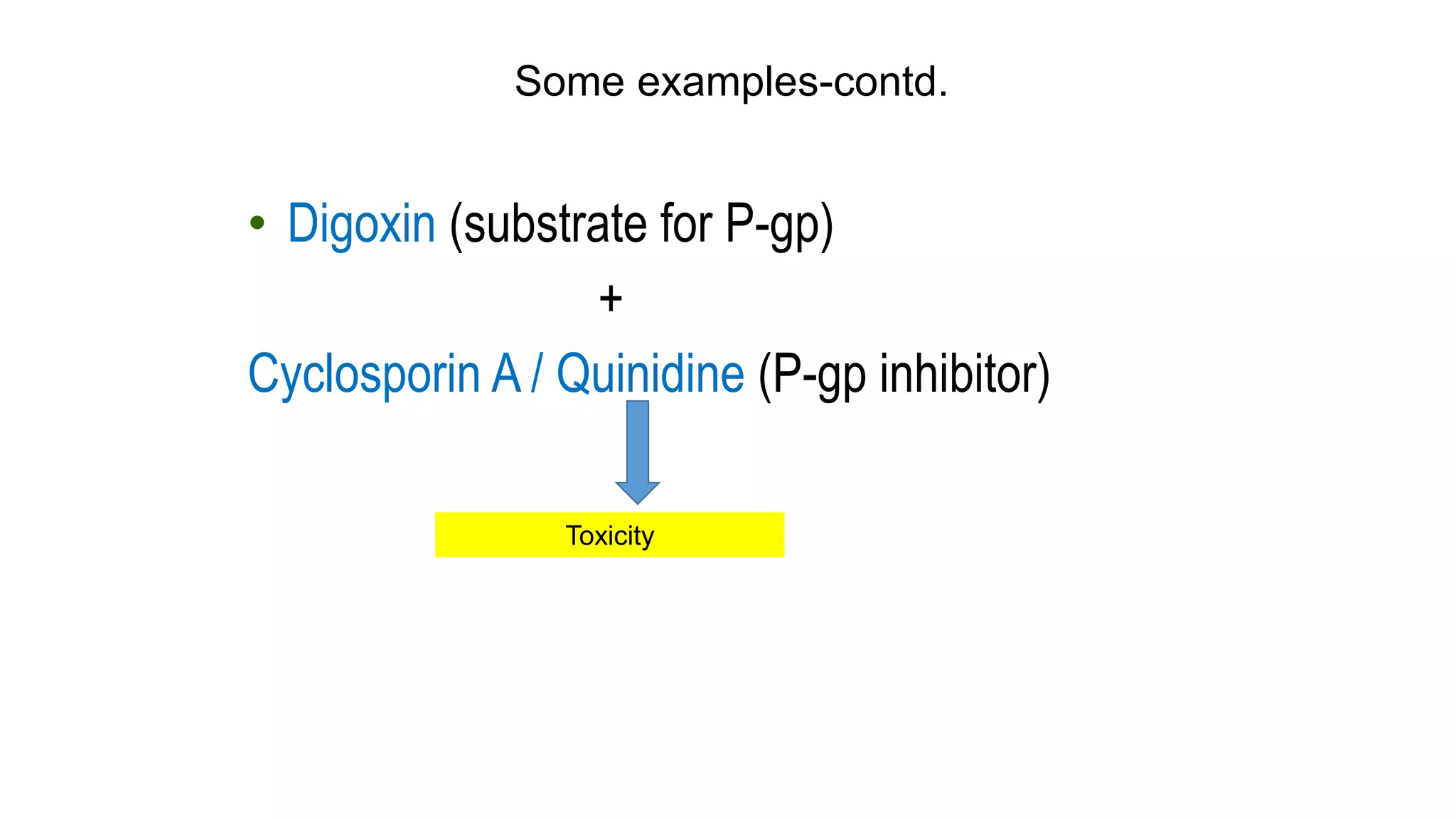
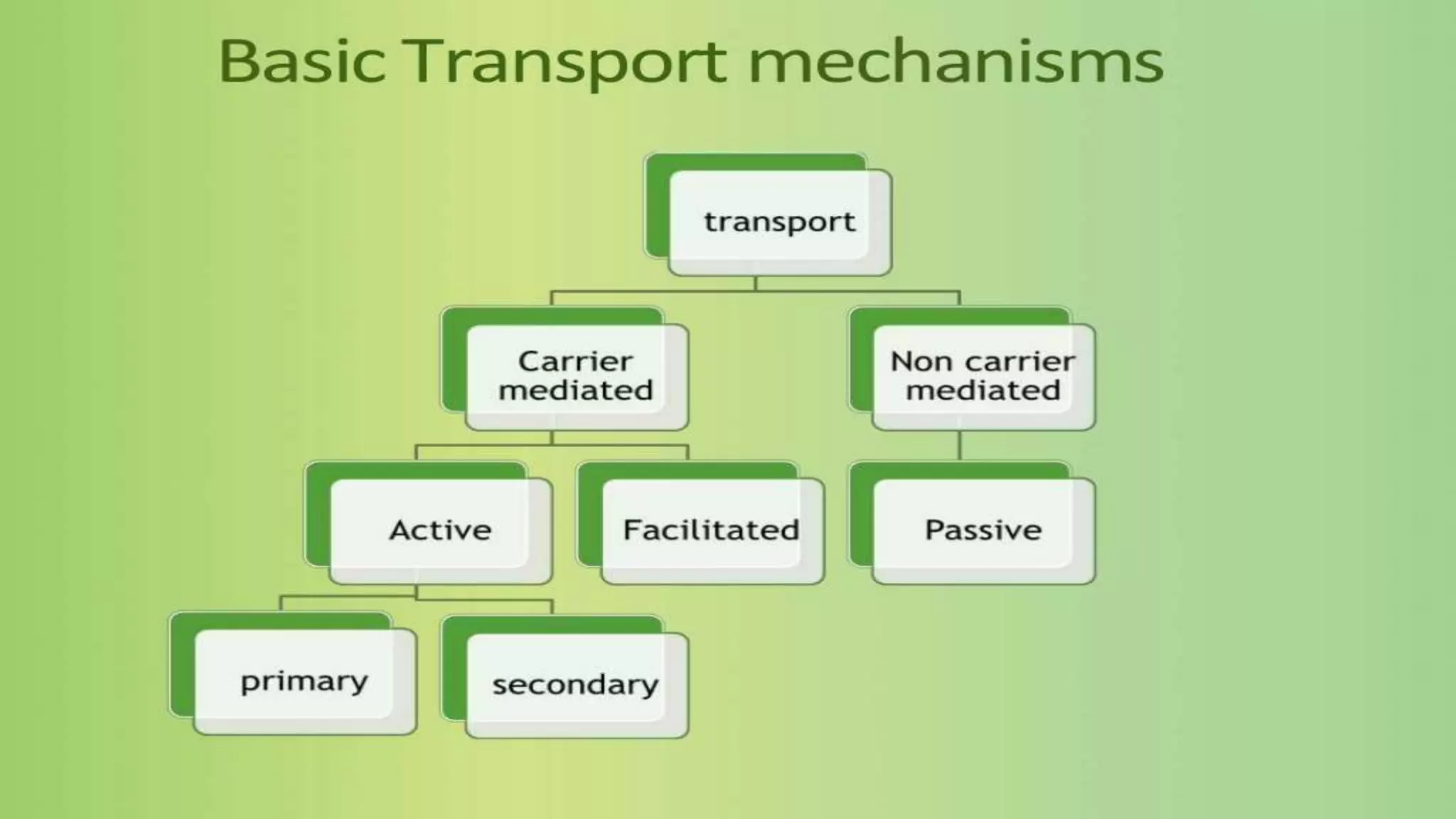
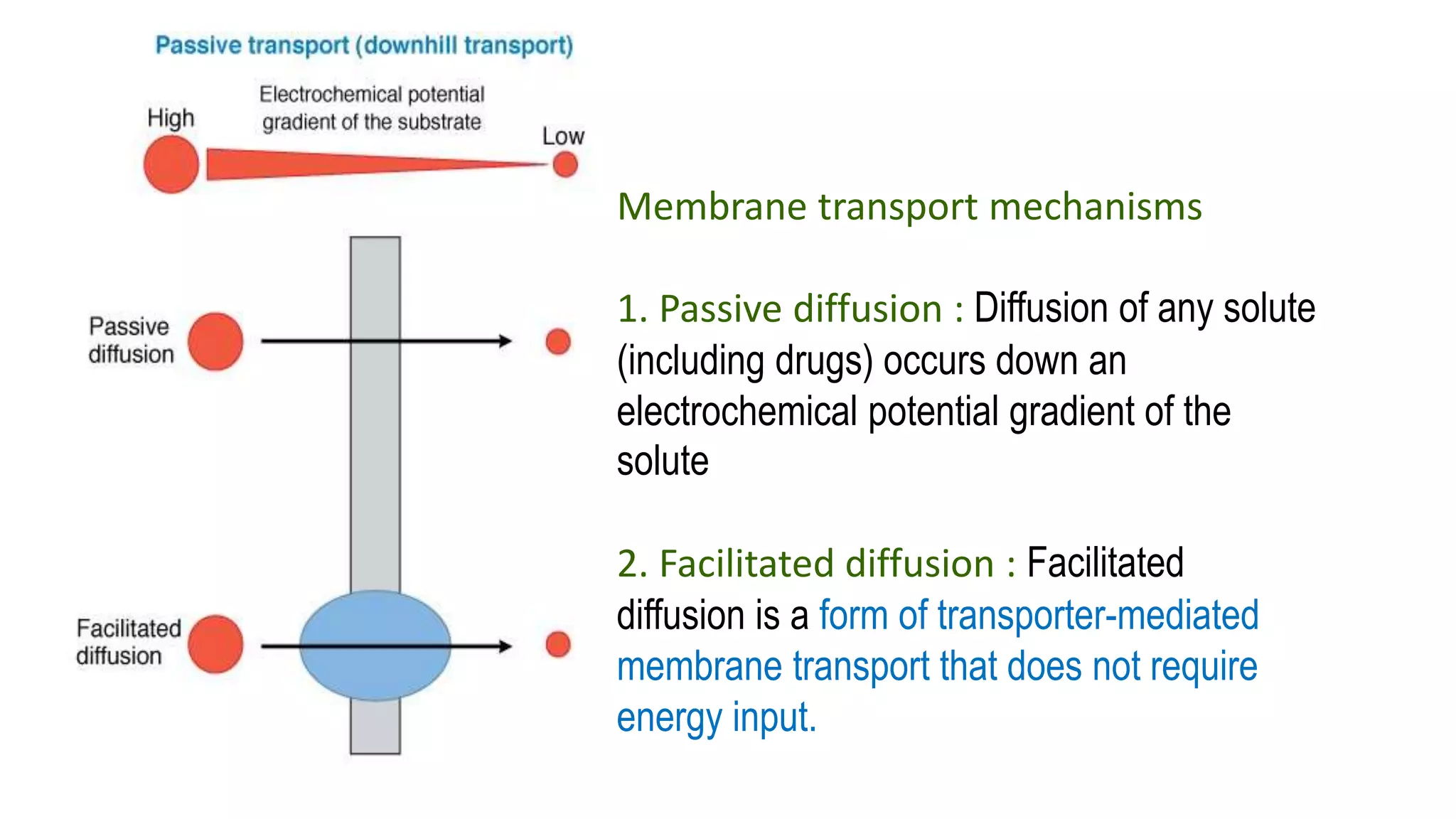
