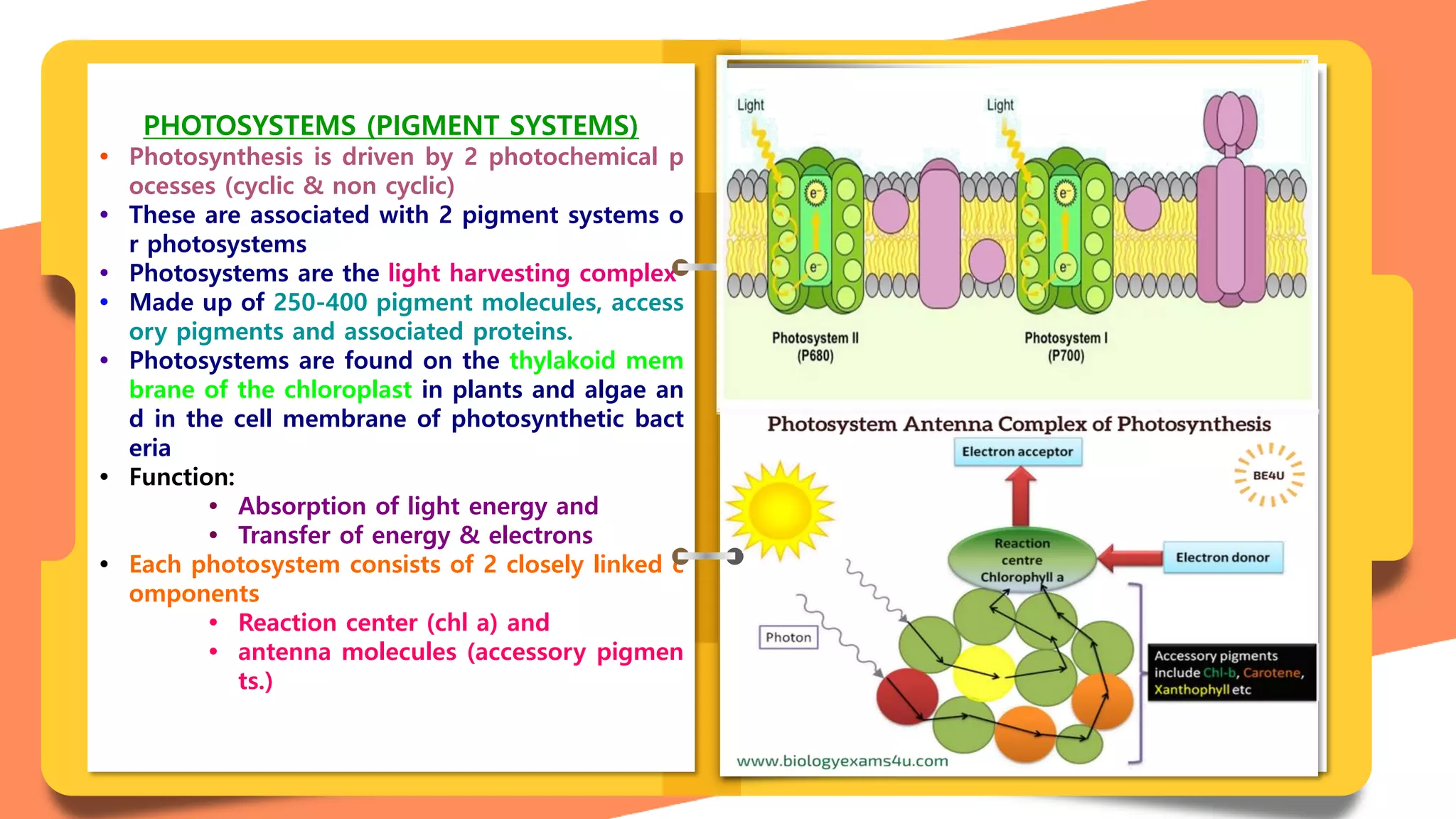
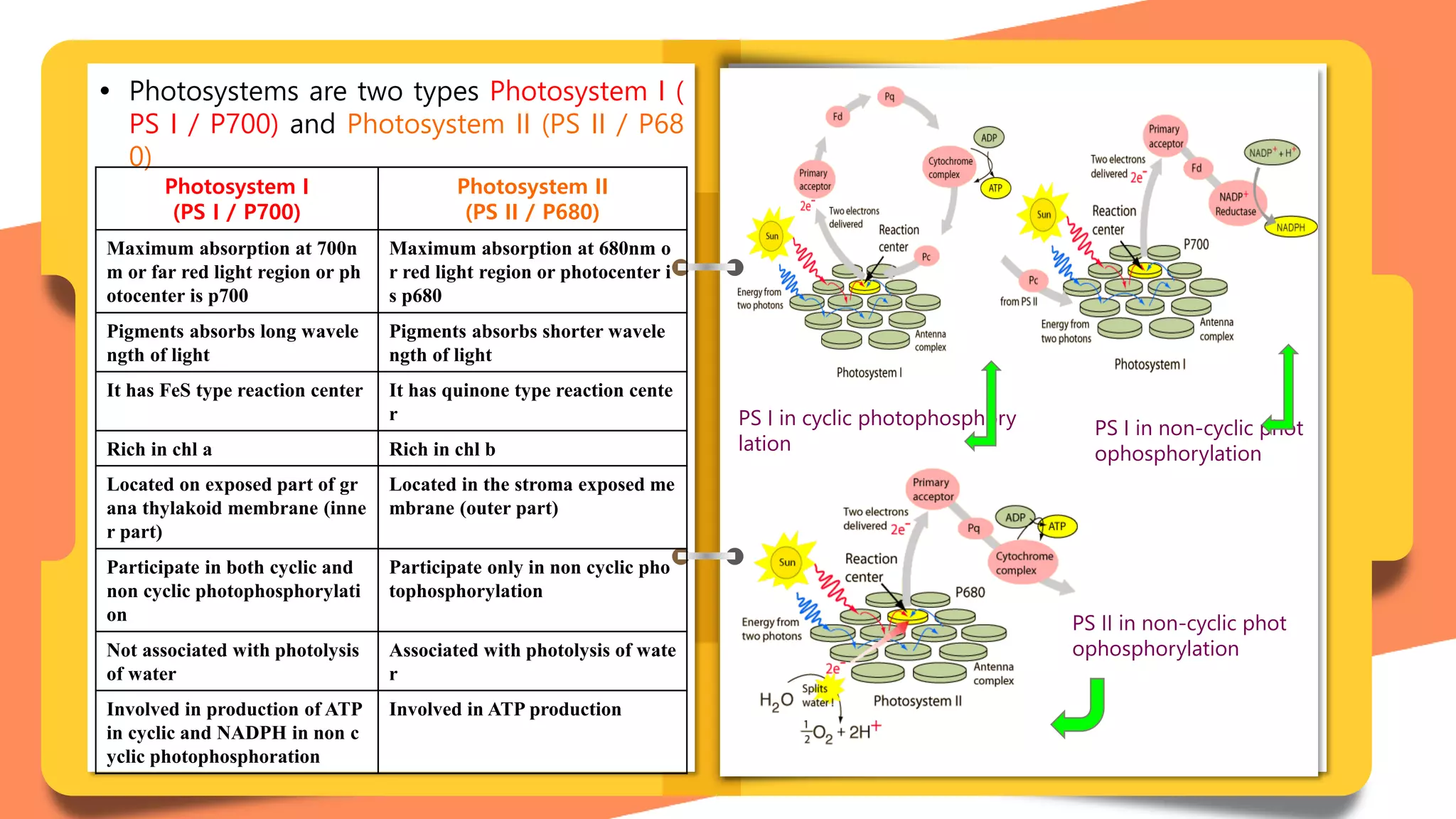
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using light energy, occurring in chloroplasts. It involves two main reactions: light-dependent reactions (cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation) occurring in the thylakoid membranes, and light-independent reactions (dark reactions) happening in the stroma. Key components include photosystems I and II, which facilitate light absorption and energy transfer.