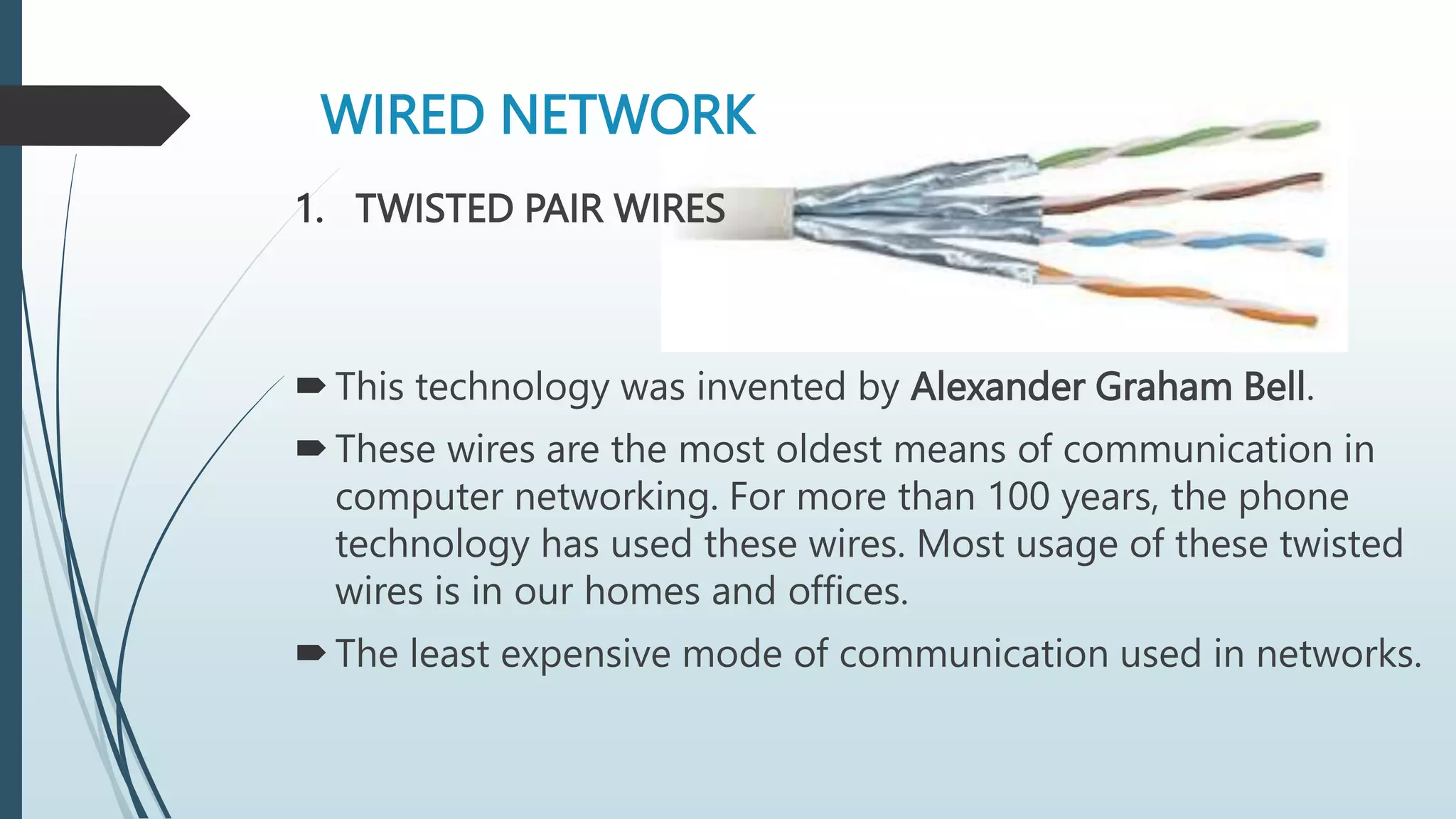
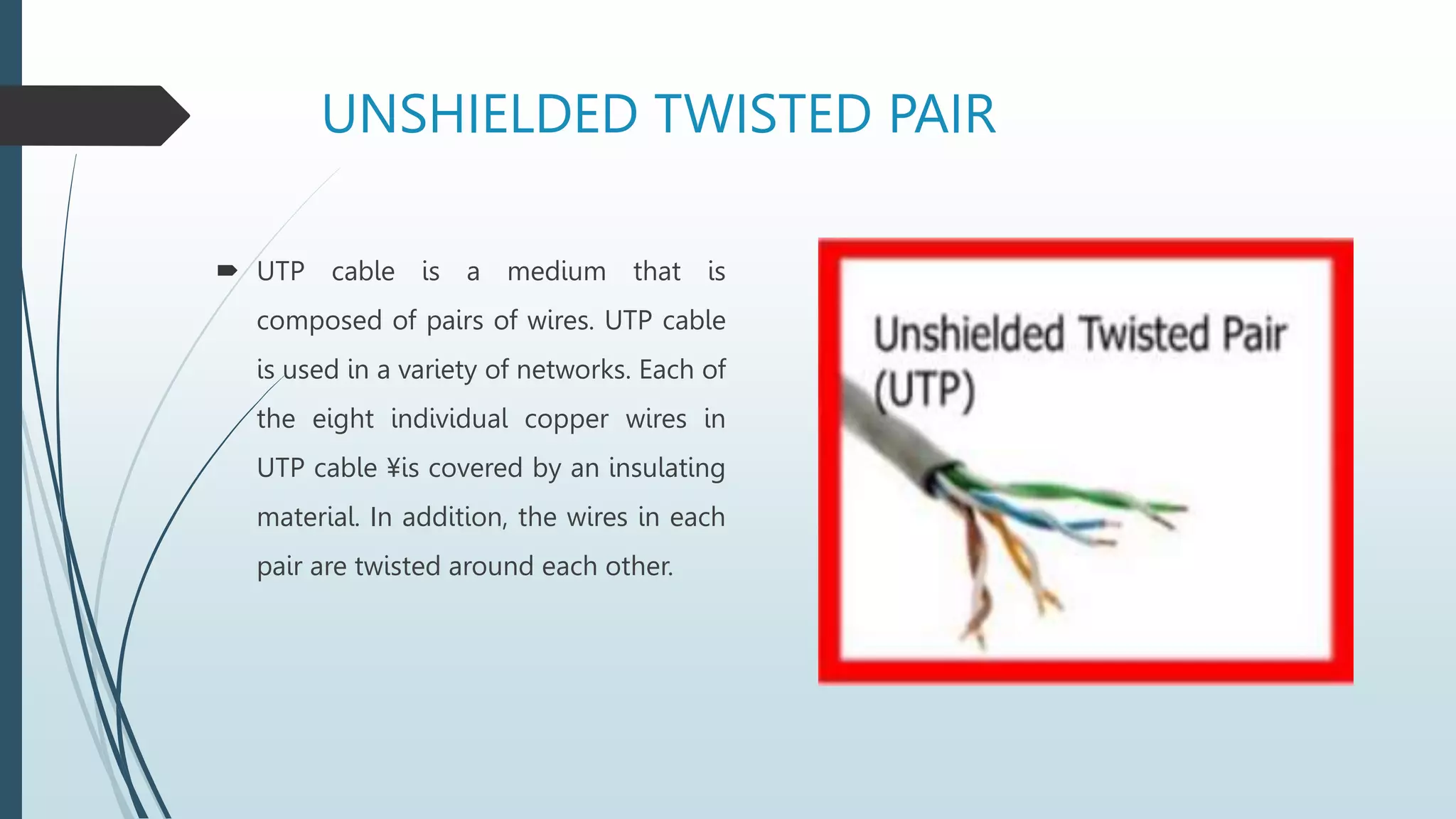
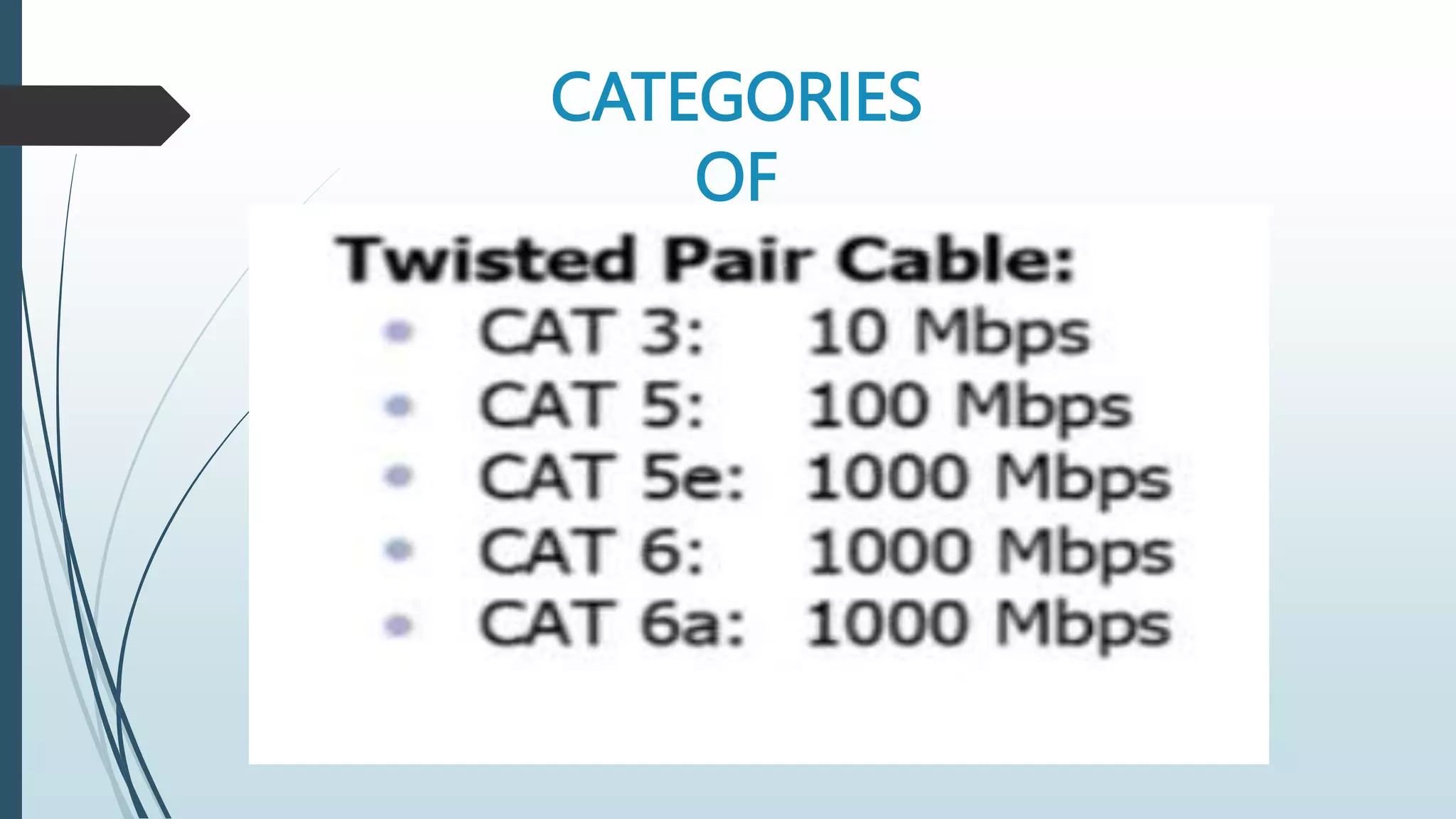
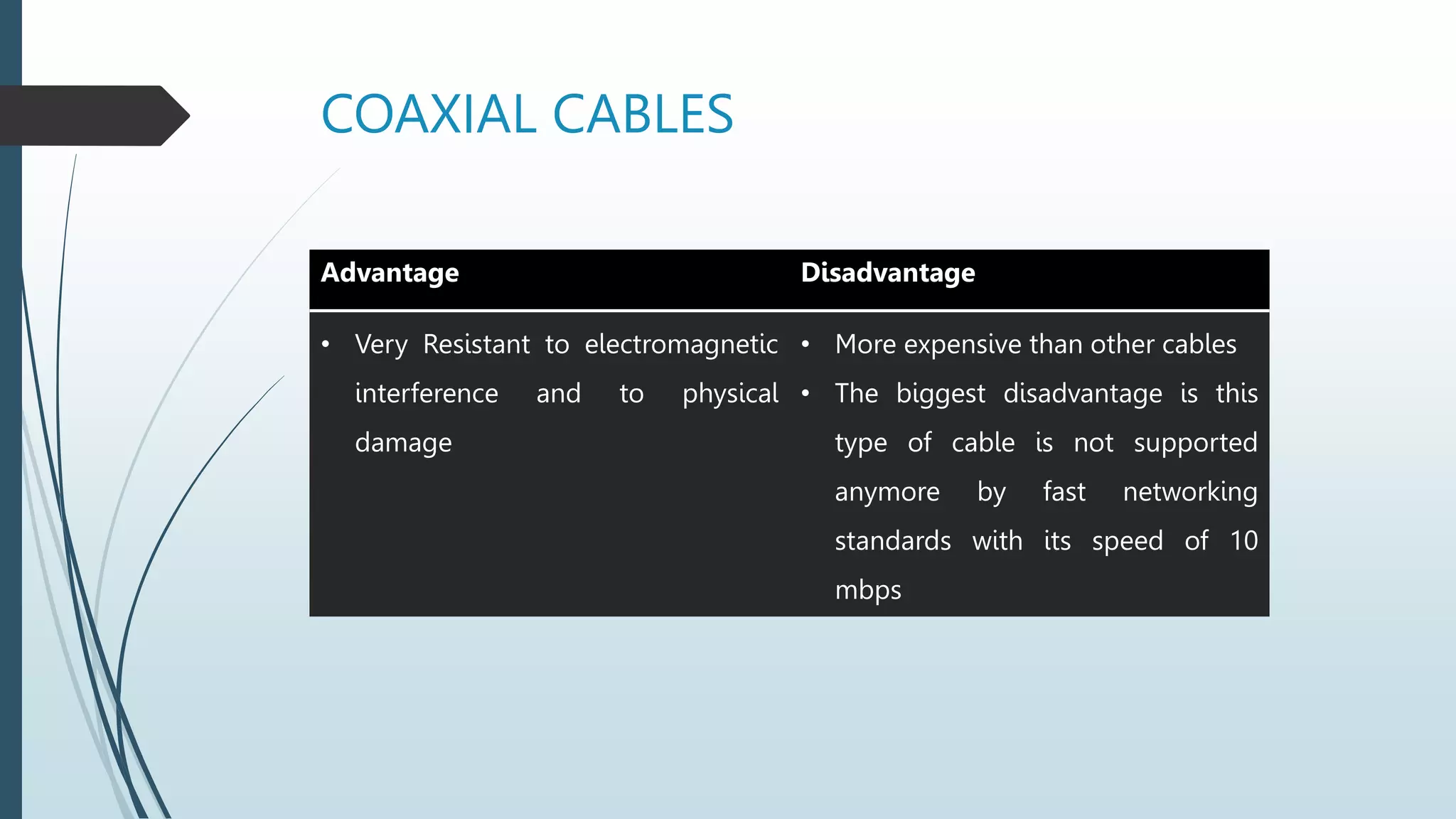
