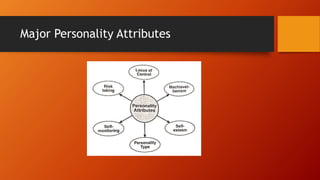
Personality can be defined as a dynamic set of characteristics that uniquely influence a person's cognitions, motivations, and behaviors. Personality encompasses thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that describe a person. It is generally stable but can change, especially during development. For organizational behavior studies, personality strongly impacts an individual's daily behavior and actions in given situations. Personality is influenced by both inherited and learned characteristics. Major determinants include physical, social, psychological, and intellectual factors. Common personality attributes that influence organizational behavior include locus of control, Machiavellianism, introversion/extroversion, problem solving style, and achievement orientation.