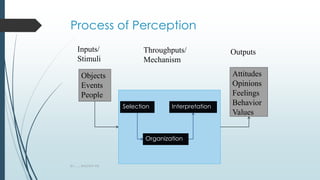
The document discusses perception as the process through which individuals interpret sensory information from their environment, influenced by internal and external factors. It outlines the stages of perception, including selection, organization, and interpretation, and highlights common perceptual errors like stereotyping and selective perception. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of perception in organizational behavior and suggests ways to improve perceptions, such as empathy and open communication.