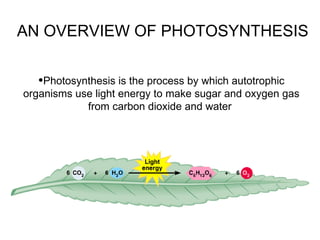
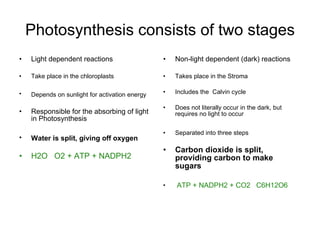
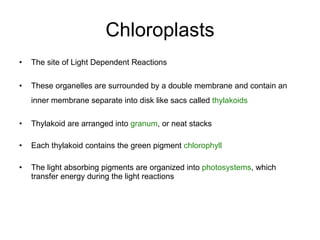
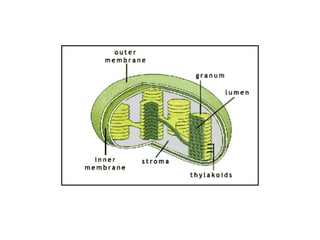
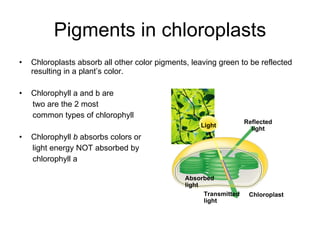
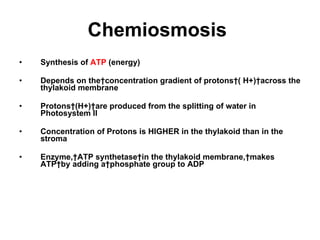
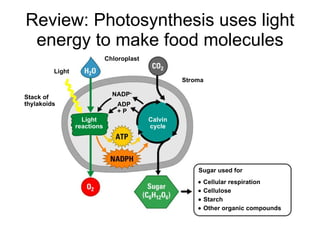
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and energy in the form of sugar. It occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions in the chloroplasts absorb sunlight and split water, producing oxygen and energized molecules. The Calvin cycle then uses this energy to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into organic compounds like glucose. Chlorophyll and other pigments capture sunlight and transfer the energy through electron transport chains to produce ATP and NADPH, which power the Calvin cycle to reduce carbon dioxide into sugars.