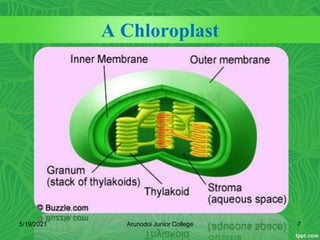
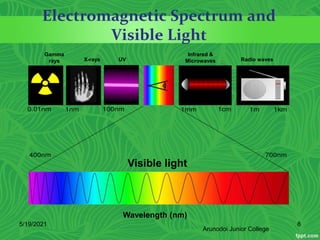
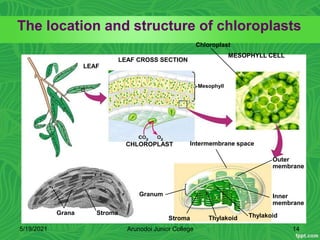
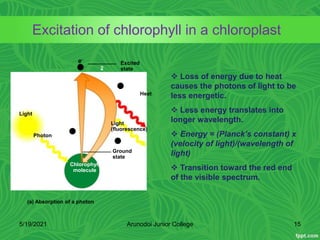
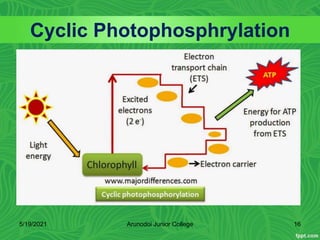
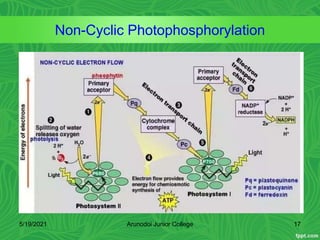
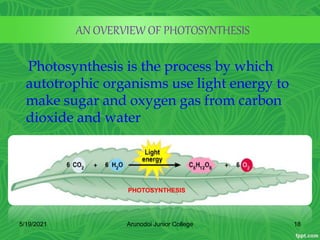
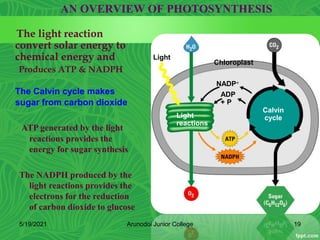
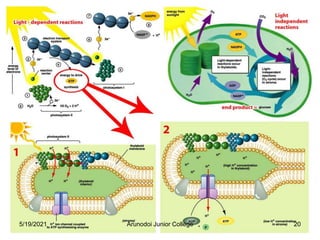
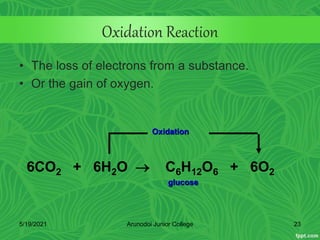
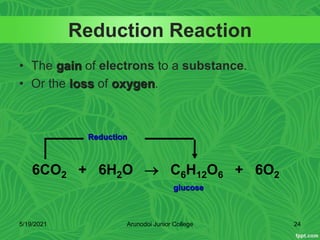
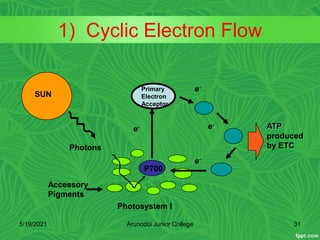
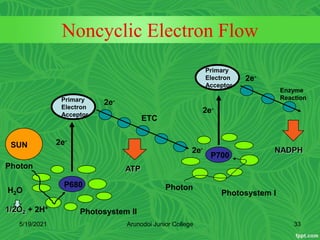
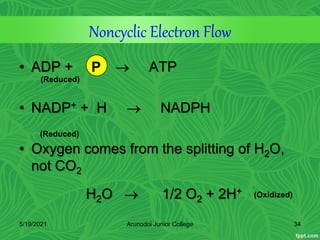
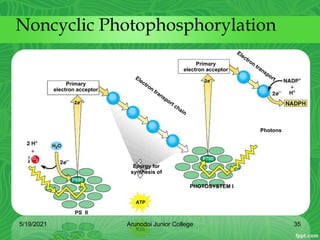
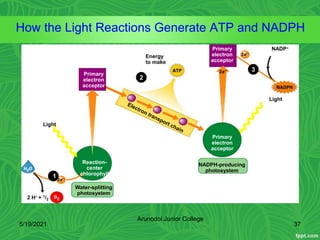
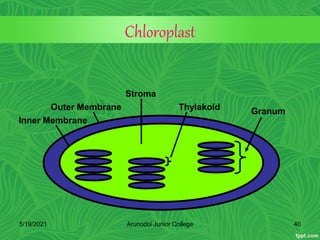
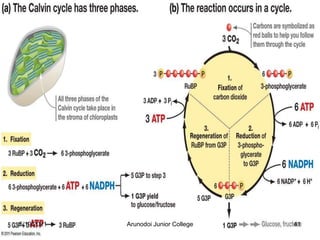
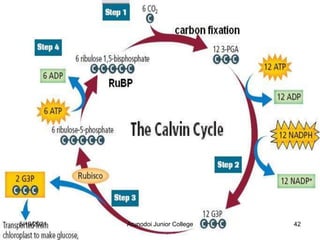
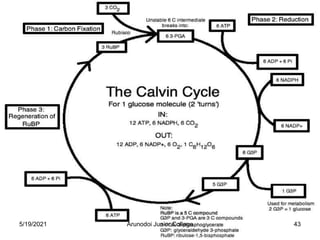
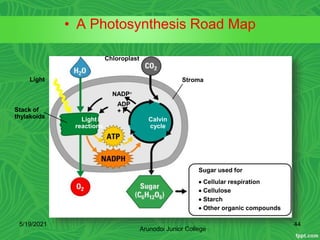
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light-dependent reactions where light energy is captured to form ATP and NADPH using chlorophyll, and the light-independent reactions of the Calvin cycle where carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic compounds to form glucose using ATP and NADPH. Photosynthesis provides the primary source of energy and organic molecules that sustain life on Earth and produces oxygen as a byproduct.