This document discusses ataxia and provides information on cerebellar ataxia, sensory ataxia, and vestibular ataxia. It defines cerebellar ataxia and describes the types and symptoms, including dysfunction of the vestibulocerebellum, spinocerebellum, and cerebrocerebellum. Assessment and management are discussed, with physical therapy focusing on improving relaxation, balance exercises, gait training, strengthening, and functional training. Sensory ataxia and vestibular ataxia are also briefly introduced.

![QUESTIONS
Q1- PT Mx for sensory ataxia. (2016) [5marks]
Q2- Ataxia (2015,2014) [5marks]
Q3- Mx of cerebellar ataxia. (2014) [5marks]
Q4- Describe different types of ataxia & write down
detail assessment of 25 year old pt with
cerebellar ataxia. (2013) [16marks]
Q5- Sensory ataxia. (2013, 2003) [5marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-2-2048.jpg)
![Q6- How will you differentiate cerebellar & sensory
ataxia? Write Mx of cerebellar ataxia. (2012)
[16marks]
Q7- Discuss evaluation & Mx of a pt with
cerebellar ataxia. (2011) [16marks]
Q8- Write about etiopathogenesis, pathology, C.F.
& PT Mx of a pt with cerebral ataxia. (2009)
[16marks]
Q9- What is ataxia? Write about C.F. & rehab. of a
pt with cerebellar ataxia. (2008) [16marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-3-2048.jpg)
![Q10- Cerebellar ataxia. (2006) [5marks]
Q11- Discuss assessment & Mx of a case of
cerebellar ataxia. (2006) [16marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-4-2048.jpg)
![CONTENTS
• Definition
• Types
[1] cerebellar ataxia
-definition
- types and symptoms
- etiology
- clinical features
- assessment
- management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-5-2048.jpg)
![[2] Sensory ataxia
- introduction
- cause
- assessment
- management
[3] Vestibular ataxia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-6-2048.jpg)

![TYPES
• 1] Cerebellar
• 2] Sensory
• 3] Vestibular](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-8-2048.jpg)
![[1] Cerebellar Ataxia
Definition
• It is a term used to describe certain
behavior like postural unsteadiness,
difficulty in coordinating movements &
clumsiness experienced by an individual
with cerebellar dysfunction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-9-2048.jpg)














![[A] Personal database
• Name
• Age
• Gender
• Address
• Occupation
• C/C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-25-2048.jpg)
![[B] HISTORY
[C] INVESTIGATION
• CT scan , MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy
- cerebellar tumor
- cerebellar infarction
- tonsilar invagination & hydroceplaus
- Arnold Chiari malformation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-26-2048.jpg)
![[C] On Observation
• General observation
- postural tremor, tone (hypotonic), gait (ataxic),
external appliances (walking aids), nystagmus
• Posture
- sit with an increased thoracic kyphosis & forward
head.
- sit with hyperlordosis due to abdominal muscle
weakness.
- stand with a wide BOS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-27-2048.jpg)

![[E] On Examination
• Vitals
• Higher function examination
or
Examination of communication & cognitive
skills
- may exhibit delirium ( restlessness,
irritability, tremors, confusion, disorientation or
hallucination) dementia or short term memory
problems in pt’s with alcoholic CD (Coeliac
diesease).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-29-2048.jpg)





