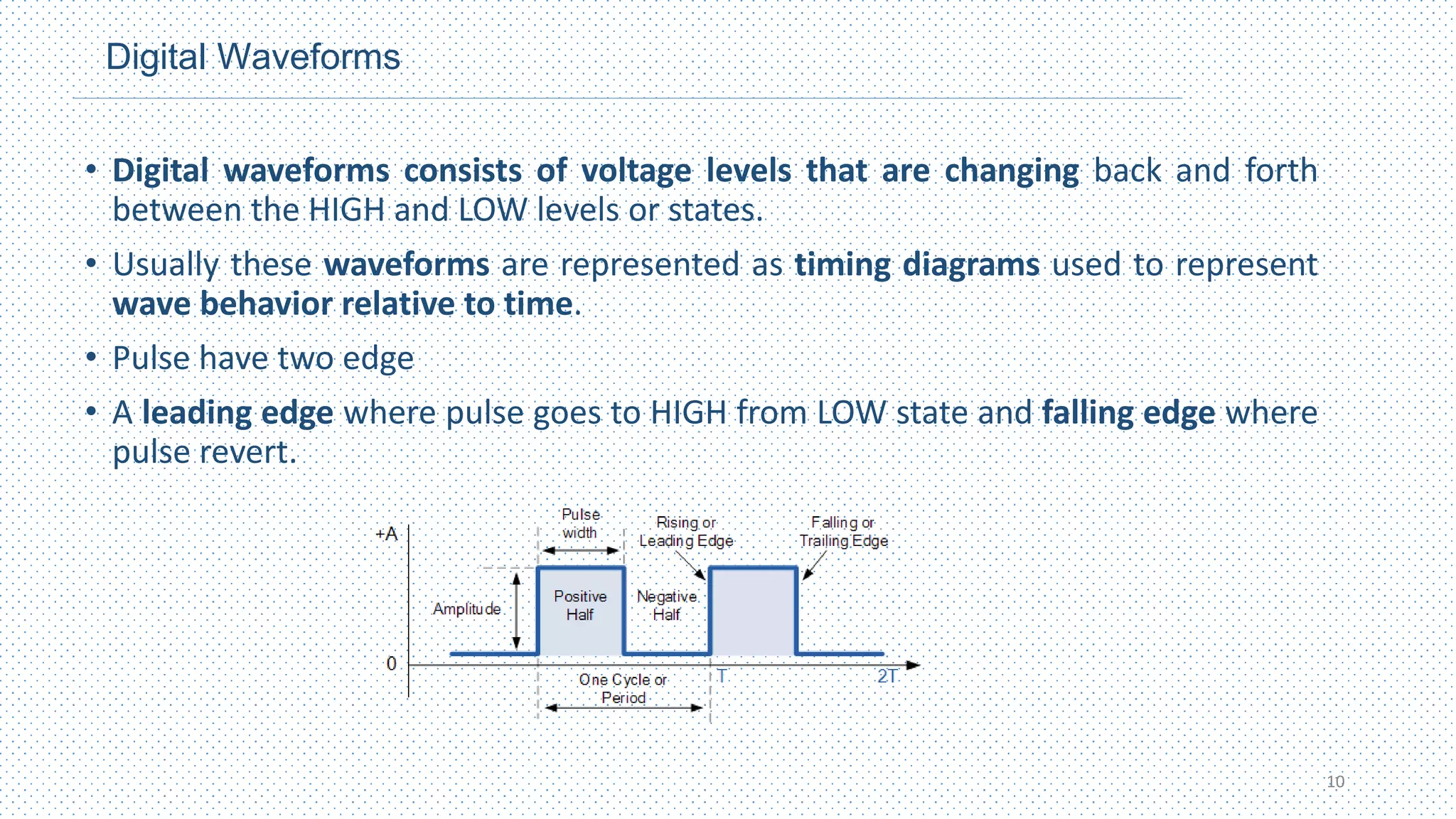
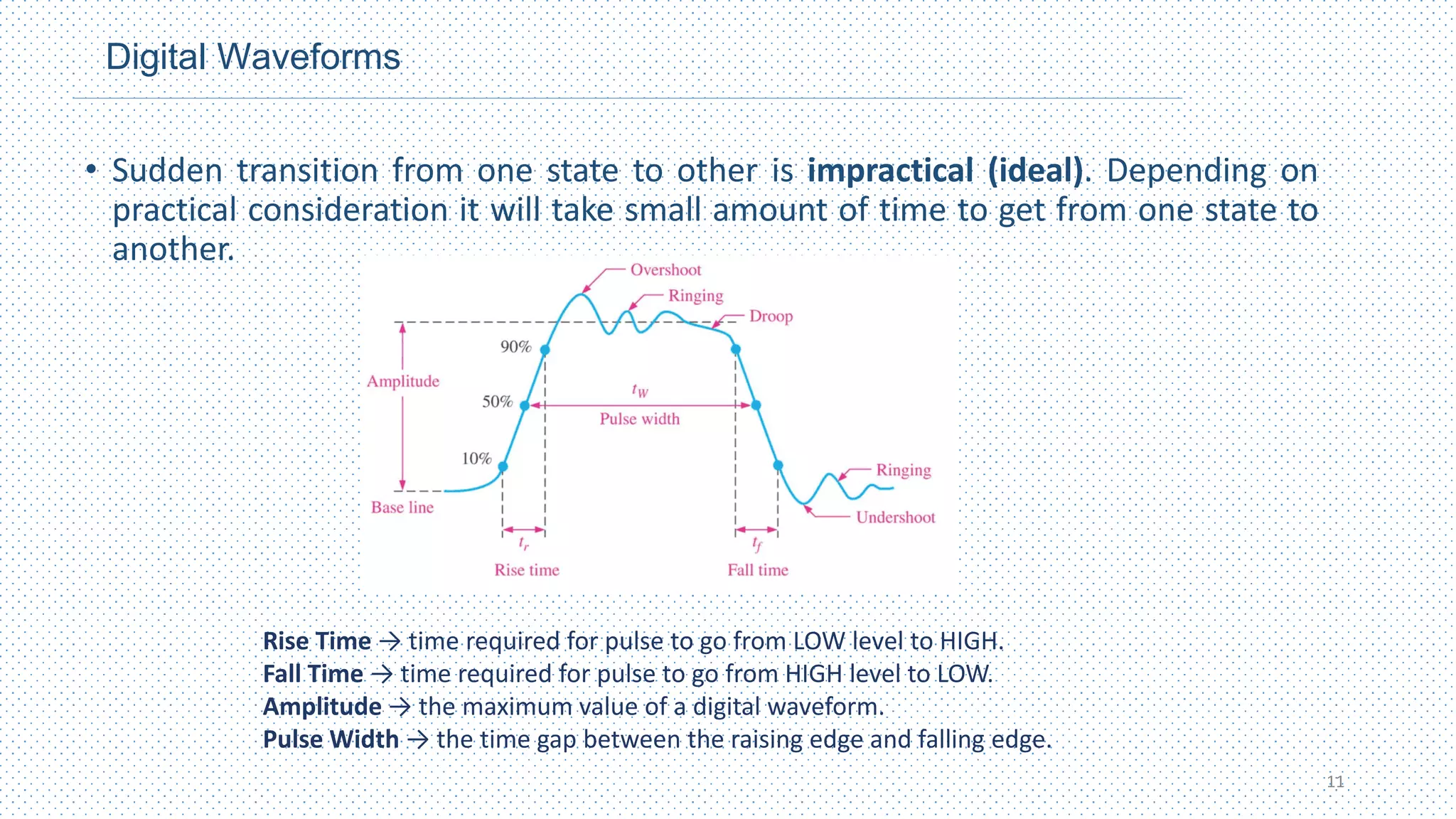
This document provides an introduction to digital design. It defines digital and analog signals, with digital signals using discrete voltage levels to represent binary digits of 1 and 0, while analog signals have continuously varying voltage levels. Digital signals are more efficient for processing, transmission, storage and reproduction compared to analog signals. Logic levels define the high and low voltage ranges used to represent 1s and 0s. Digital waveforms switch between these logic levels over time. Digital logic design uses binary numbers to perform logic operations like AND, OR and NOT through logic gates to process inputs and outputs for computing and electronics applications.