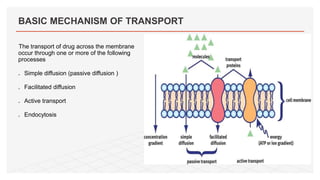
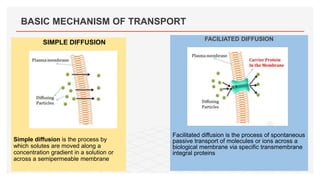
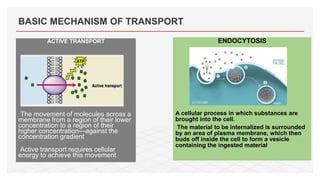
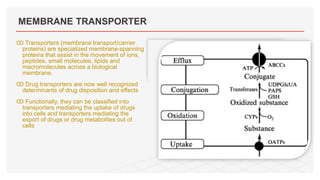
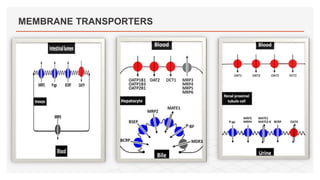
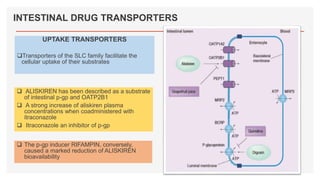
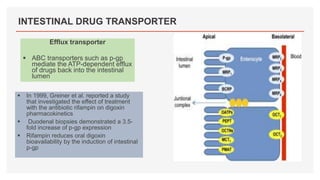
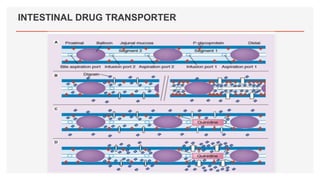
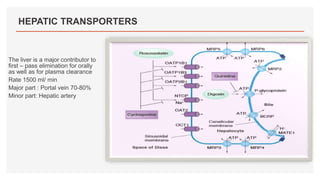
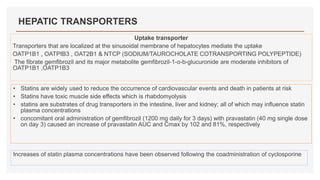
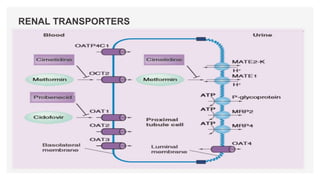
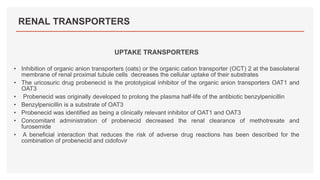
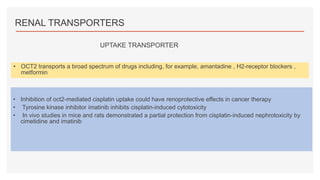
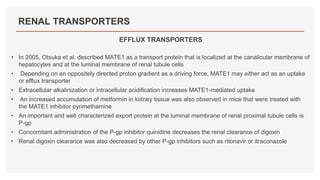
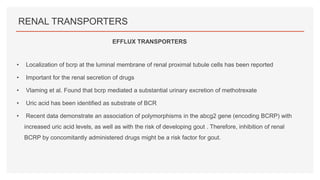
Drug transporters play an important role in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. They are located in organs like the intestine, liver, and kidney and can influence the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs through drug-drug interactions. Transporters can be either uptake transporters that move drugs into cells or efflux transporters that move drugs out of cells. Inhibition or induction of these transporters by coadministered drugs can increase or decrease the intracellular concentrations of victim drugs, altering their effects. This is an important consideration for drug interactions.