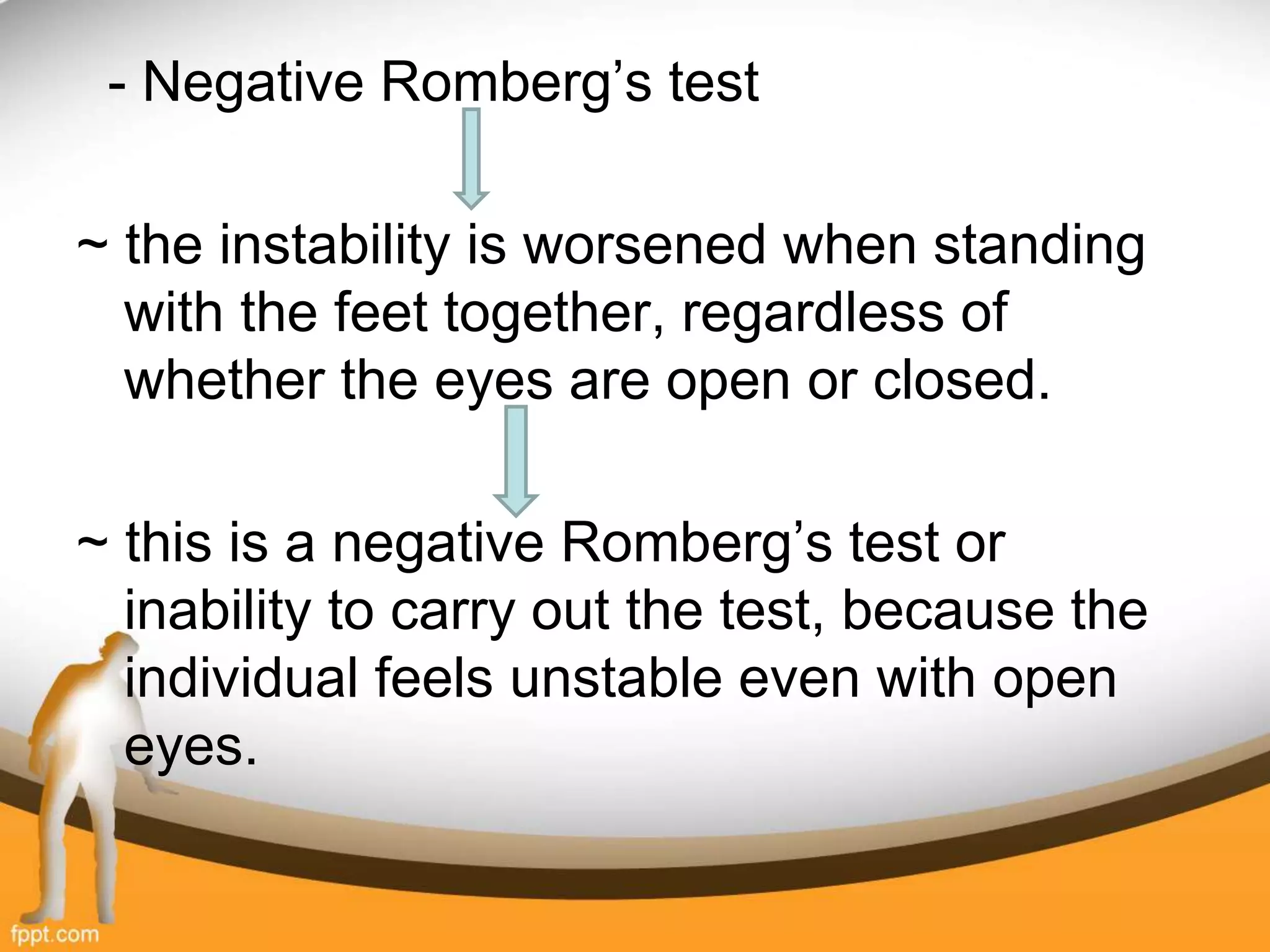
![[H] Special Test
• Romberg’s test : The extent of the sway
envelope when standing with about 4
inches between the feet can be 12˚ in the
sagittal plane & 16˚ in the frontal plane.
[I] PFD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-35-2048.jpg)












![[2] Sensory Ataxia
INTRODUCTION
• Ataxia due to loss of proprioception.
CAUSE
• By dysfunction of dorsal columns of spinal cord.
• May also due to dysfunction of various parts of
brain, which receive positional information,
including cerebellum, thalamus & parietal lobes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-48-2048.jpg)
![ASSESSMENT
[A] Personal database
[B] History
[C] Ix
[D] On observation
- Gait: ~ unsteady “stomping” gait with heavy
heel strikes.
~ Postural instability that worsens when
lack of proprioceptive input cannot be
compensated by visual input, s/a in poorly lit
envt.s.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-49-2048.jpg)
![[E] On examination
[F] Reflex examination
[G] Co-ordination & balance
- worsening of finger- pointing test with eyes
closed.
[H] Special test
- positive Romberg’s test
[I] PFD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-50-2048.jpg)

![[3] Vestibular Ataxia
• It is employed to indicate ataxia due to
dysfunction of vestibular system, which in
acute & unilateral cases is associated with
prominent vertigo, nausea & vomiting.
• In slow-onset, chronic b/l cases of
vestibular dysfunction, these characteristic
manifestations may be absent &
disequilibrium may be the sole
presentation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ataxia-11q-200821102438/75/Ataxia-52-2048.jpg)

