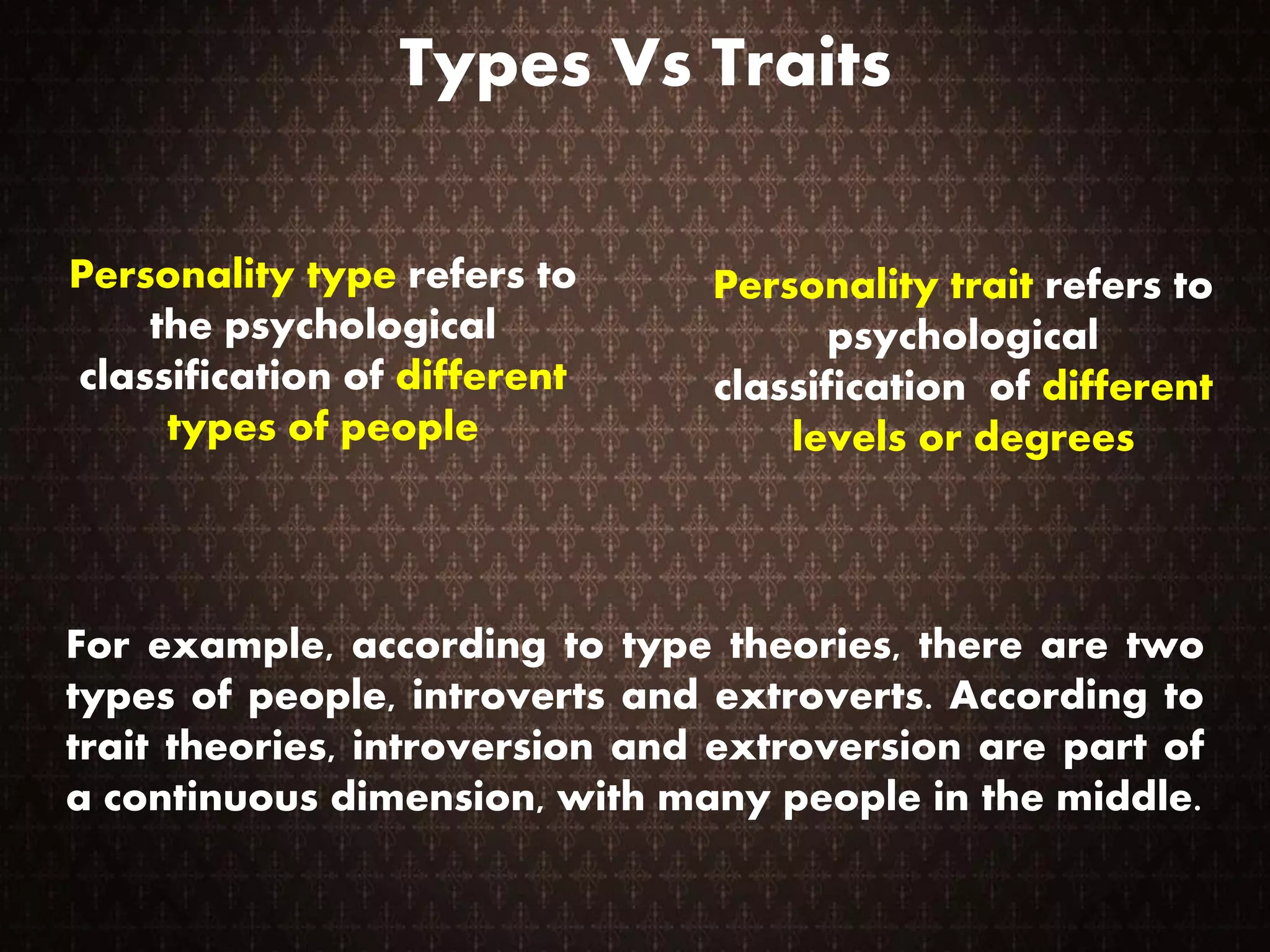
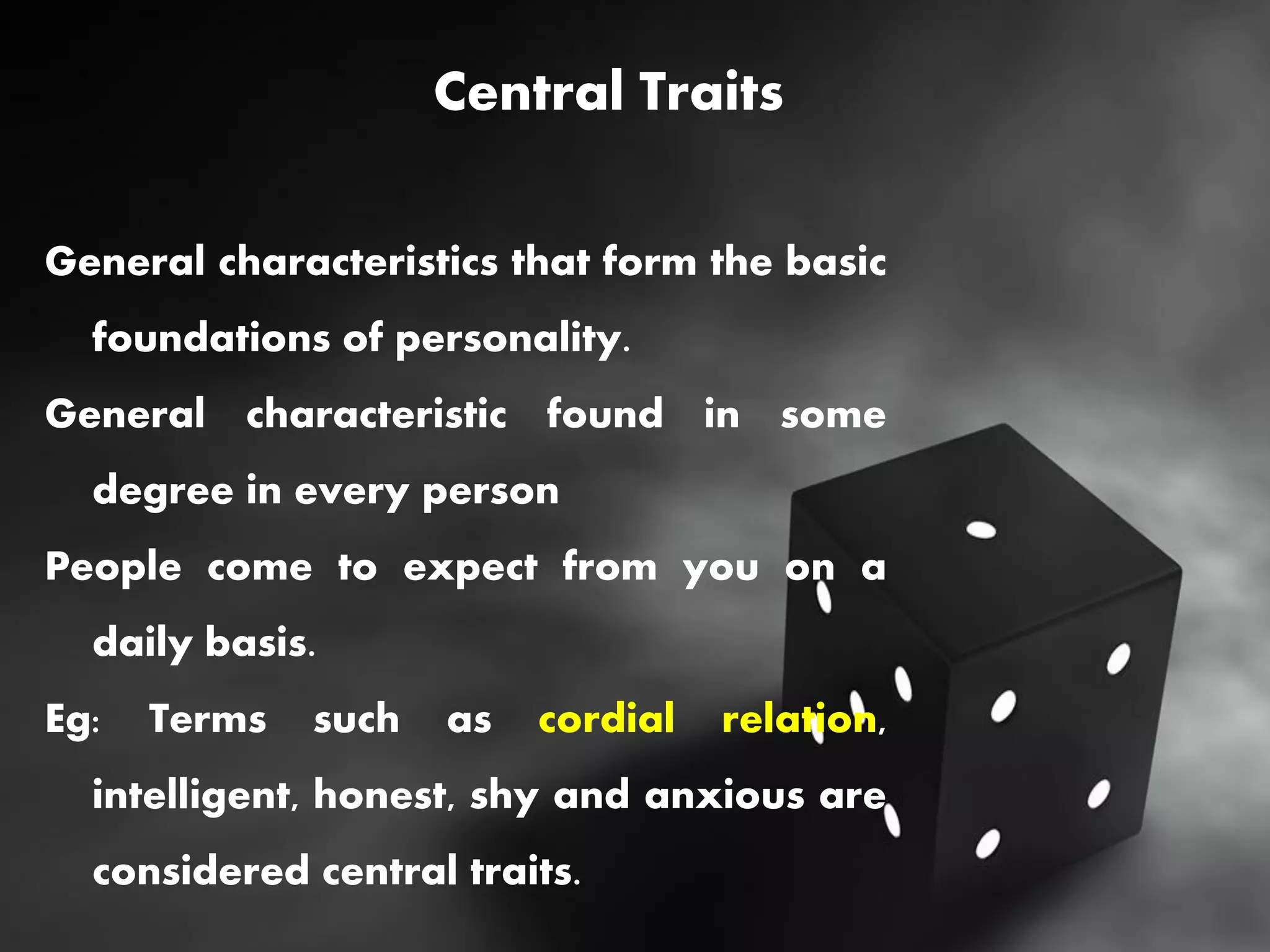
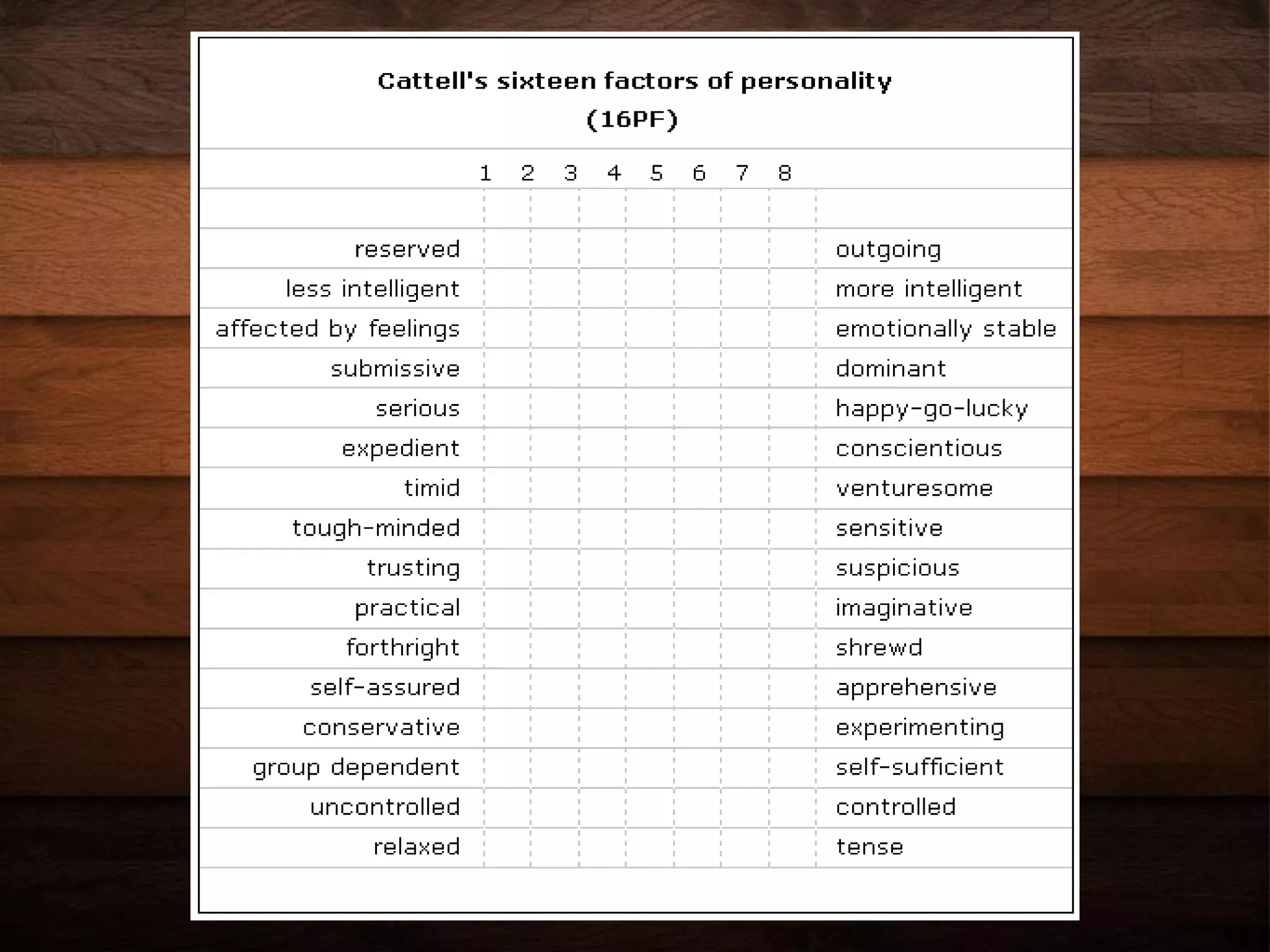
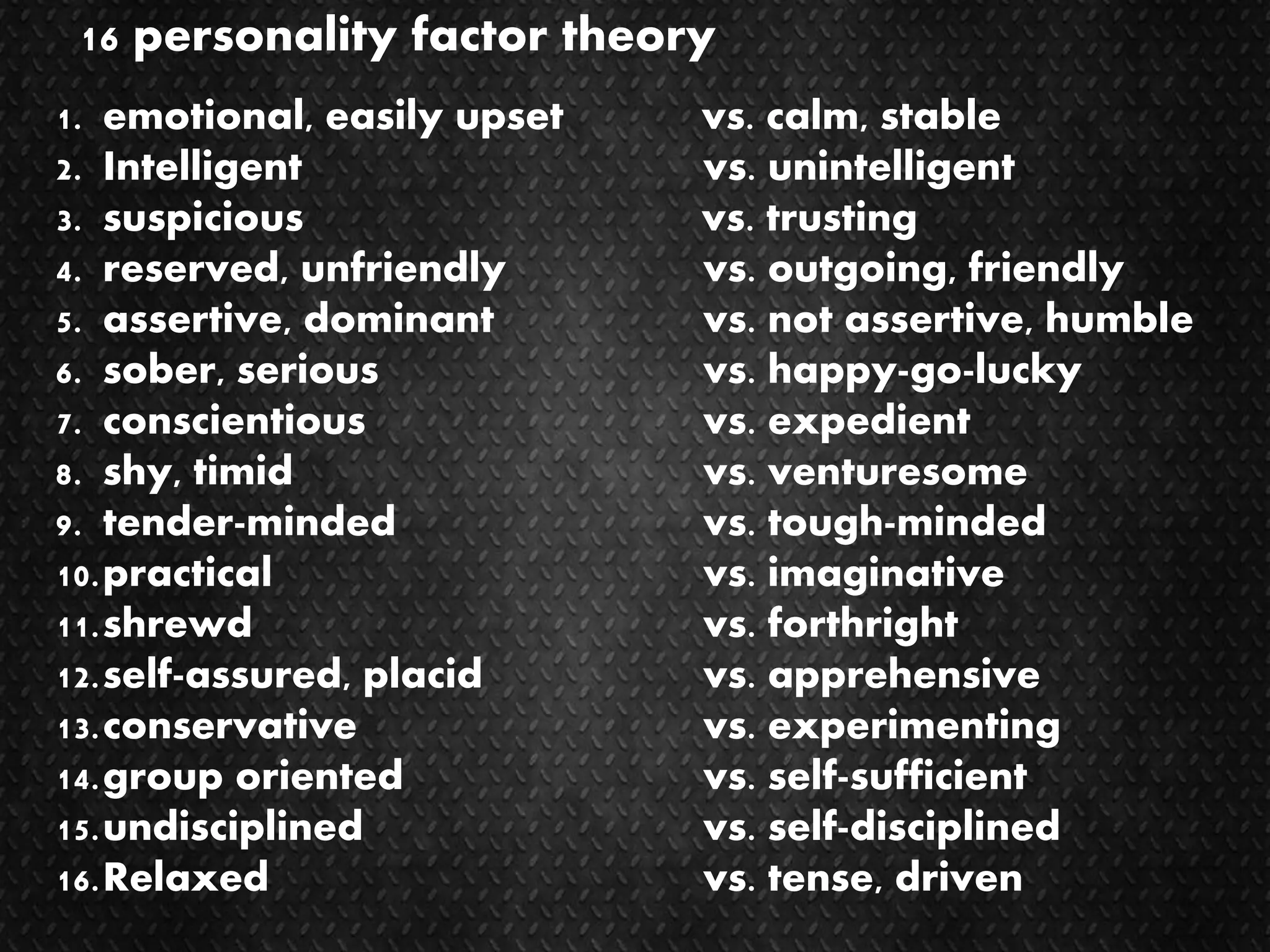
