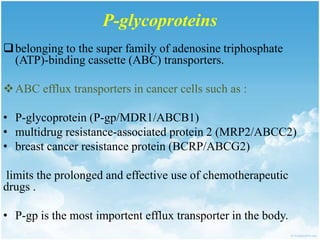
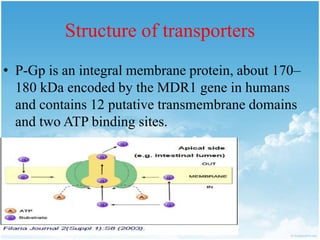
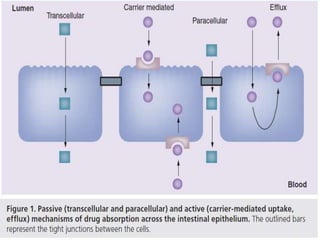
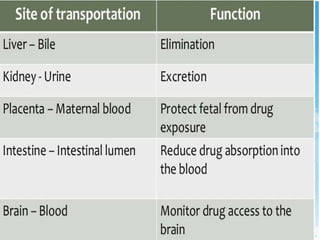
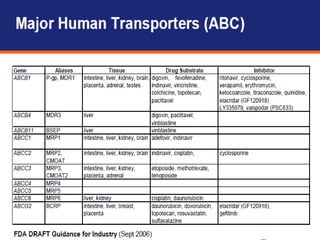
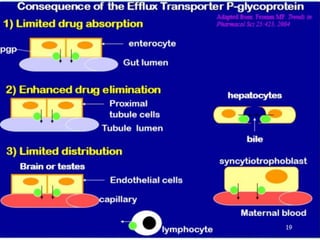
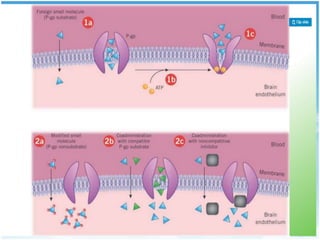
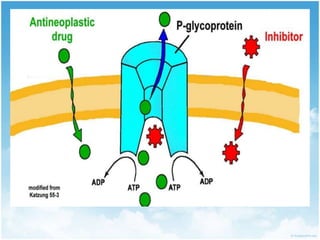
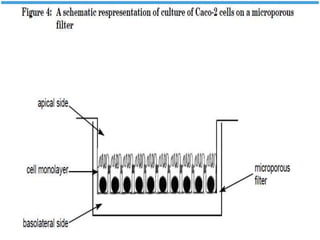
P-glycoprotein transporters are ATP-binding cassette transporters that pump substances out of cells and limit the prolonged effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs. P-glycoprotein is encoded by the MDR1 gene, contains 12 transmembrane domains and two ATP binding sites. It is expressed in the intestine, kidney, liver, placenta, and blood-brain barrier, protecting against toxins. Many chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, and cardiovascular drugs are substrates. P-glycoprotein uses ATP hydrolysis to actively transport substrates unidirectionally out of cells. First generation inhibitors were substrates themselves and toxic. Second generation inhibitors had low affinity. Third generation inhibitors have high specificity and potency. Caco-2 cells are used