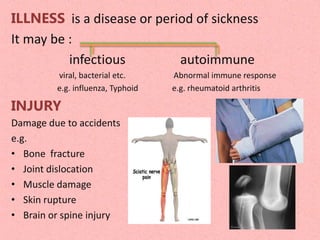
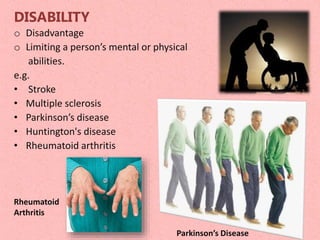
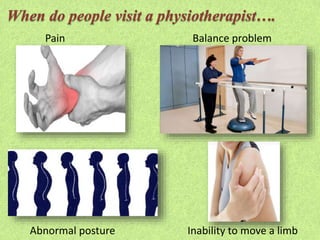
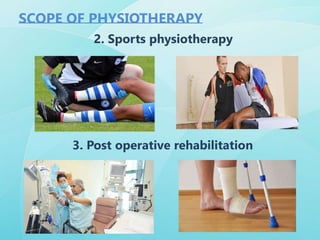
Physiotherapy is essential for individuals experiencing movement difficulties due to health problems, including illness, injury, or disability, as it can relieve pain and restore physical functions. It is beneficial for a range of conditions, such as cardiovascular, pulmonary, degenerative diseases, and musculoskeletal disorders. Physiotherapists provide treatments, promote general health through exercise, and help patients adapt to mobility aids.