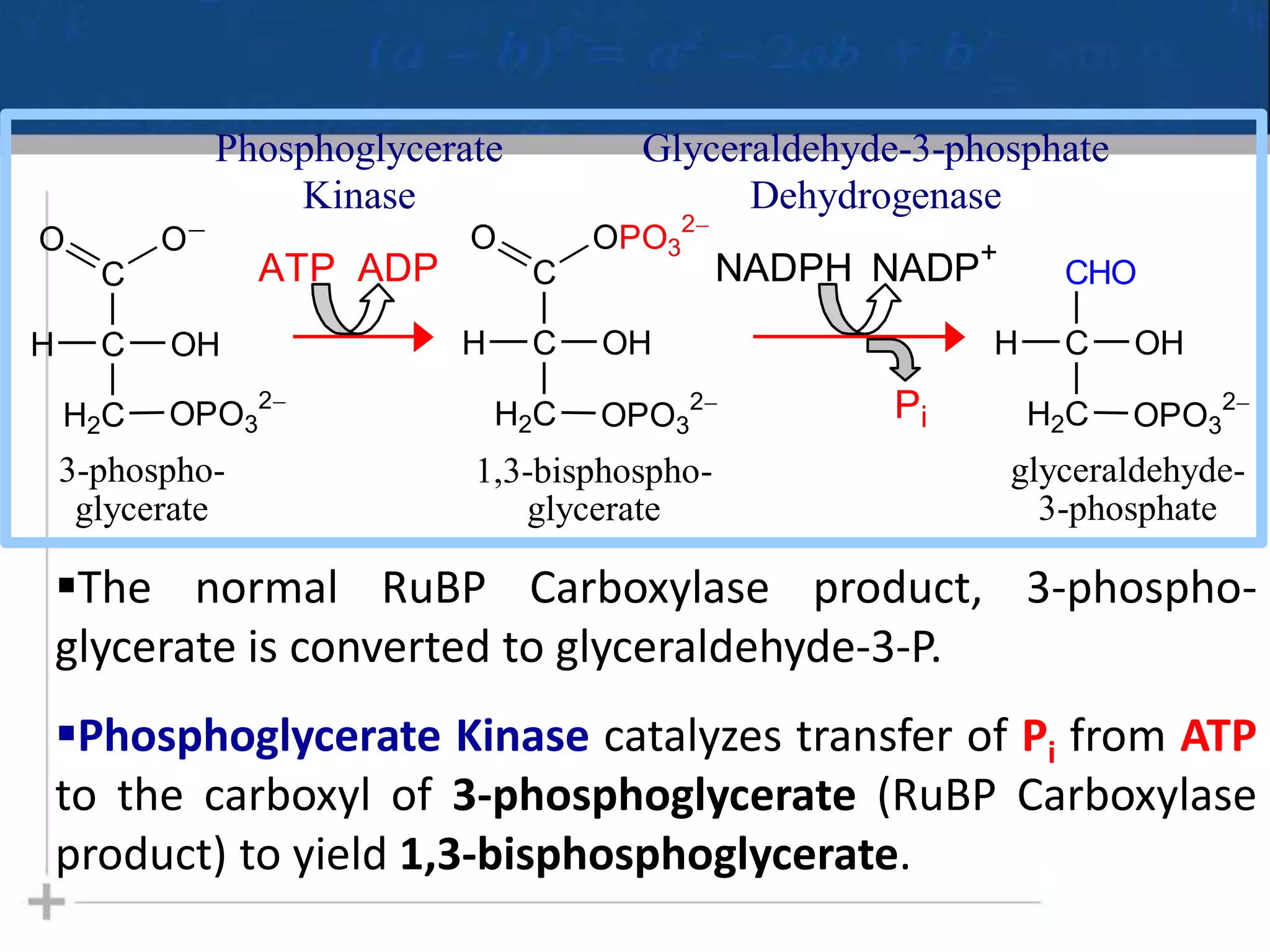
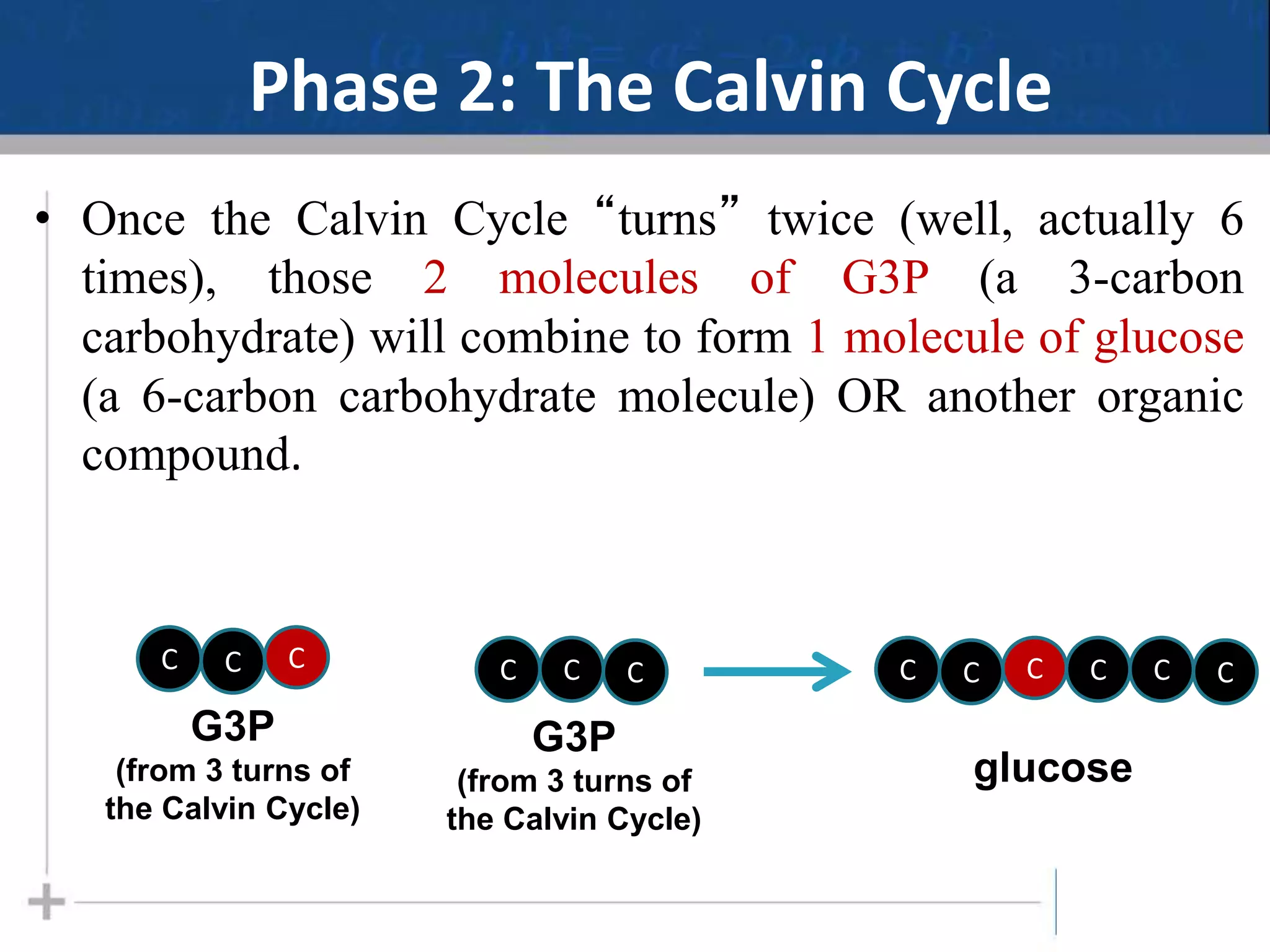
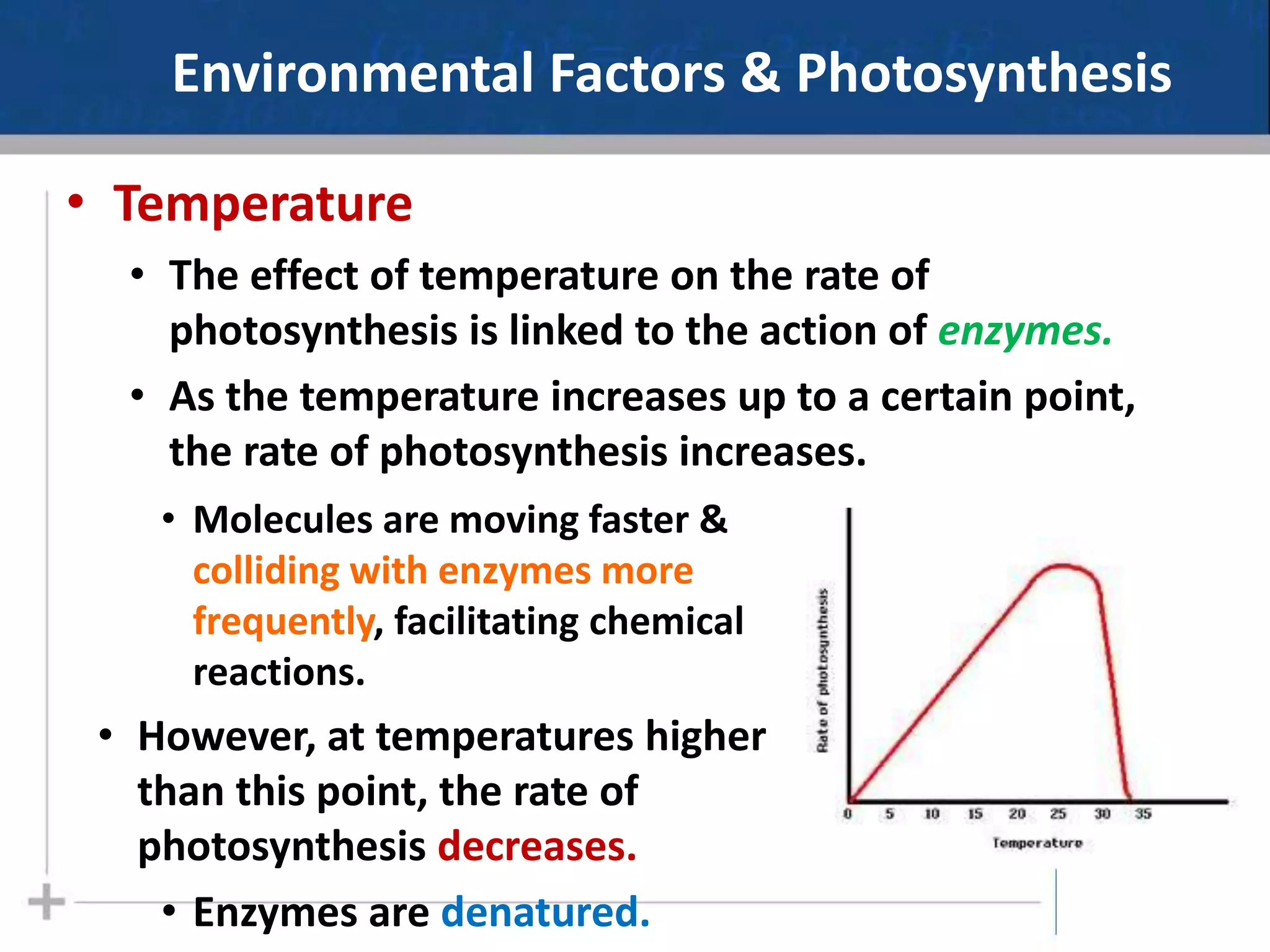
