The document provides an overview of the periodic table including its development, characteristics, and positioning of elements. It discusses:
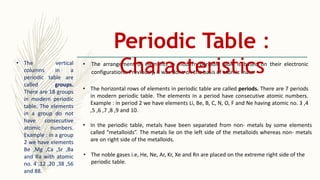
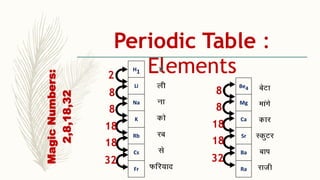
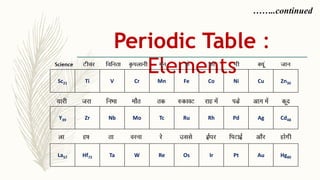
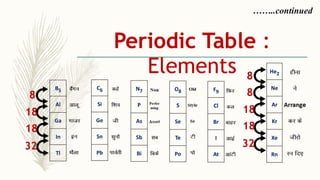
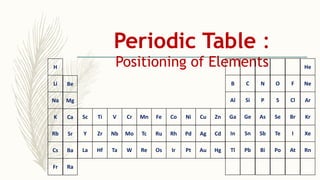
- There are 118 known elements placed in the periodic table based on their electronic configurations. Metals lie on the left side and non-metals on the right, separated by metalloids.
- The horizontal rows are called periods and there are 7 periods. Elements in the same period have consecutive atomic numbers. The vertical columns are called groups and elements in the same group have similar properties despite having different atomic numbers.
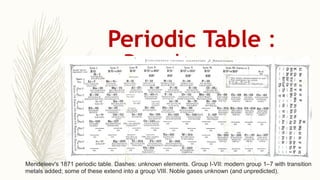
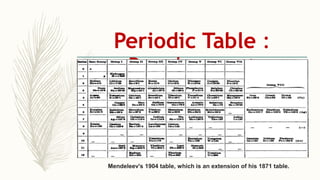
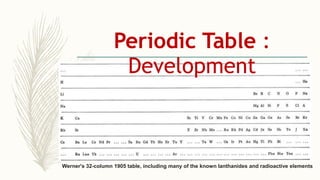
- Noble gases are placed on the far right. Early periodic tables were arranged by atomic mass but Mendeleev organized his 1871 table based on properties, allowing prediction of unknown