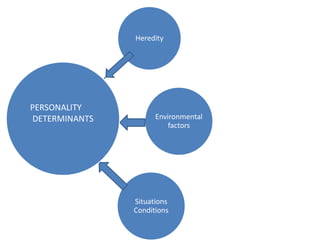
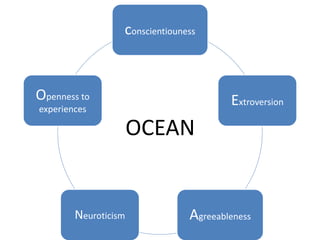
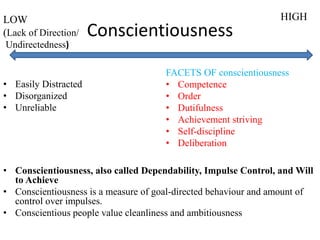
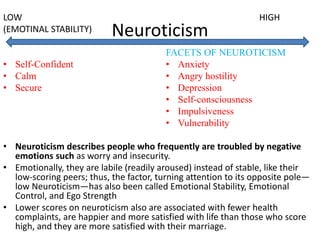
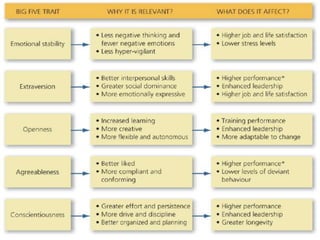
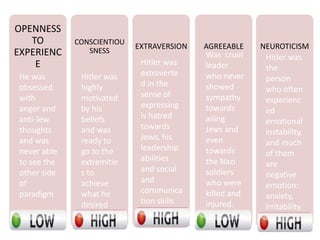
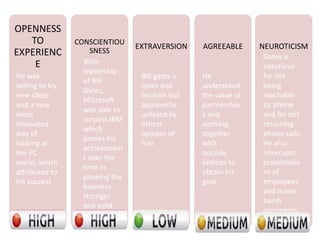
The document discusses the Big Five Factor personality model. It describes the five factors - Extraversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Neuroticism, and Openness to Experience. Extraversion relates to energy levels and sociability. Agreeableness indicates friendliness and cooperation. Conscientiousness is about self-discipline and achievement orientation. Neuroticism relates to stress, anxiety, and emotional stability. Openness involves intellectual curiosity and creativity. The document provides descriptions and examples of each factor and how they relate to behaviors and tendencies in individuals.