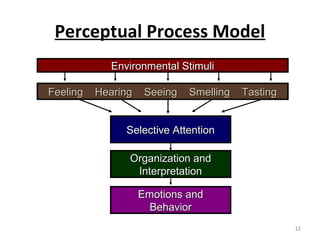
The document discusses perception and the perceptual process. It defines perception as how we organize and interpret our sensory impressions to understand the world around us. It then outlines the key stages of the perceptual process, which include receiving stimuli, selecting stimuli based on internal and external factors, organizing stimuli through grouping and figure-ground perception, interpreting stimuli based on perceptual sets and biases, checking perceptions against others', and reacting through impression formation and action. Limitations of perception like generalizations and preconceived notions are also noted.