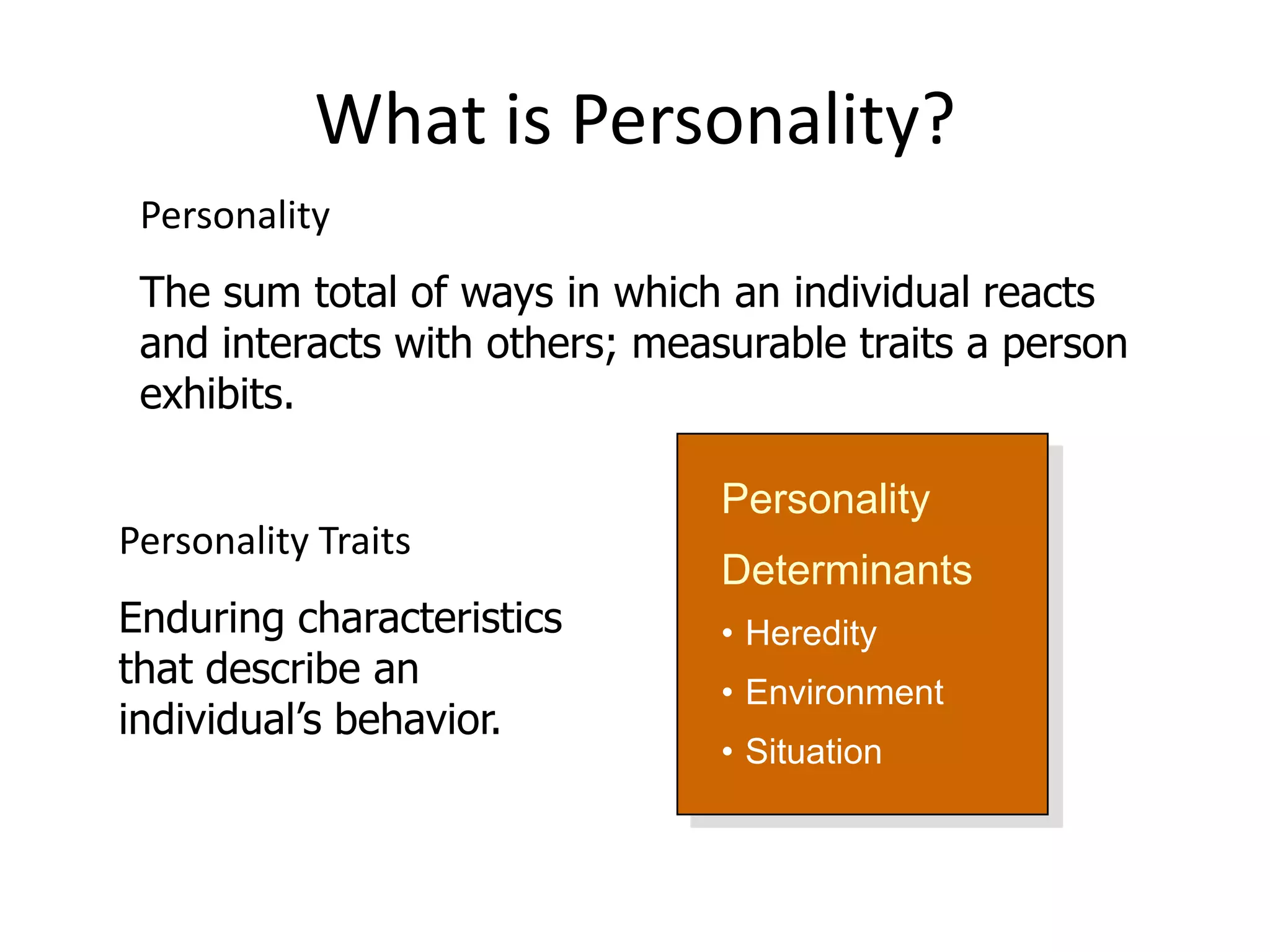
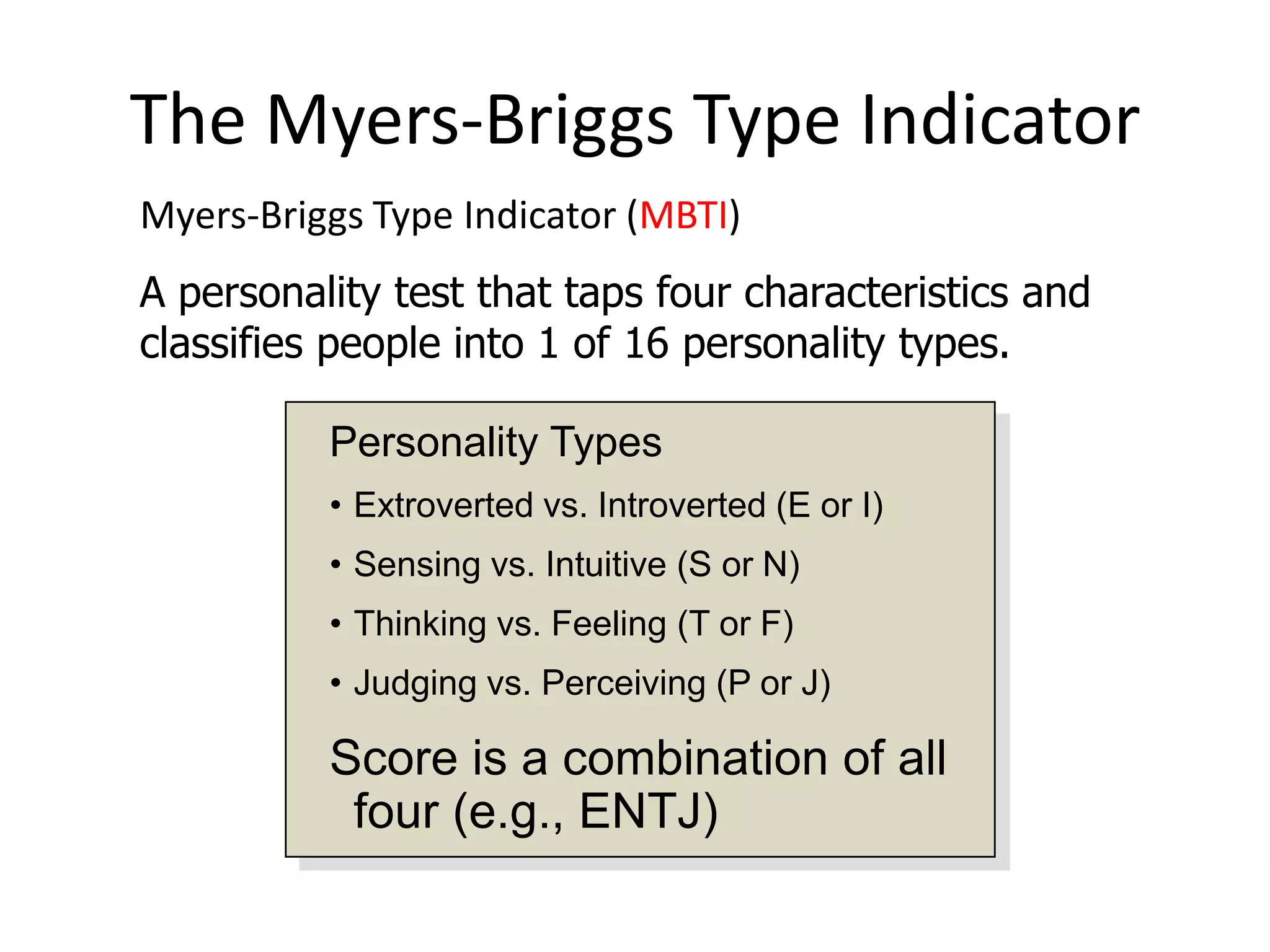
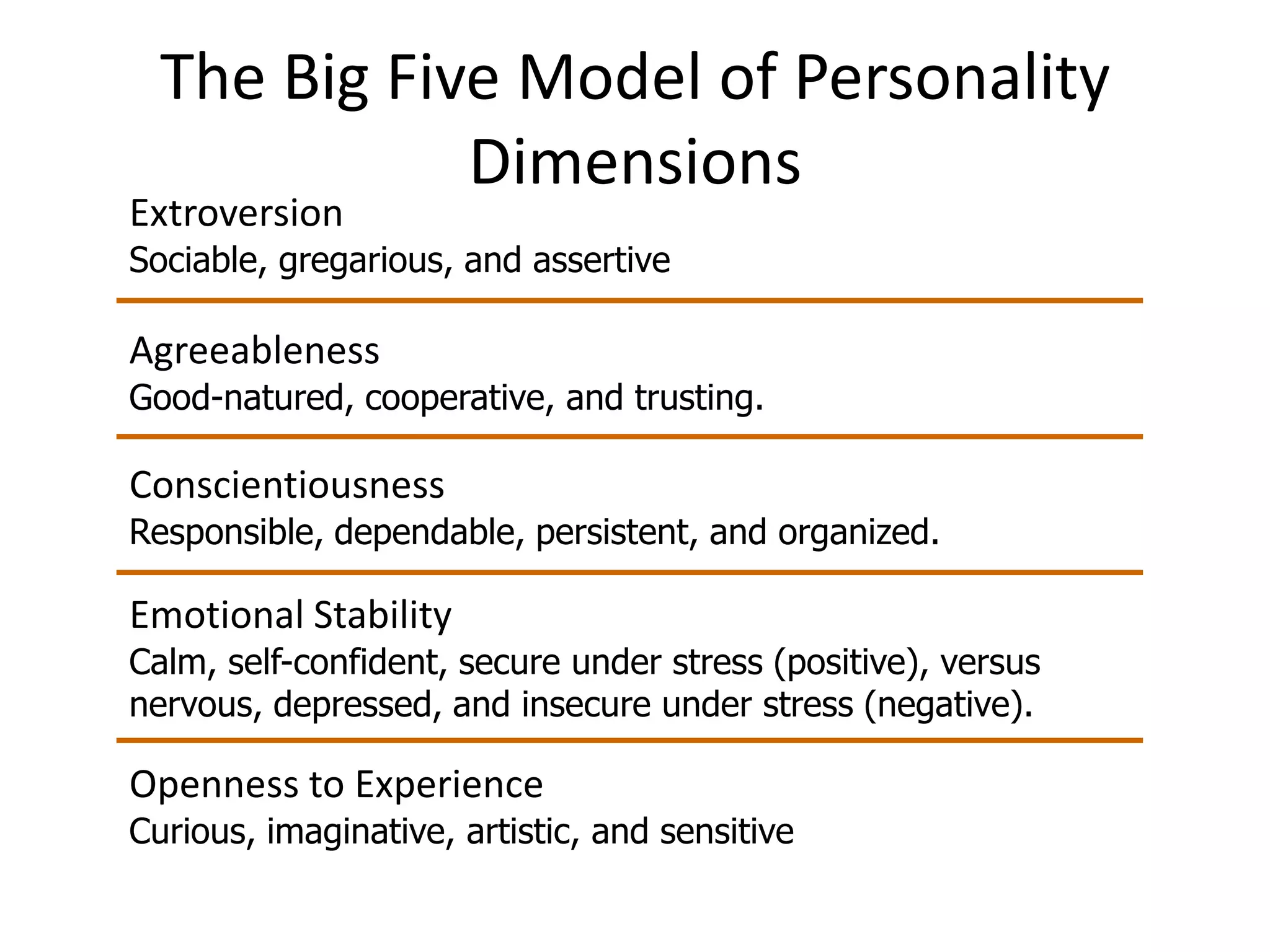
Personality is defined as the sum total of ways an individual reacts to and interacts with others, as well as measurable traits they exhibit. It is influenced by heredity, environment, and situation, and described through enduring characteristics like the Big Five model of extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness to experience. The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator assesses personality types based on four dichotomous scales of extraversion/introversion, sensing/intuition, thinking/feeling, and judging/perceiving.