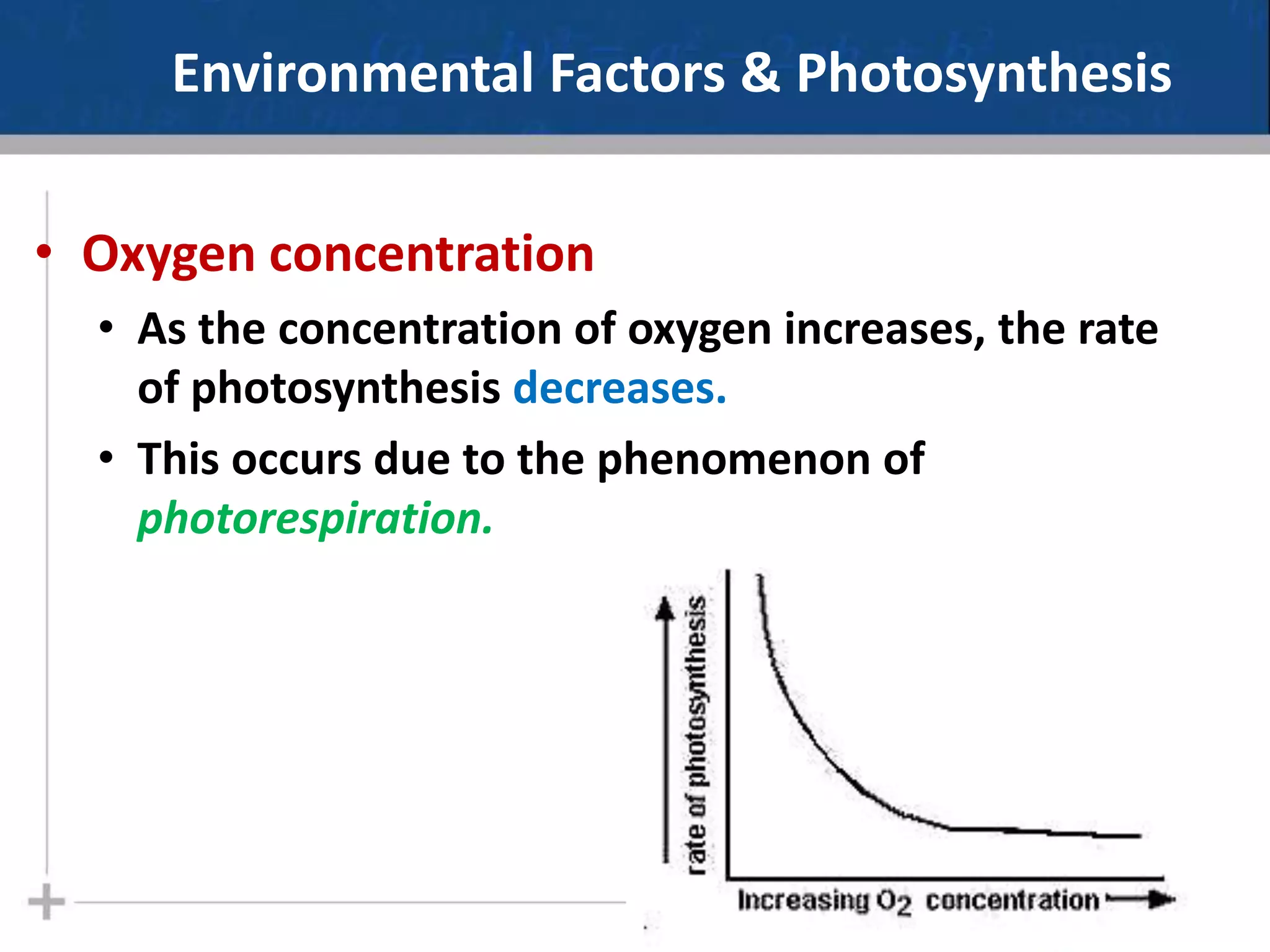
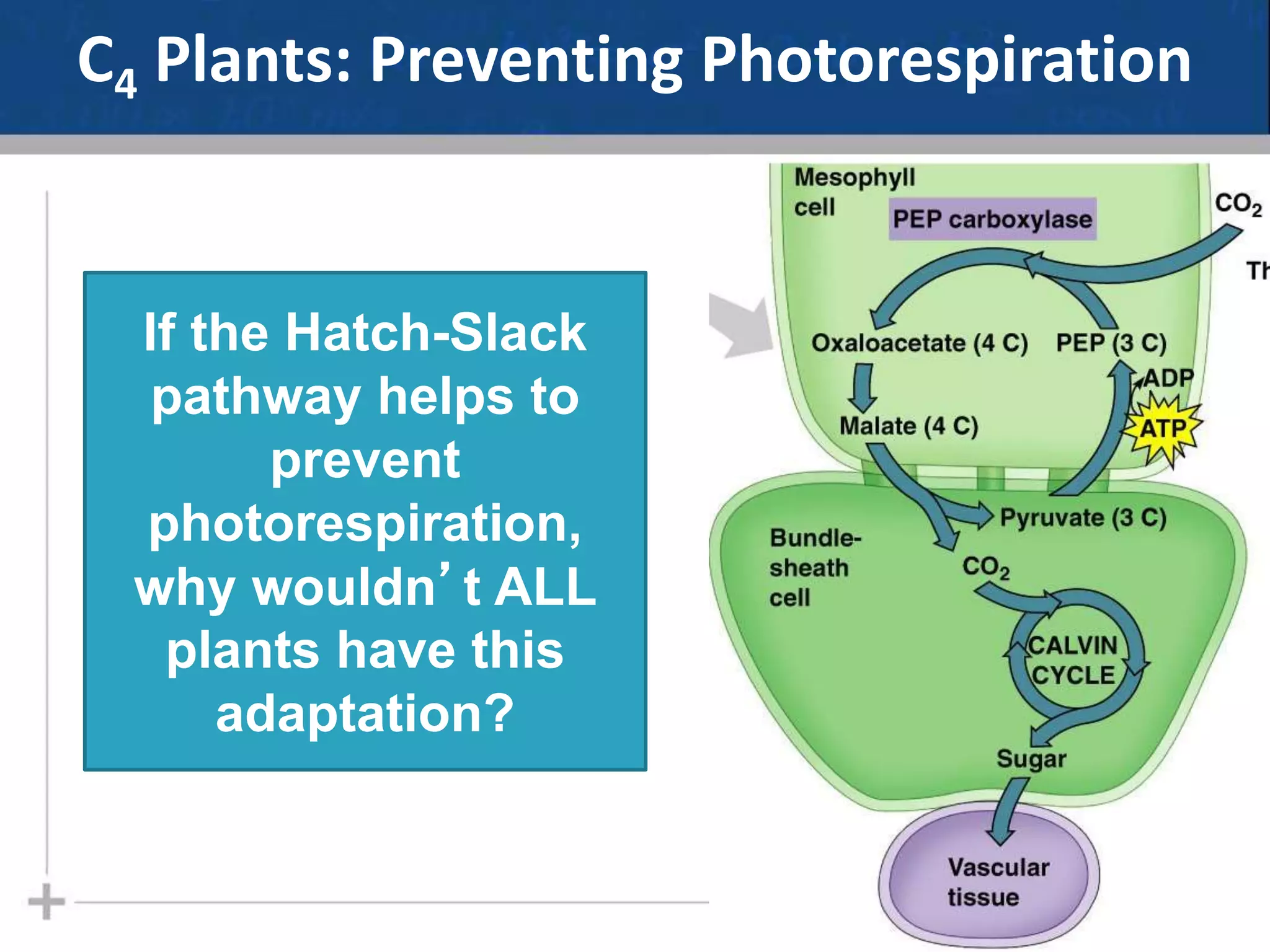
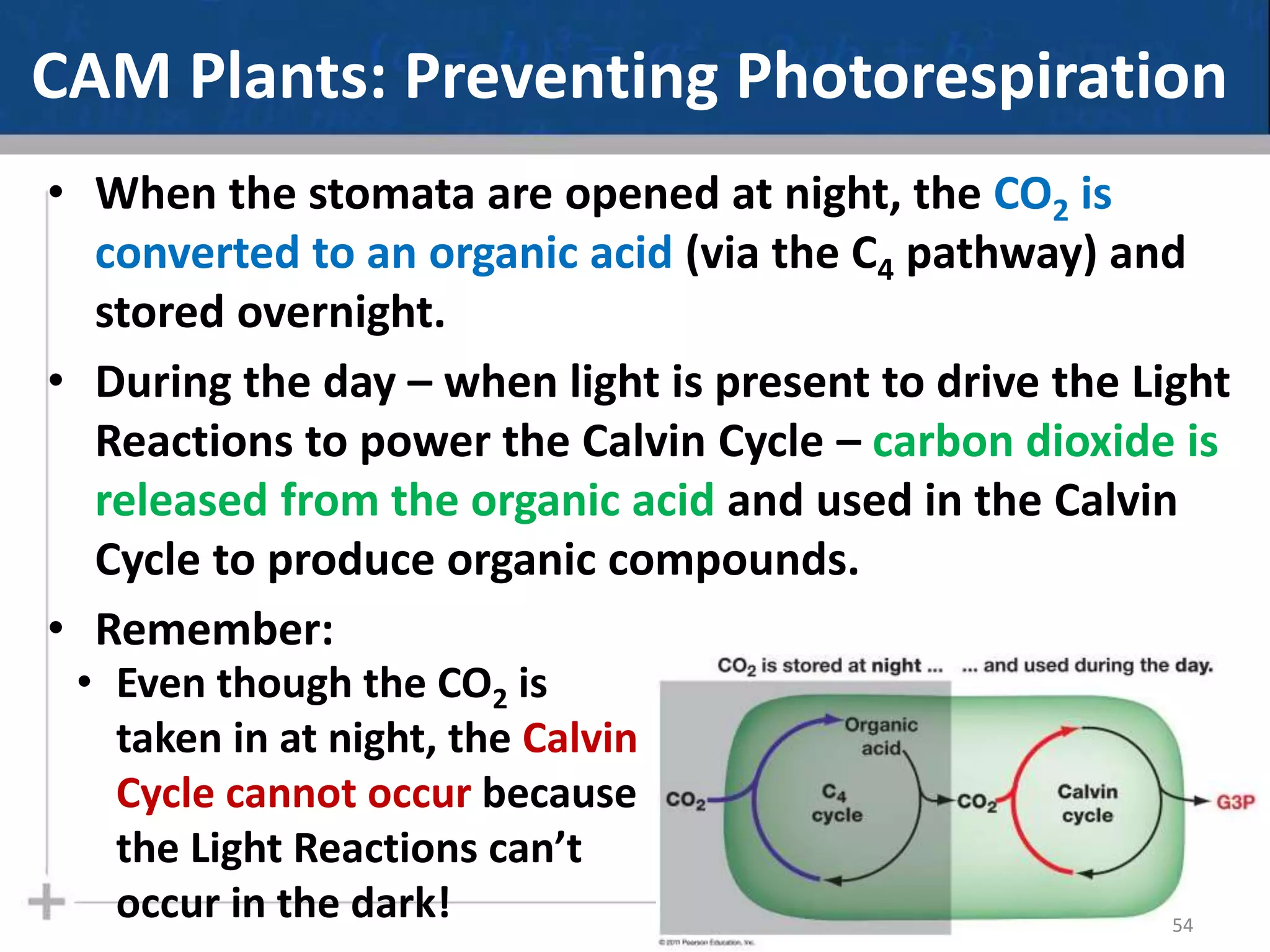
