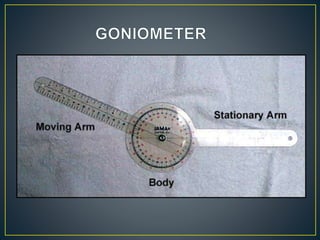
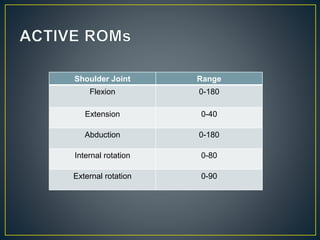
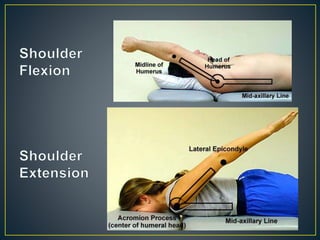
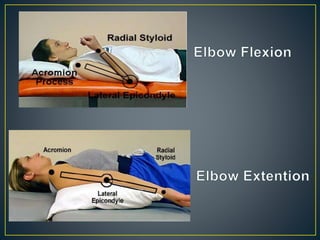
This document defines goniometry as a technique used to measure range of motion in joints. It discusses the definition, uses, parts of a goniometer, degrees of freedom in joints, and procedures for goniometric measurement. Key points covered include that a goniometer consists of stationary, moving, and body arms to measure angles in degrees, and it is used to identify contractures or decreased range of motion from injury or disuse, help develop treatment goals, and evaluate rehabilitation progress. Normal ranges of motion are provided for the shoulder and elbow.