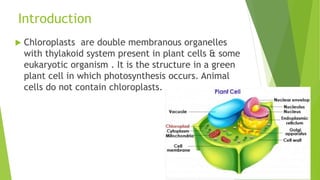
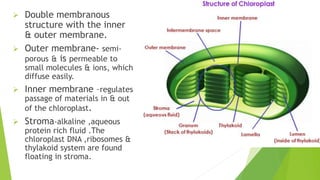
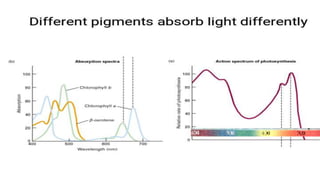
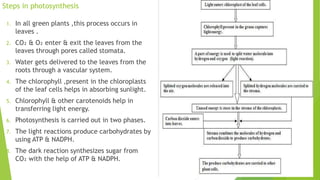
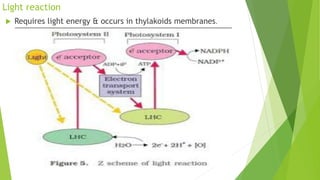
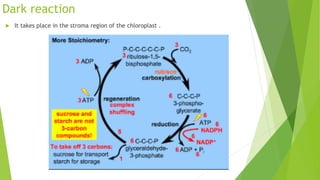
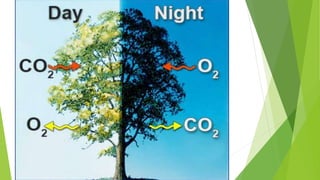
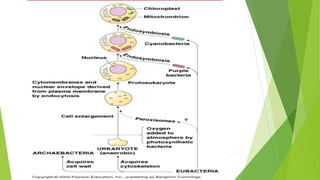
Chloroplasts are double membranous organelles within plant cells where photosynthesis occurs, absorbing sunlight to convert it into sugar molecules and free energy stored as ATP and NADPH. They consist of a stroma containing DNA and ribosomes, and a thylakoid system where the light reactions of photosynthesis take place. The overall process supports life on Earth by producing oxygen and carbohydrates, essential for both plants and animals.