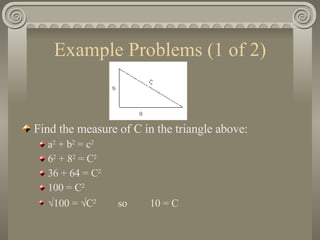
Pythagoras was a Greek mathematician born around 570 BCE in Samos, Greece. He founded a school in Croton, Italy where he studied mathematics and developed the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Pythagoras made many contributions to mathematics and music. He discovered that the musical scale is based on string length ratios and ratios of whole numbers.