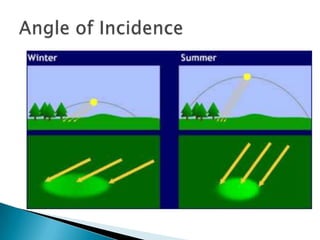
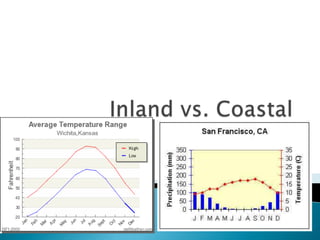
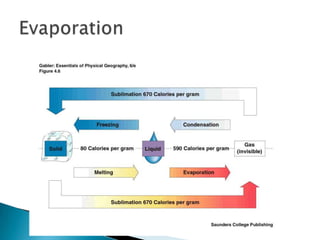
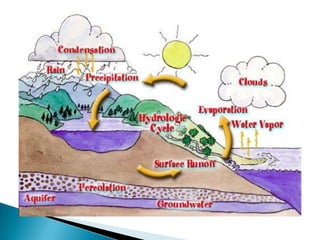
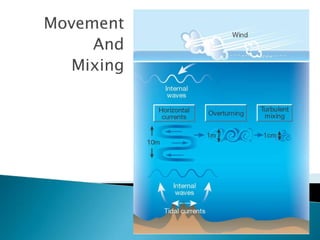
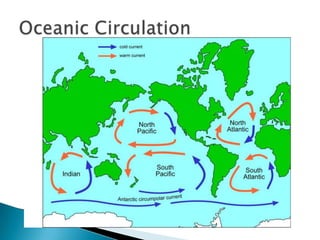
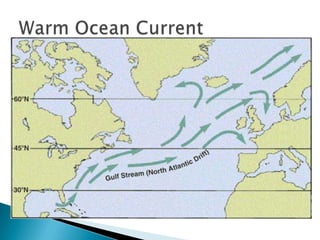
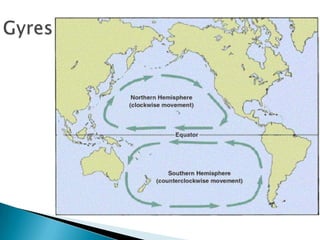
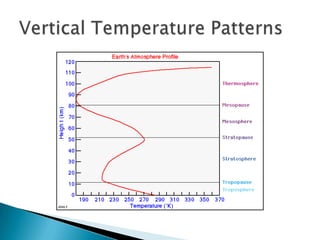
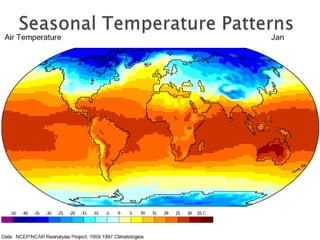
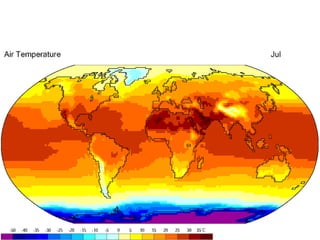
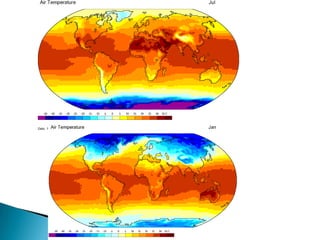
This document discusses factors that influence worldwide temperature patterns, including latitude, season, time of day, atmospheric conditions, day length, and land versus water. It notes that isotherms generally run east-west and are pulled northward in July and southward in January. Areas covered by glaciers are cold year-round, while southern hemisphere land stays warmer in winter than northern hemisphere land. The hottest areas are continental interiors in summer and the coldest are continental interiors in winter, while coastal areas are warmer in winter and cooler in summer.