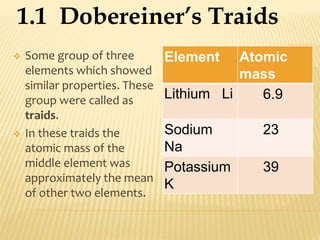
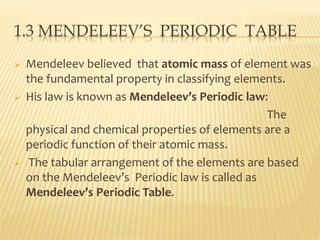
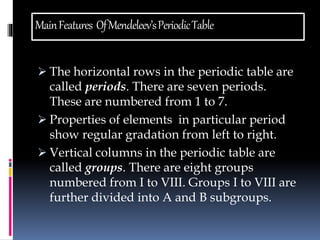
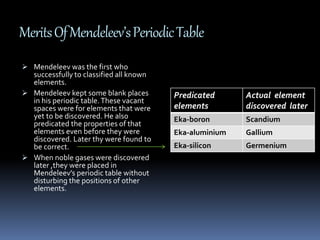
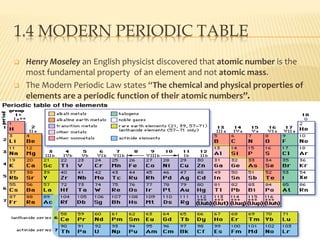
This document discusses the development of the periodic table. It describes Dobereiner's discovery of triads of elements with similar properties (lithium, sodium, potassium). It also discusses Newlands' law of octaves and how he arranged elements in order of increasing atomic mass and found every 8th element had similar properties. Most of the document focuses on Mendeleev's periodic table, including its key features like periods and groups, how he arranged elements and left gaps for undiscovered elements, and its merits in classifying all known elements. It notes some demerits too, like position issues caused by isotopes and atomic mass inconsistencies. Finally, it mentions Moseley discovered atomic number was a better property to use