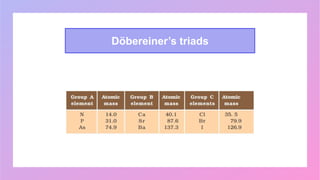
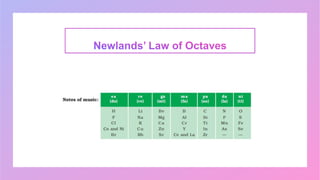
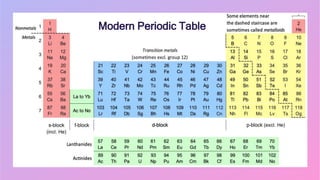
Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner studied chemistry and became a professor of chemistry and pharmacy. He discovered similar triads of elements with increasing atomic masses, which led to the development of the periodic table. John Newlands arranged elements in order of increasing atomic mass and found they repeated properties every eighth element, calling this the Law of Octaves. However, this law did not apply to all elements as more were discovered. Dmitri Mendeleev arranged elements based on atomic mass and chemical properties, leaving gaps for undiscovered elements, which contributed greatly to the early periodic table. The modern periodic table is based on atomic number according to Henry Moseley's discovery that it is a more fundamental property than atomic mass.