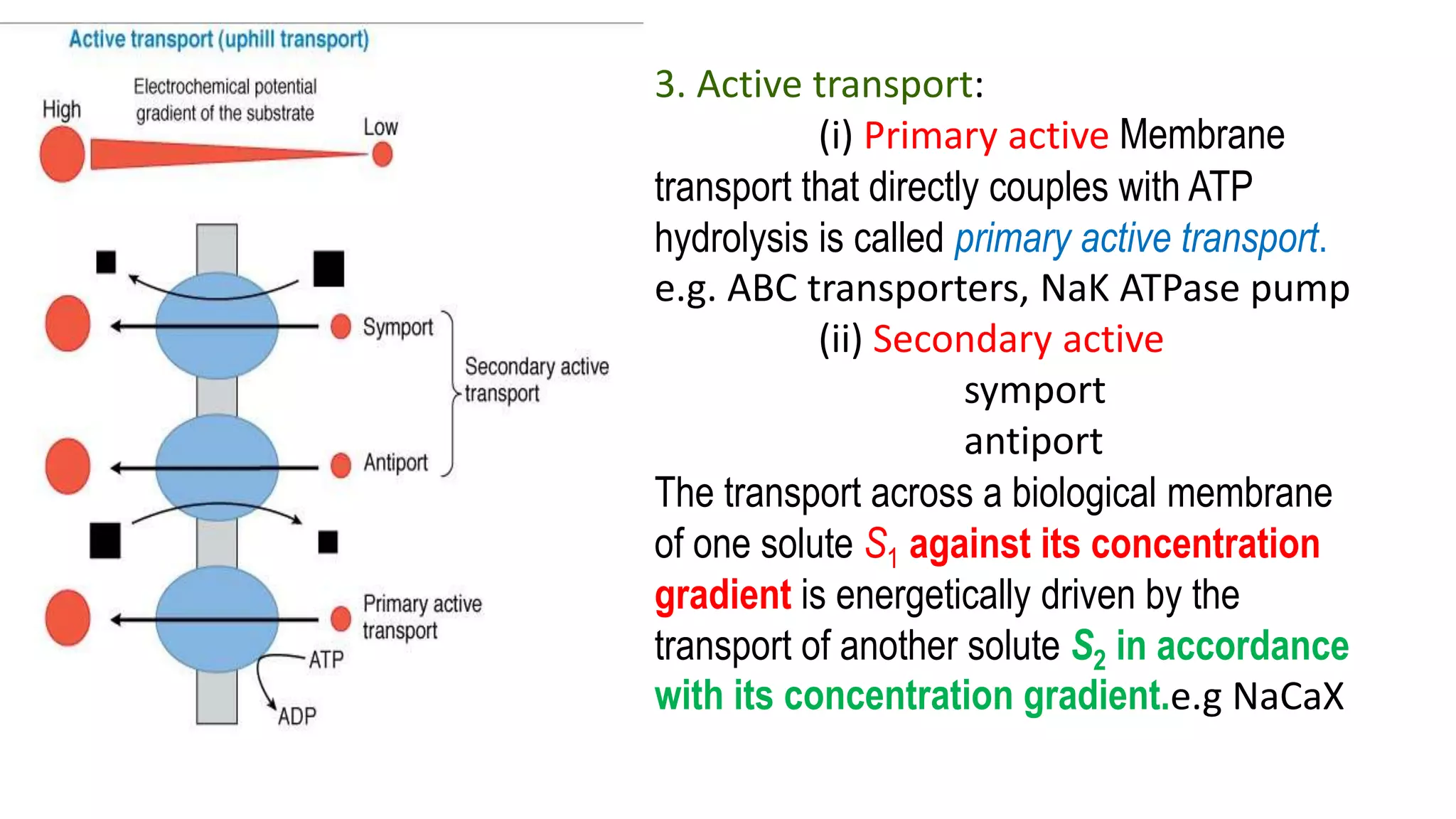
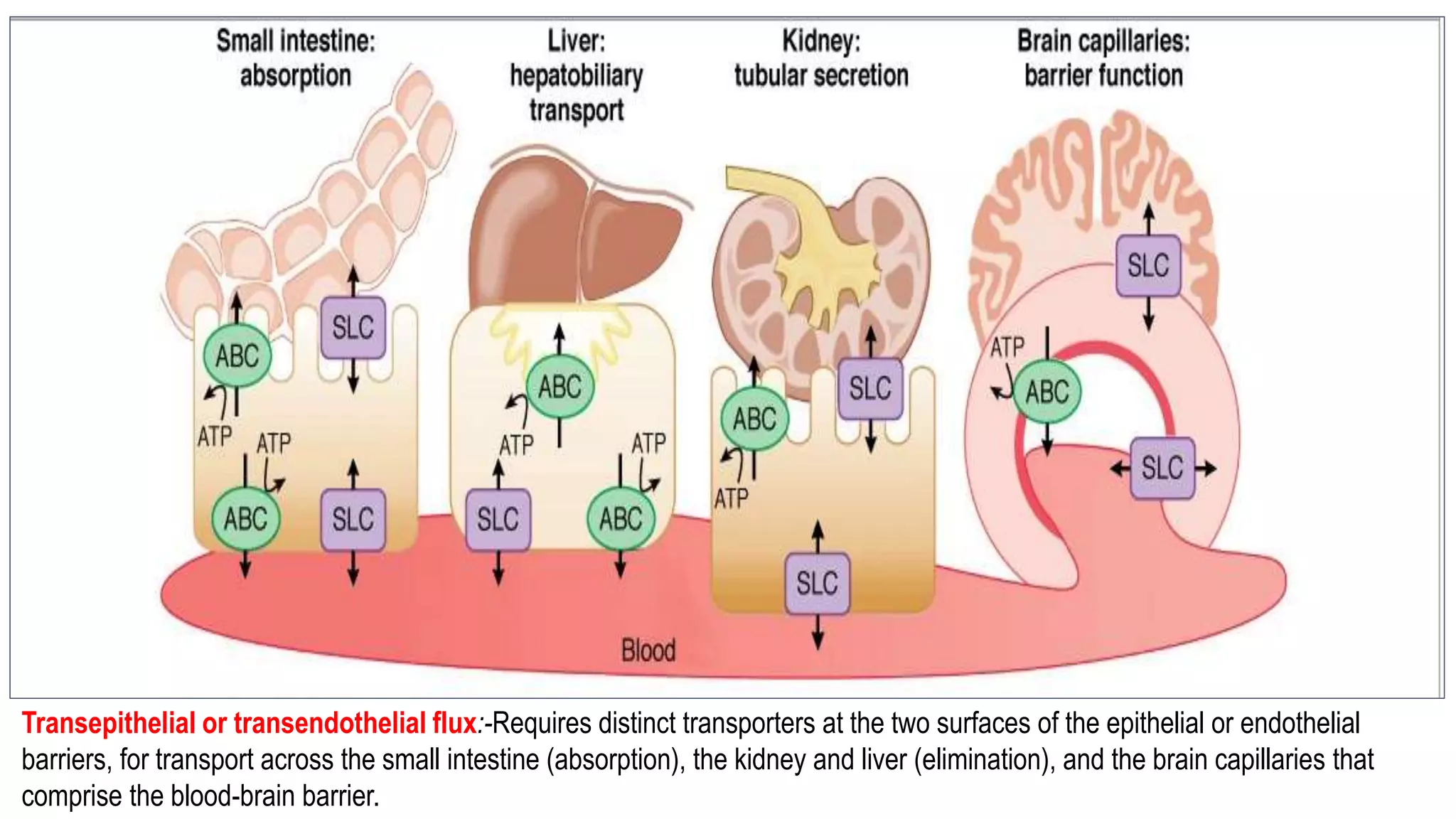
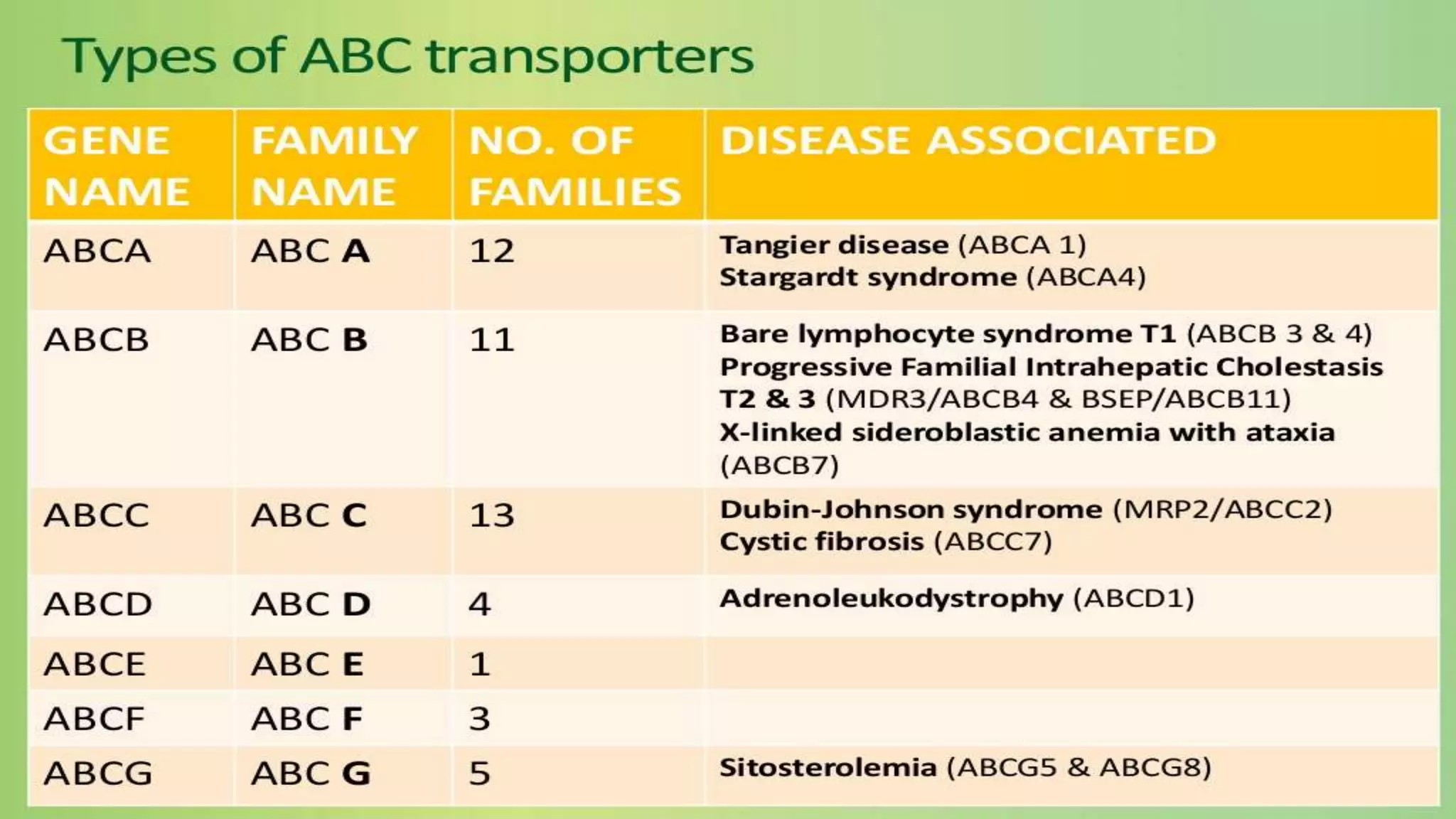
