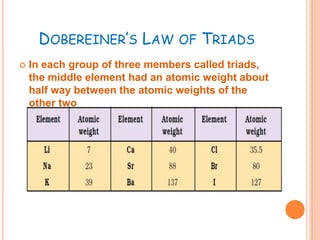
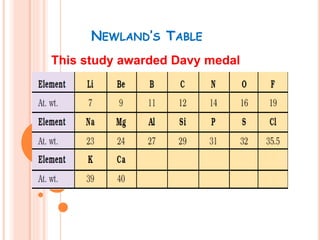
The document summarizes the development of the periodic table over time. It describes Dobereiner's Law of Triads, Newland's Law of Octaves, and Mendeleev's and Moseley's contributions which established that an element's properties are determined by its atomic number rather than atomic mass. The modern periodic table is arranged into seven periods and eighteen groups and classifies elements as metals, nonmetals, and noble gases based on their electronic configurations.