Embed presentation
Download to read offline
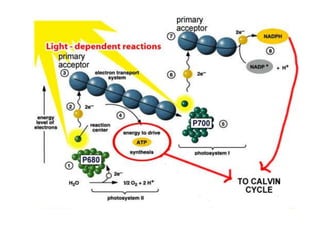

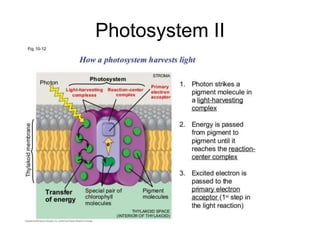

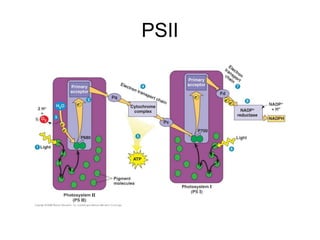




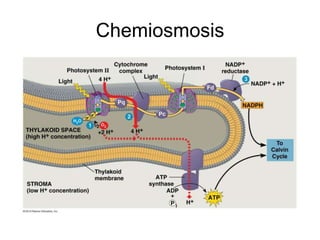
Photosynthesis begins with light being absorbed by chlorophyll in Photosystem II. Electrons in the pigment become excited and move through an electron transport chain, losing energy along the way. This provides energy to pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space, creating a gradient. ATP synthase uses this gradient to make ATP via chemiosmosis. The excited electrons then enter Photosystem I, where more are excited by light and their energy is used to convert NADP+ into NADPH, reducing it. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of water splitting in Photosystem II.









