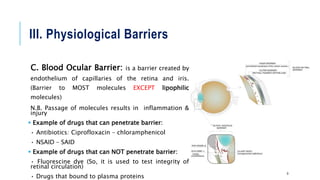
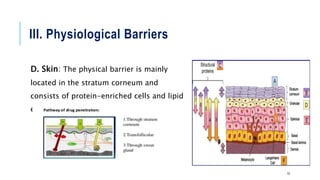
The document discusses various drug transport barriers, including physiological, biochemical, chemical, and physicochemical barriers, and their impact on drug efficacy. It emphasizes the clinical significance of p-glycoproteins in limiting drug accessibility in tumor cells and outlines methods to overcome these barriers through physical, chemical, and biochemical techniques, as well as advanced drug delivery formulations. Conclusively, addressing these barriers is crucial for developing effective drug delivery systems to enhance treatment outcomes.