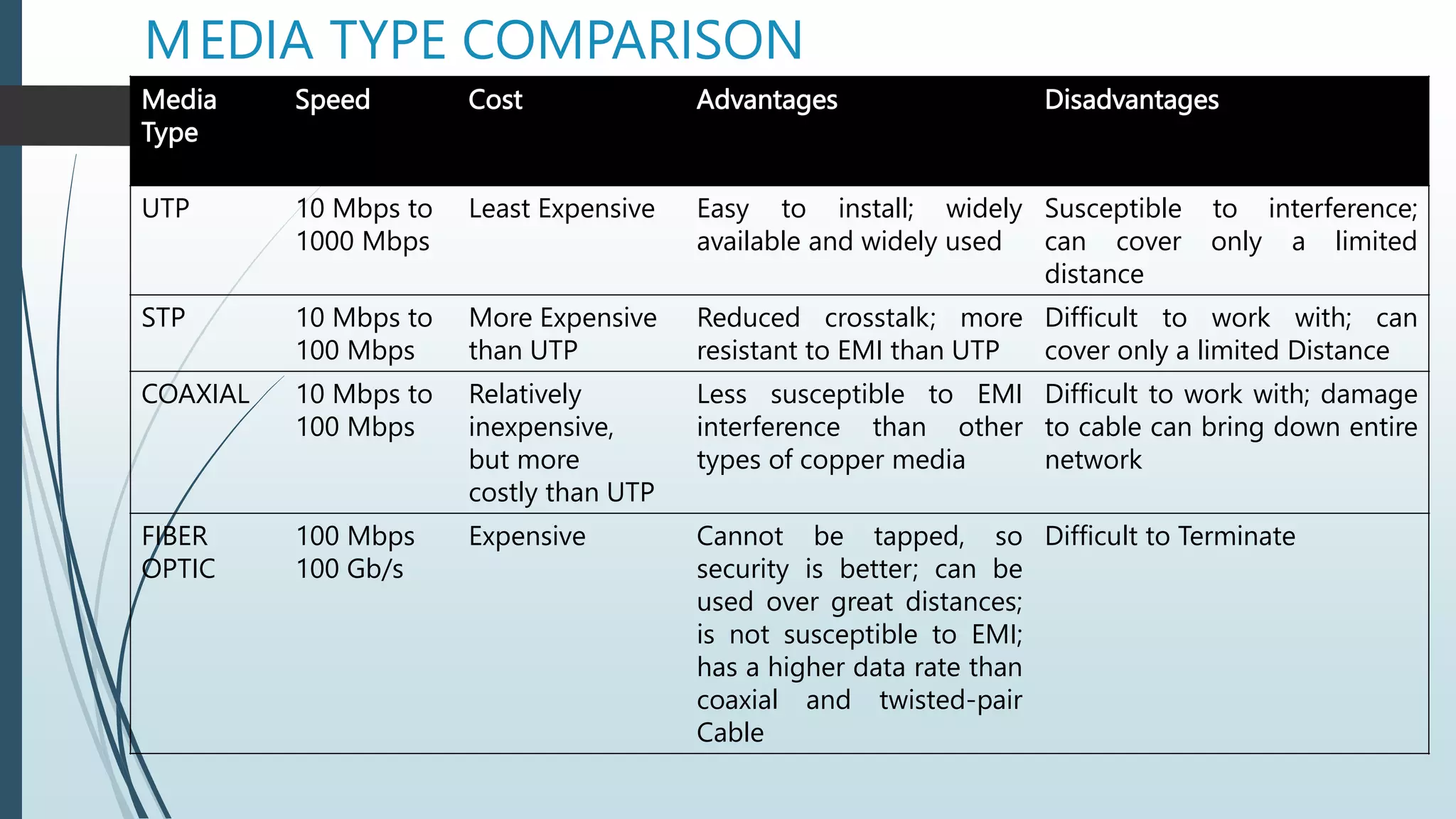
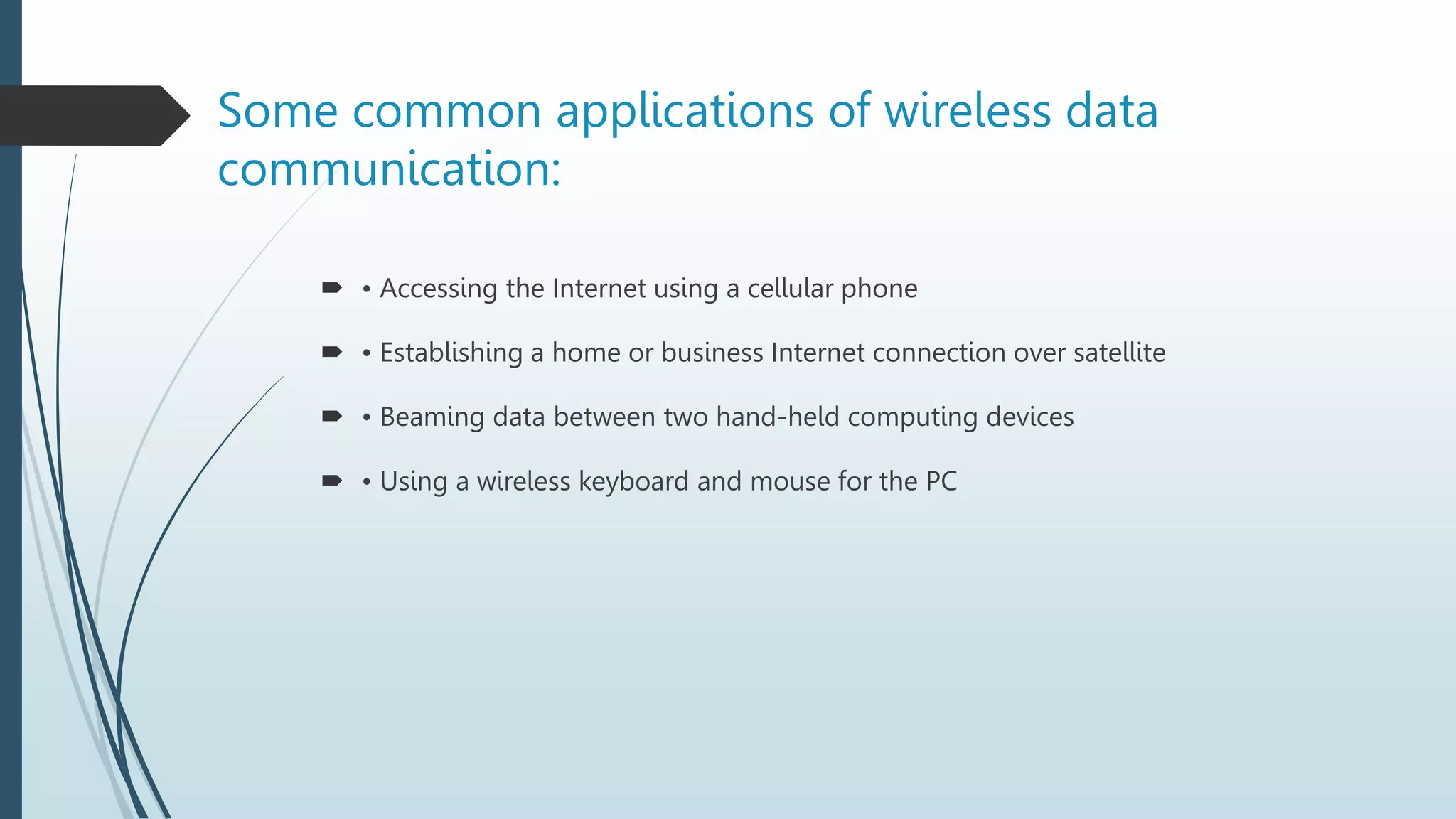
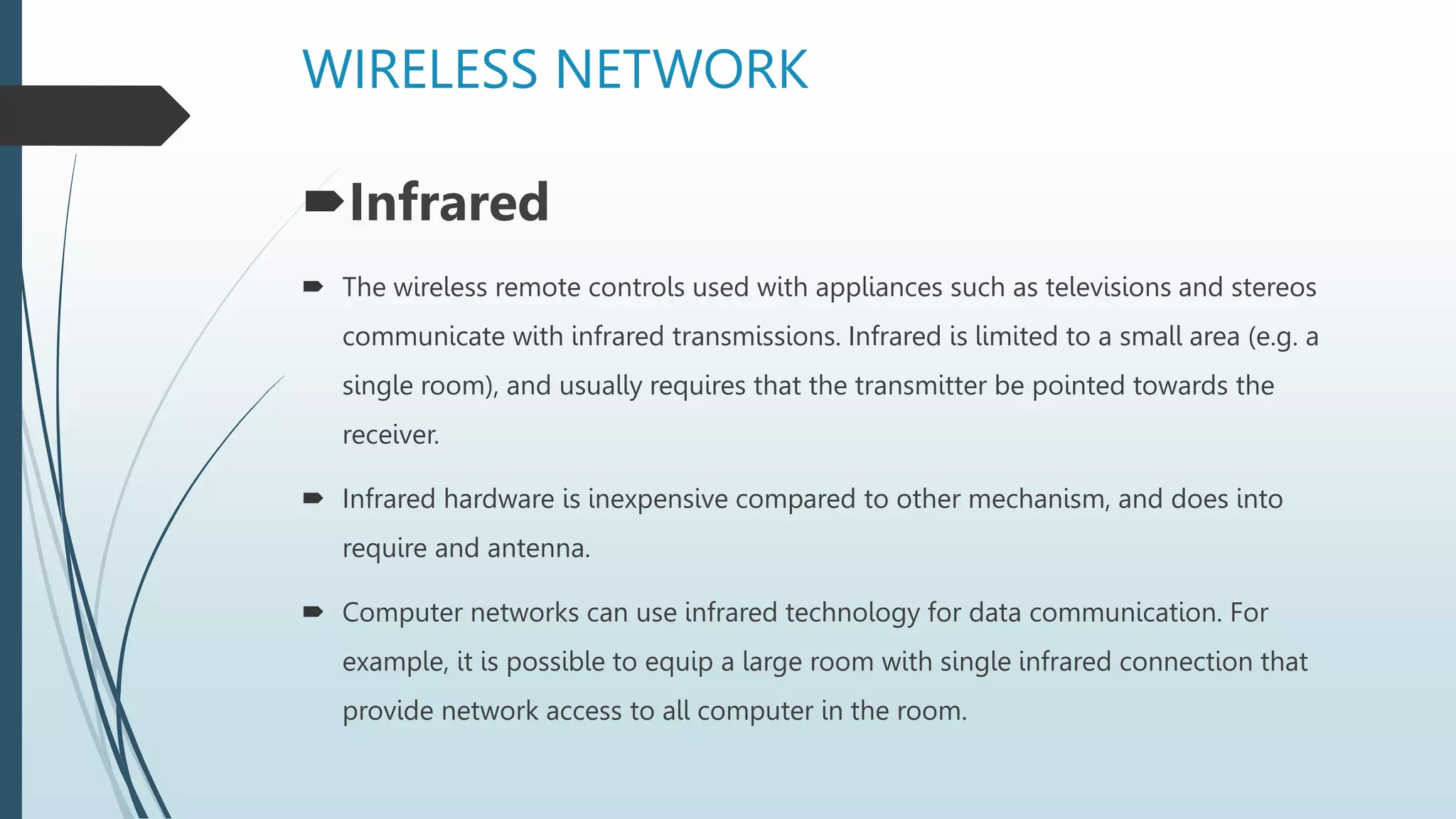
Network media types include wired and wireless options. Wired networks use twisted pair wires, coaxial cable, or fiber optic cables to transmit data via physical connections. Twisted pair wires can be unshielded or shielded, while coaxial cables have inner and outer conductors separated by insulation. Fiber optic cables transmit data via pulses of light through glass or plastic fibers. Wireless networks transmit data via radio frequencies or infrared waves without physical connections. Common wireless technologies include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and communication satellites. Wired networks have higher speeds but limited ranges, while wireless networks allow mobility but can have lower speeds and security risks. The choice of network media depends on needs and constraints like data speeds, distances, costs, and susceptibility to interference