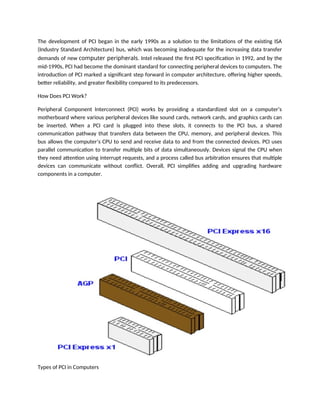
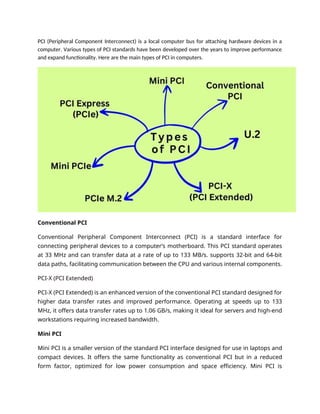
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a hardware interface standard developed by Intel in the early 1990s for connecting peripheral devices to a computer’s motherboard, facilitating efficient communication and system expansion. Various types of PCI, including conventional PCI, PCI-X, and PCI Express (PCIe), have been developed to improve performance and expand functionality, with PCIe largely replacing older standards due to its higher speed and bandwidth capabilities. Despite its advantages, such as plug-and-play functionality and support for hot swapping, PCI has limitations like bandwidth constraints compared to newer standards.