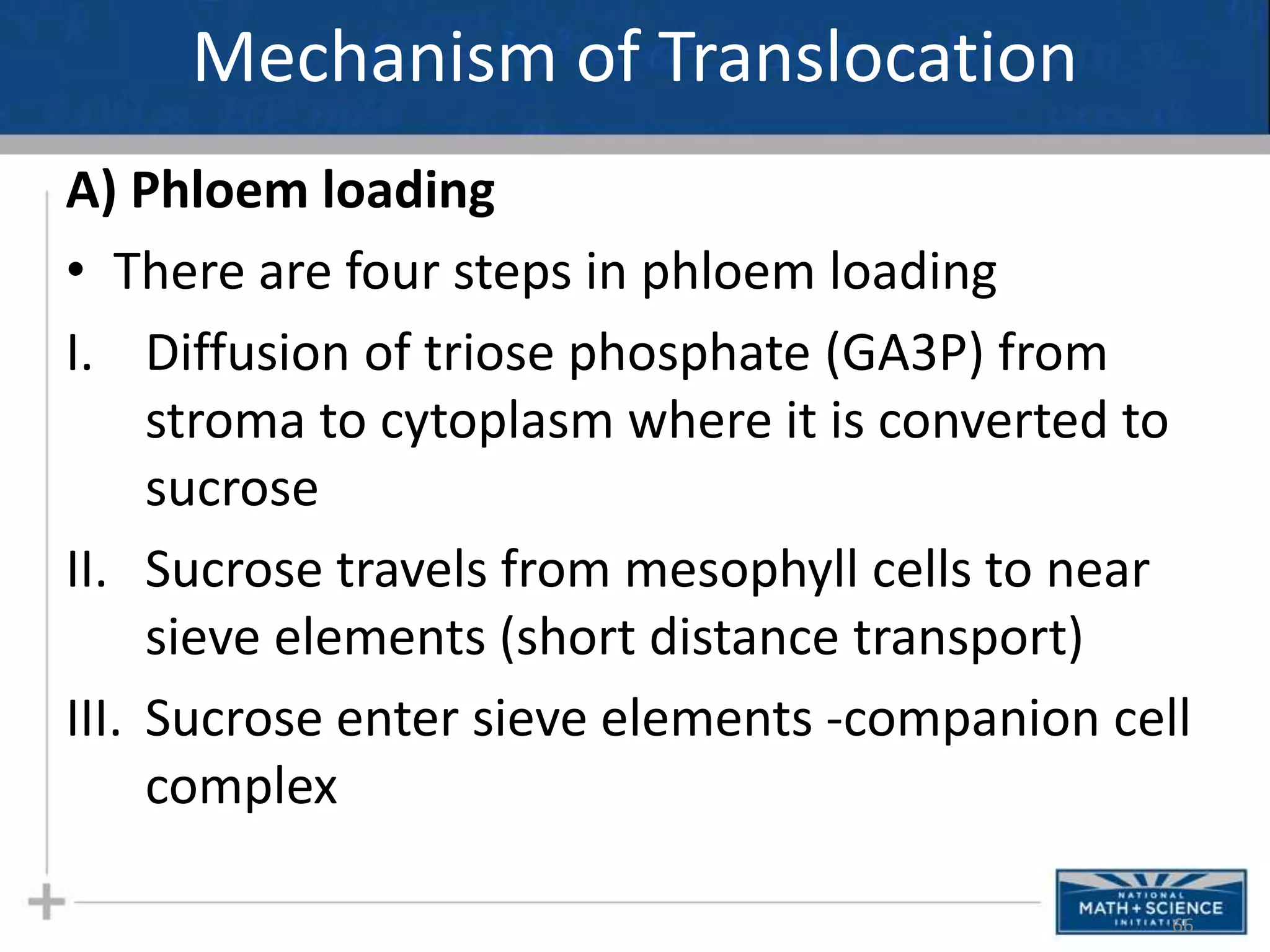
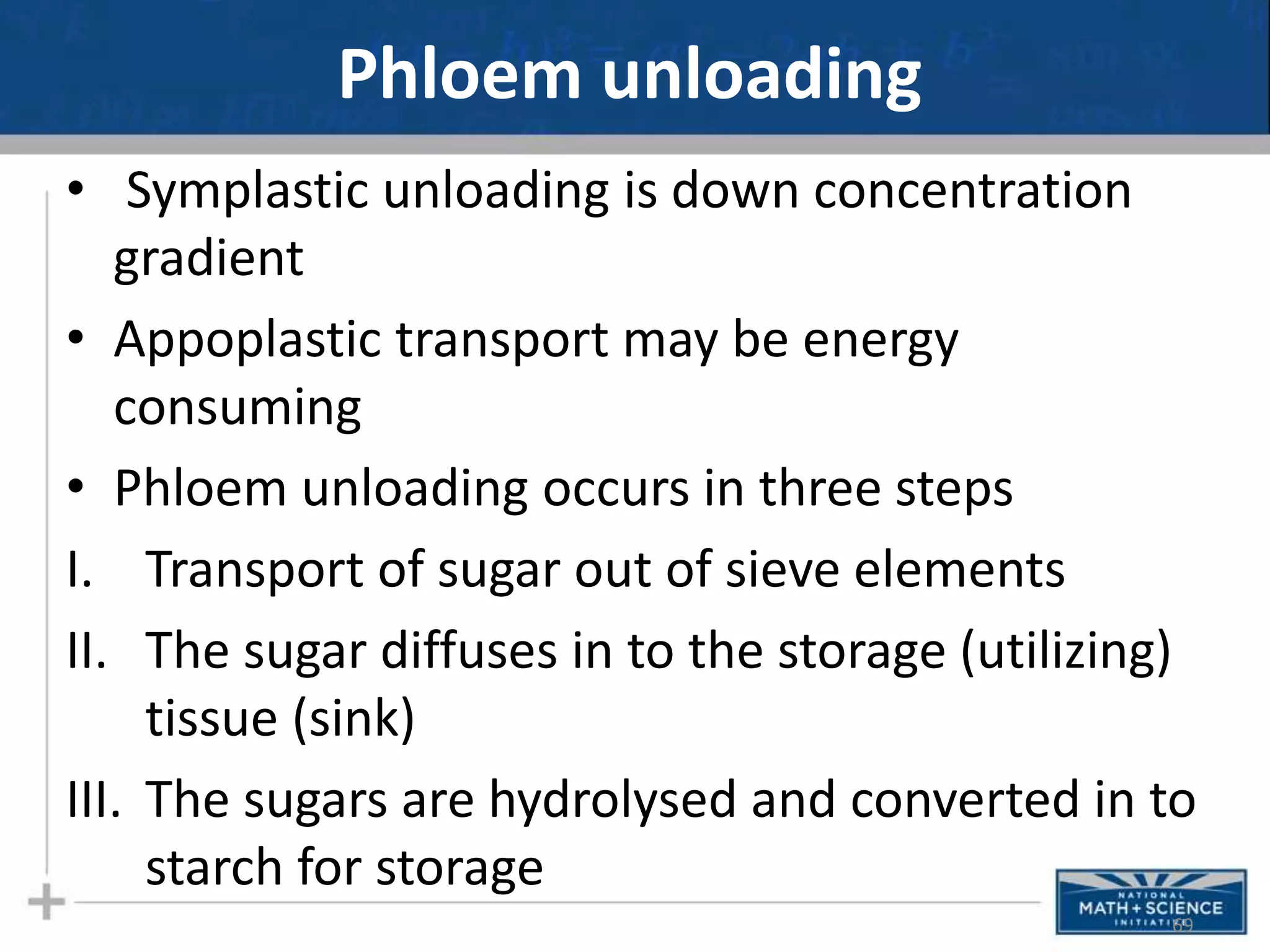
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two phases - the light-dependent reactions where ATP and NADPH are produced to store energy, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where carbon is fixed from carbon dioxide into organic compounds like glucose using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions. Environmental factors like light intensity, temperature and oxygen concentration can affect the rate of photosynthesis. Photorespiration occurs when oxygen is used instead of carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle, preventing glucose production.