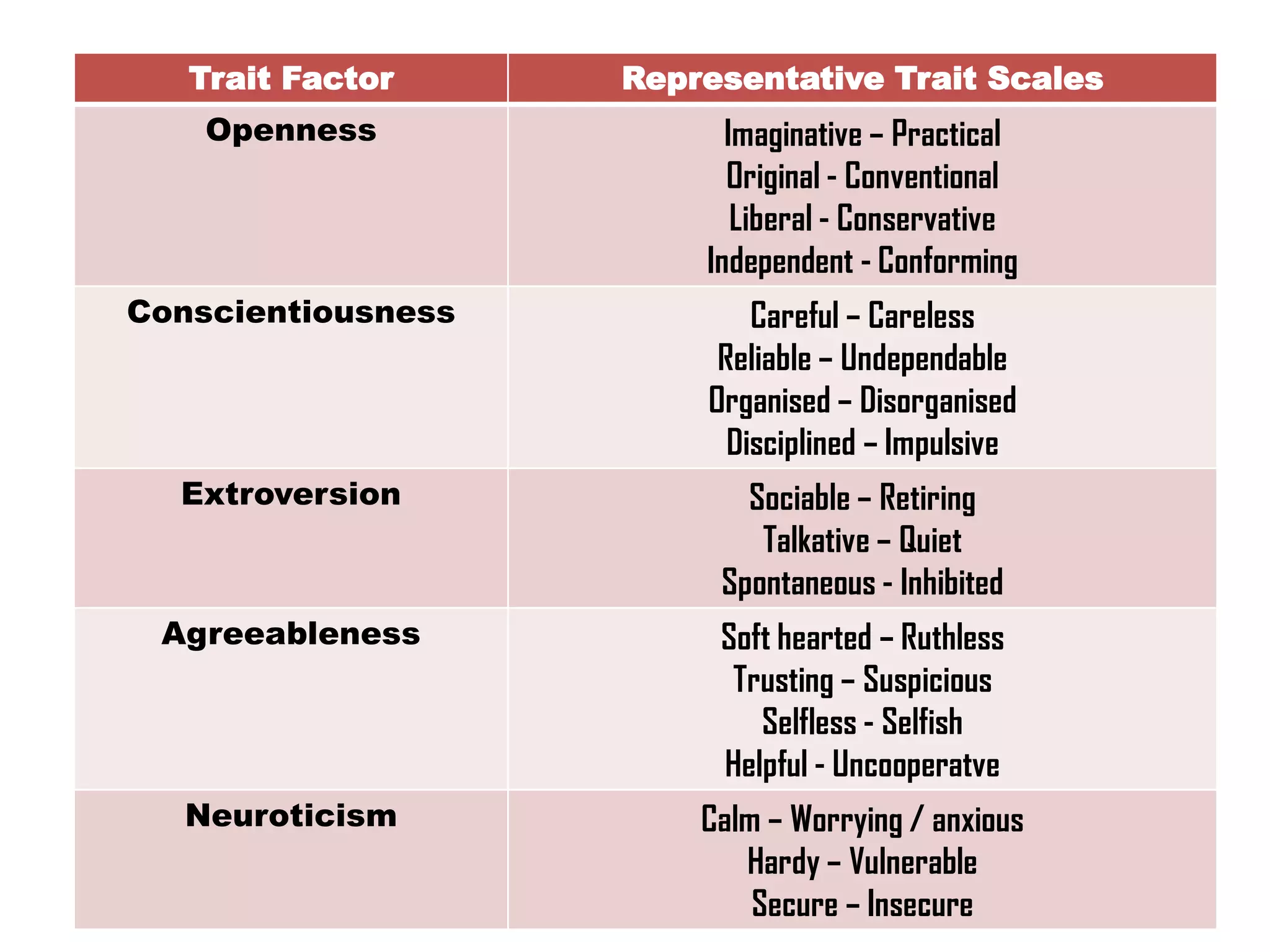
This document summarizes several major trait theories of personality psychology. It describes Gordon Allport's theory that categorized traits into cardinal, central, and secondary levels. It also discusses Raymond Cattell's 16 personality factor theory that used factor analysis to identify 16 main traits. Additionally, it outlines the Big Five model proposed by Lewis Goldberg comprising the traits of Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism. The document concludes by noting some common criticisms of trait theories, such as being descriptive rather than explanatory and underestimating situational influences on behavior.