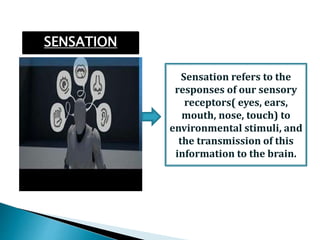
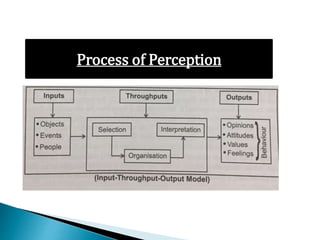
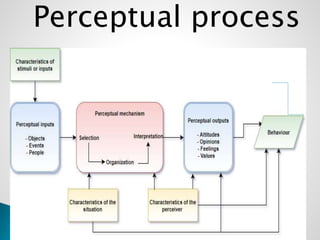
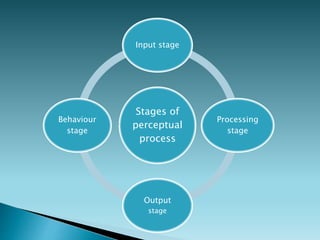
The document discusses perception and sensation. It defines perception as understanding or interpreting information acquired through the senses with a particular point of view, while sensation refers to responses of sensory receptors to external stimuli. Perception involves interpreting this sensory information based on past experiences. The perceptual process involves input, processing, and output stages. Perception is affected by internal factors like needs and motives as well as external stimuli characteristics. People selectively perceive based on their expectations and motives. Perception results from interpreting stimuli in a way that fulfills one's needs based on assumptions and previous experiences.