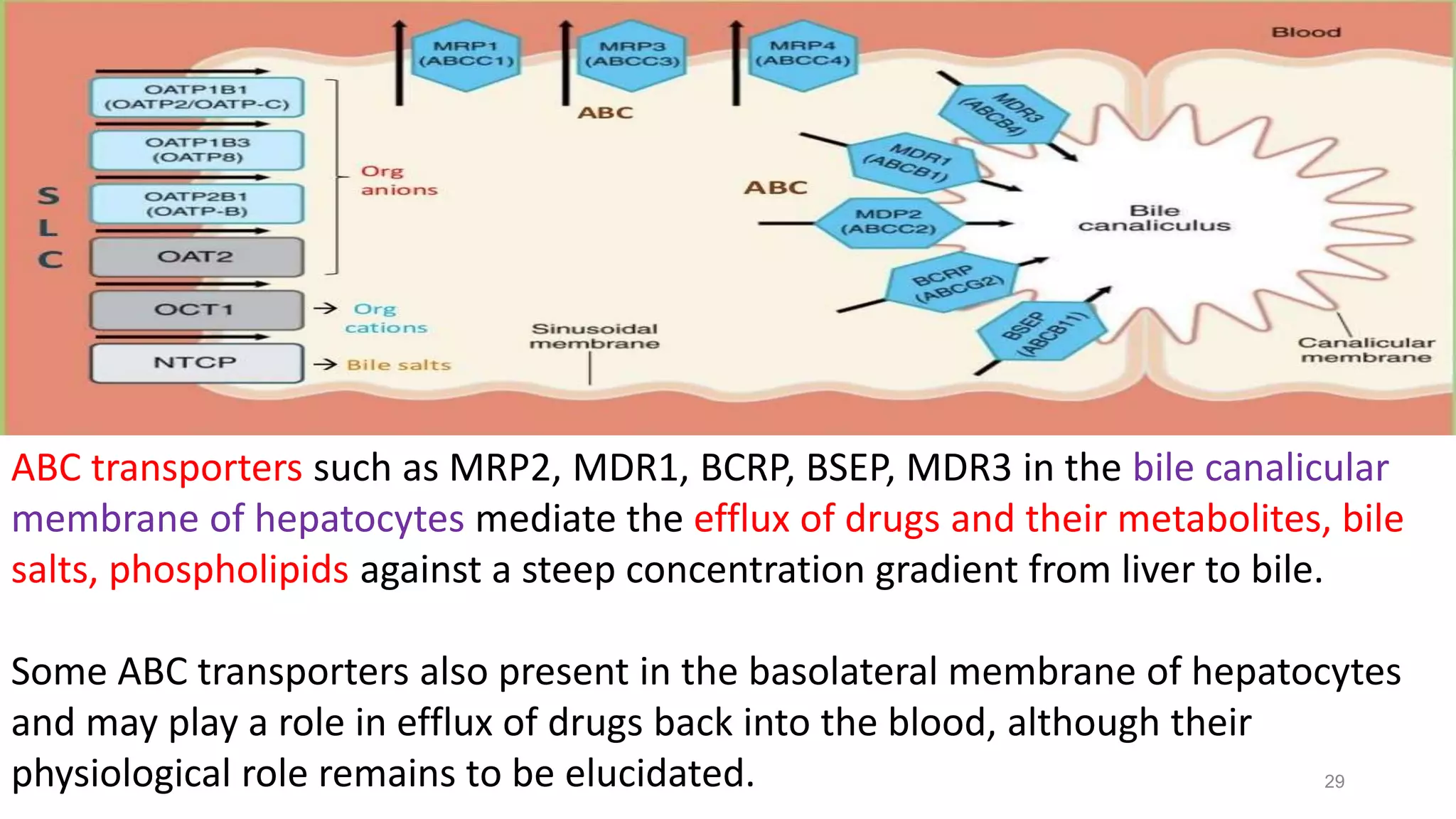
This document discusses the roles of membrane transporters in pharmacokinetics. It begins with an introduction to transporters, noting that they are membrane proteins that control the uptake and efflux of nutrients, ions, drugs and waste. Approximately 2000 human genes code for transporters. The document then covers principal sites of transporters, types of transporters including ABC transporters and SLC transporters, hepatic and renal transporters, and concludes that transporters play significant roles in drug bioavailability, efficacy and pharmacokinetics.