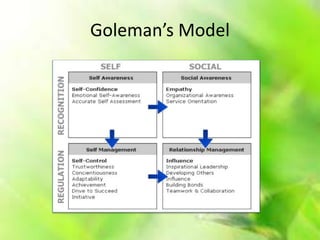
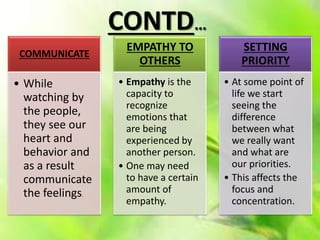
This document presents information on emotional intelligence. It defines emotional intelligence as the ability to identify, assess, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others. The document discusses models of emotional intelligence proposed by Salovey and Mayer and Goleman. It outlines components of emotional intelligence like self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document also compares emotional intelligence to IQ and argues that EQ accounts for a larger portion of success than IQ. It provides tips for developing emotional intelligence at work and enhancing brain power.