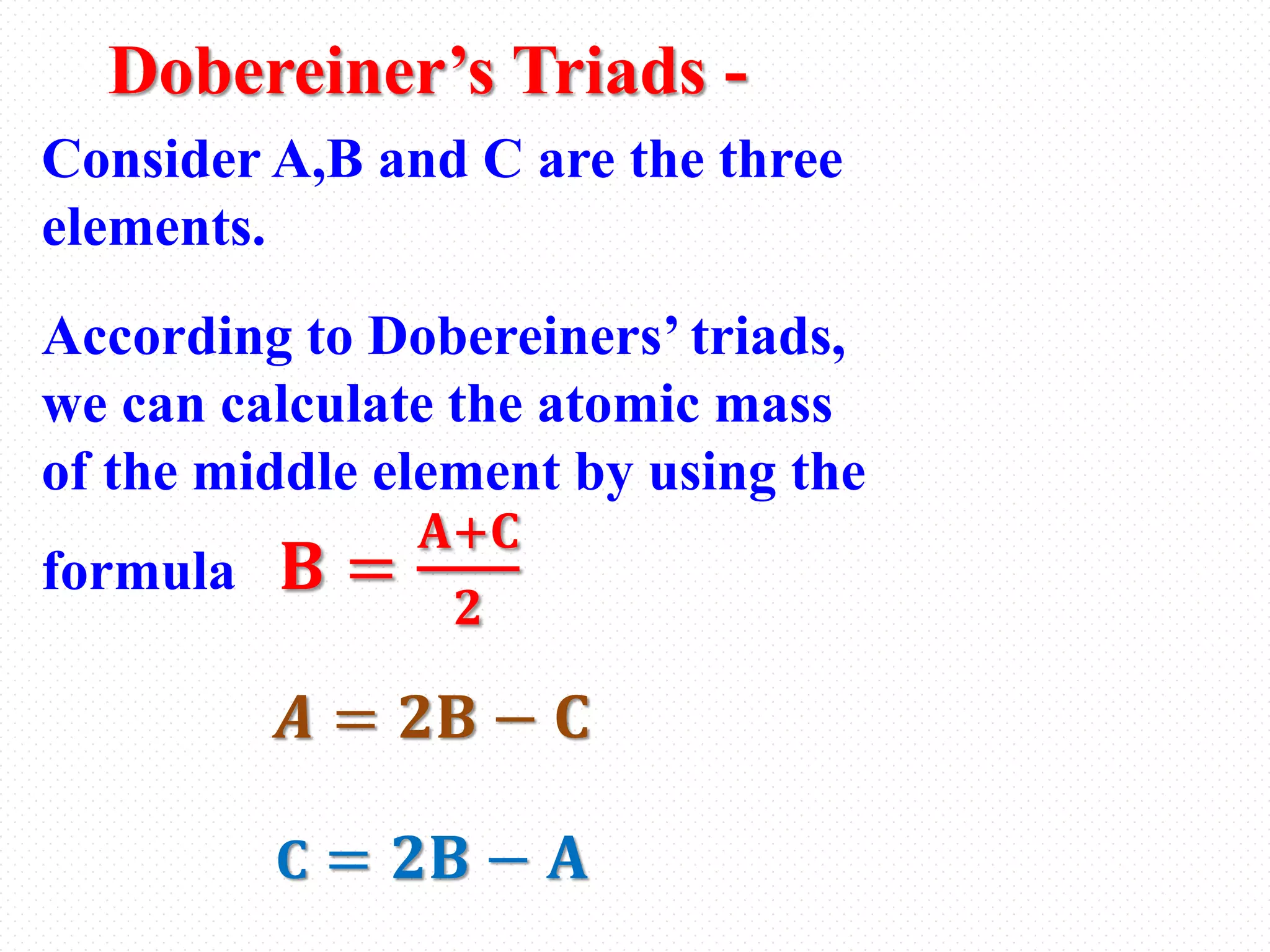
The document provides an overview of the periodic classification of elements. It discusses early attempts at classification including Dobereiner's triads and Newlands' law of octaves. It then covers Mendeleev's periodic table, including its merits and defects. Finally, it describes the modern periodic table based on atomic number, including periodic trends in properties like atomic size and electronegativity across periods and down groups. Key topics covered include the groups and periods in the modern table, how to read and understand its layout, and common questions about periodic trends and properties.